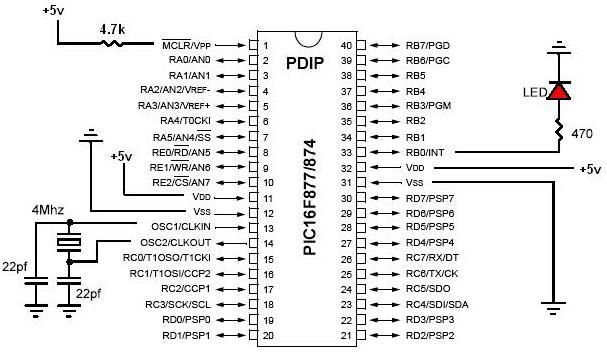
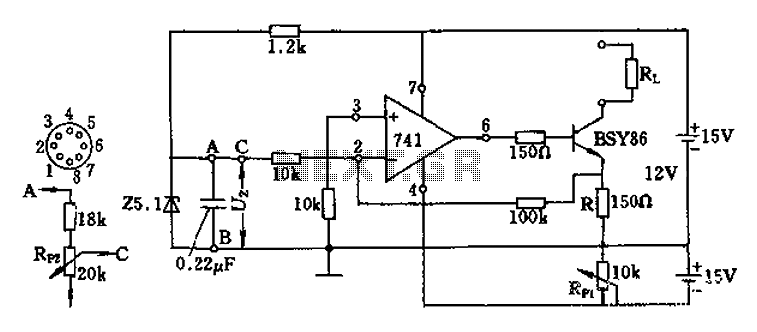
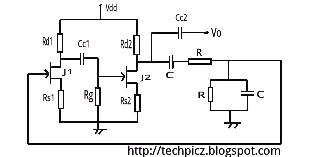
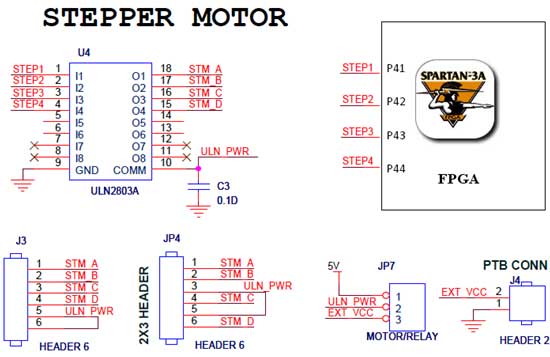
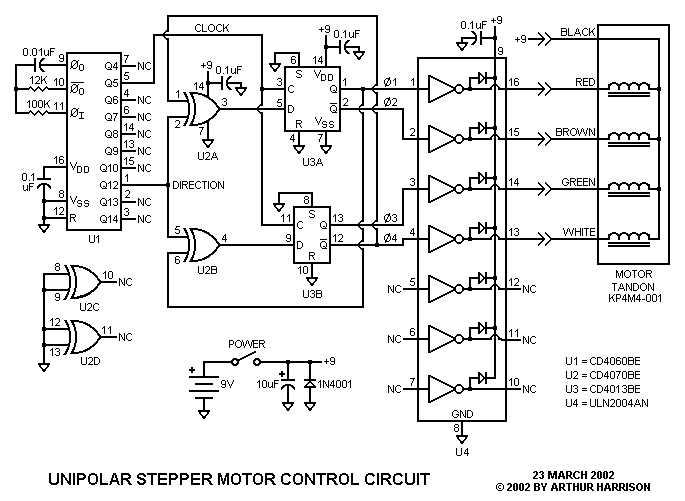
DC Motor Controller using Transistor TIP31
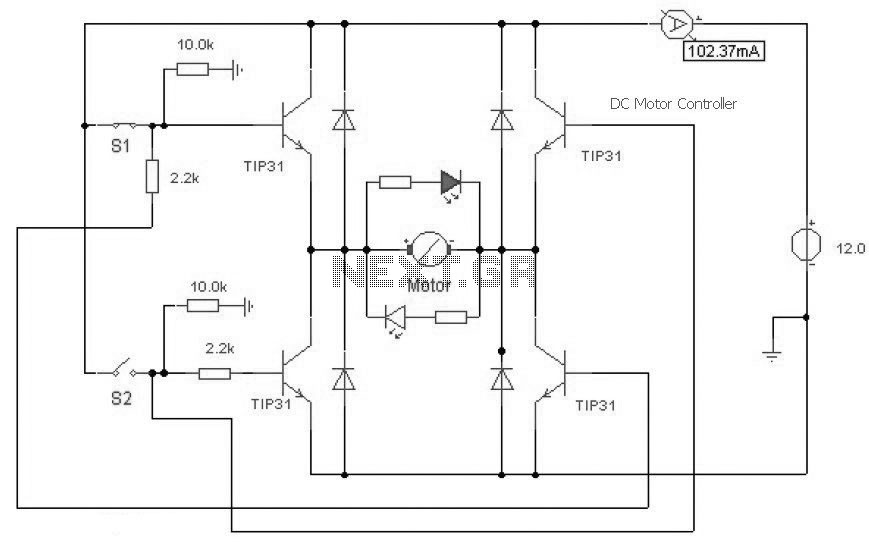
This is a DC motor controller circuit built using a TIP31 transistor based on the H-Bridge concept. The switches S1 and S2 are normally open, push-to-close buttons. The LED serves to indicate the direction of motor rotation.
The described DC motor controller circuit utilizes an H-Bridge configuration to control the direction and speed of a DC motor. The TIP31 transistor, which is a power transistor, is employed in the circuit to handle the current required by the motor. The H-Bridge configuration allows for bidirectional control of the motor, enabling it to rotate in either direction based on the state of the control switches.
In this circuit, the switches S1 and S2 function as user inputs. When either switch is pressed, it closes the circuit and activates the corresponding leg of the H-Bridge, allowing current to flow through the motor in one direction or the other. If S1 is pressed, the motor will rotate in one direction, while pressing S2 will reverse the motor's rotation. The normally open configuration of these switches ensures that the motor remains off until the user actively engages one of the switches.
The inclusion of an LED indicator is a critical feature of this design. This LED visually signals the current direction of the motor's rotation. For instance, if the motor is set to rotate clockwise, the LED may light up in one color, while a counterclockwise rotation could trigger the LED to change to another color or turn off, depending on the specific design choices made in the circuit.
Overall, this DC motor controller circuit is a practical and efficient solution for applications requiring precise control of motor direction and operation, such as in robotics, automation systems, or remote-controlled devices. The simplicity of using a TIP31 transistor in conjunction with push-button switches makes this circuit accessible for both educational purposes and practical implementations.This is a DC motor controller circuit, built using transistor TIP31 based on H-Bridge concept. The switch S1 and S2 are normally open, push to close, press button switches. The LED function is to indicate the direction of motor rotation, y.. 🔗 External reference
The described DC motor controller circuit utilizes an H-Bridge configuration to control the direction and speed of a DC motor. The TIP31 transistor, which is a power transistor, is employed in the circuit to handle the current required by the motor. The H-Bridge configuration allows for bidirectional control of the motor, enabling it to rotate in either direction based on the state of the control switches.
In this circuit, the switches S1 and S2 function as user inputs. When either switch is pressed, it closes the circuit and activates the corresponding leg of the H-Bridge, allowing current to flow through the motor in one direction or the other. If S1 is pressed, the motor will rotate in one direction, while pressing S2 will reverse the motor's rotation. The normally open configuration of these switches ensures that the motor remains off until the user actively engages one of the switches.
The inclusion of an LED indicator is a critical feature of this design. This LED visually signals the current direction of the motor's rotation. For instance, if the motor is set to rotate clockwise, the LED may light up in one color, while a counterclockwise rotation could trigger the LED to change to another color or turn off, depending on the specific design choices made in the circuit.
Overall, this DC motor controller circuit is a practical and efficient solution for applications requiring precise control of motor direction and operation, such as in robotics, automation systems, or remote-controlled devices. The simplicity of using a TIP31 transistor in conjunction with push-button switches makes this circuit accessible for both educational purposes and practical implementations.This is a DC motor controller circuit, built using transistor TIP31 based on H-Bridge concept. The switch S1 and S2 are normally open, push to close, press button switches. The LED function is to indicate the direction of motor rotation, y.. 🔗 External reference