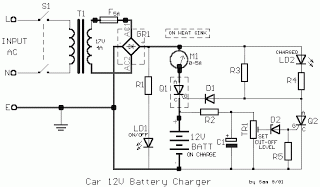
decibel meter circuit
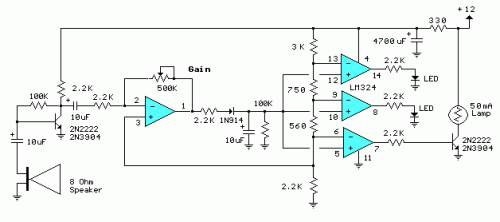
The series of decibel meters functions to determine the signal strength level delivered to the speakers in an audio system. This decibel meter circuit is commonly referred to as VU meters in high-fidelity audio systems. The series of decibel meters discussed in this article showcases advanced techniques with signal lights and LEDs. The input circuit for the decibel meter is derived from the audio system's output, which connects to the speakers. This series employs an LM324 integrated circuit as a comparator and a single-level amplifier with gain control. The construction of the decibel meter or VU meter is relatively straightforward, and the circuit details can be observed in the accompanying figure. The series requires a 12V DC voltage source and an input signal from the audio power output connected to the speakers. These decibel meters can be installed in powered speakers or other audio amplifier systems. The sensitivity of the audio signal reception can be adjusted by modifying the value of VR500K, which acts as a feedback and reinforcement factor, influencing the amplifier circuit preceding the decibel meter.
The decibel meter circuit, or VU meter, is a valuable tool in audio systems for visualizing signal strength. This circuit typically utilizes an LM324 operational amplifier, which serves dual purposes: as a comparator to assess the input signal level and as an amplifier to enhance the signal for accurate representation. The circuit design allows for the integration of multiple LED indicators that light up in response to varying signal levels, providing a clear visual cue of audio intensity.
The input stage of the circuit is connected directly to the output of the audio amplifier, ensuring that the decibel meter accurately reflects the audio signal being sent to the speakers. The circuit is powered by a 12V DC supply, which is standard for many audio applications. The use of a variable resistor, VR500K, is critical for tuning the sensitivity of the meter. By adjusting this resistor, users can calibrate the circuit to respond appropriately to different signal levels, ensuring that the meter provides a meaningful representation of audio output without distortion or clipping.
Furthermore, the design can be adapted for various applications, such as in powered speakers or standalone audio amplifier systems. The simplicity of the circuit allows for easy assembly and integration into existing audio setups, making it an ideal project for both hobbyists and professional audio engineers. The visual feedback provided by the decibel meter enhances the user experience, allowing for real-time monitoring of audio levels and ensuring optimal performance of the audio system.The series of decibel meter function to determine the level of signal strength that is given to the speaker on the audio system. Decibel meter circuit is often also known as the VU meters on audio hifi system. For a series of decibel meters in this article displays strong technique with signal lights and LED. Decibel meter input circuit is taken f rom the output of the audio system that will connect to the speakers. The series uses a decibel meter this fruit as a comparator LM324 IC and 1 level amplifier with gain control. The series of decibel meter or VU meter is quite simple to make and circuit details can be seen in the following figure.
The series of decibel meters above requires 12VDC voltage source and an input signal from the audio power output that is connected to the speakers. The series of decibel meters can be installed on powered speakers or other audio amplifier system. To adjust the audio signal reception sensitivity is set by adjusting the value VR500K which serves as feedback and reinforcement factors will affect the amplifier circuit ahead of the decibel meter.
🔗 External reference
The decibel meter circuit, or VU meter, is a valuable tool in audio systems for visualizing signal strength. This circuit typically utilizes an LM324 operational amplifier, which serves dual purposes: as a comparator to assess the input signal level and as an amplifier to enhance the signal for accurate representation. The circuit design allows for the integration of multiple LED indicators that light up in response to varying signal levels, providing a clear visual cue of audio intensity.
The input stage of the circuit is connected directly to the output of the audio amplifier, ensuring that the decibel meter accurately reflects the audio signal being sent to the speakers. The circuit is powered by a 12V DC supply, which is standard for many audio applications. The use of a variable resistor, VR500K, is critical for tuning the sensitivity of the meter. By adjusting this resistor, users can calibrate the circuit to respond appropriately to different signal levels, ensuring that the meter provides a meaningful representation of audio output without distortion or clipping.
Furthermore, the design can be adapted for various applications, such as in powered speakers or standalone audio amplifier systems. The simplicity of the circuit allows for easy assembly and integration into existing audio setups, making it an ideal project for both hobbyists and professional audio engineers. The visual feedback provided by the decibel meter enhances the user experience, allowing for real-time monitoring of audio levels and ensuring optimal performance of the audio system.The series of decibel meter function to determine the level of signal strength that is given to the speaker on the audio system. Decibel meter circuit is often also known as the VU meters on audio hifi system. For a series of decibel meters in this article displays strong technique with signal lights and LED. Decibel meter input circuit is taken f rom the output of the audio system that will connect to the speakers. The series uses a decibel meter this fruit as a comparator LM324 IC and 1 level amplifier with gain control. The series of decibel meter or VU meter is quite simple to make and circuit details can be seen in the following figure.
The series of decibel meters above requires 12VDC voltage source and an input signal from the audio power output that is connected to the speakers. The series of decibel meters can be installed on powered speakers or other audio amplifier system. To adjust the audio signal reception sensitivity is set by adjusting the value VR500K which serves as feedback and reinforcement factors will affect the amplifier circuit ahead of the decibel meter.
🔗 External reference