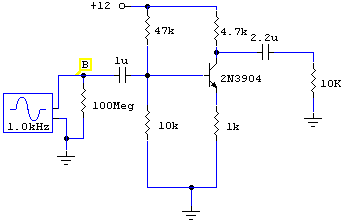
Halogen Lamp Protector Circuit
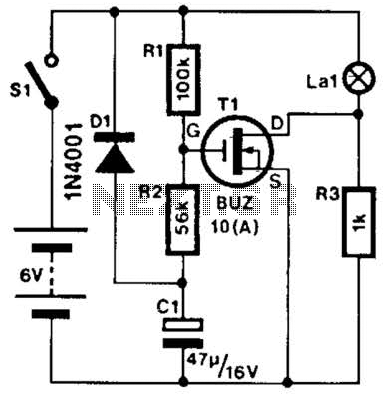
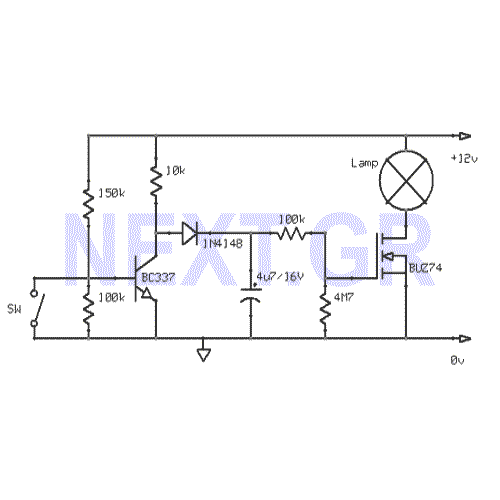
This circuit produces a soft turn-on for halogen lamp filaments upon powering up. The MOSFET used is a BUZ10, which has a resistance of 0.2 ohms. Resistors R1, R2, and capacitor C1 set the turn-on rate, while diode D1 discharges capacitor C1 at turn-off.
The circuit employs a BUZ10 MOSFET to control the power delivered to halogen lamp filaments, allowing for a gradual increase in brightness rather than an abrupt illumination. This soft start feature is particularly beneficial for extending the lifespan of the halogen lamps, as it reduces thermal stress on the filaments during power-up.
Resistor R1 and resistor R2 form a voltage divider that influences the gate voltage of the MOSFET, effectively controlling the turn-on time. The time constant for the turn-on process is determined by the values of R1, R2, and the capacitance of C1. A larger capacitance or higher resistance values will result in a slower increase in voltage at the gate, leading to a softer turn-on.
Capacitor C1 plays a crucial role in the timing of the turn-on process. When power is applied, C1 charges through the resistors, gradually increasing the gate voltage until it reaches the threshold voltage of the MOSFET, causing it to turn on. The diode D1 is connected in parallel with C1 and ensures that when the power is turned off, C1 discharges quickly, allowing the MOSFET to turn off rapidly and preventing any residual voltage that could keep the lamp glowing.
The design of this circuit is essential for applications where a sudden surge of current could damage sensitive components or reduce the lifespan of the halogen lamps. By utilizing the BUZ10 MOSFET, which has a low on-resistance of 0.2 ohms, the circuit minimizes power loss and heat generation during operation, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Overall, this soft turn-on circuit is a practical solution for controlling halogen lamps in various lighting applications. This circuit, produces a soft turn-on for halogen lamp filaments upon powering up. MOSFET used is a BUZ10, which has 0.2 Rm on. Rl, R2, and CI set the turn-on rate and D1 discharges CI at turn-off. 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs a BUZ10 MOSFET to control the power delivered to halogen lamp filaments, allowing for a gradual increase in brightness rather than an abrupt illumination. This soft start feature is particularly beneficial for extending the lifespan of the halogen lamps, as it reduces thermal stress on the filaments during power-up.
Resistor R1 and resistor R2 form a voltage divider that influences the gate voltage of the MOSFET, effectively controlling the turn-on time. The time constant for the turn-on process is determined by the values of R1, R2, and the capacitance of C1. A larger capacitance or higher resistance values will result in a slower increase in voltage at the gate, leading to a softer turn-on.
Capacitor C1 plays a crucial role in the timing of the turn-on process. When power is applied, C1 charges through the resistors, gradually increasing the gate voltage until it reaches the threshold voltage of the MOSFET, causing it to turn on. The diode D1 is connected in parallel with C1 and ensures that when the power is turned off, C1 discharges quickly, allowing the MOSFET to turn off rapidly and preventing any residual voltage that could keep the lamp glowing.
The design of this circuit is essential for applications where a sudden surge of current could damage sensitive components or reduce the lifespan of the halogen lamps. By utilizing the BUZ10 MOSFET, which has a low on-resistance of 0.2 ohms, the circuit minimizes power loss and heat generation during operation, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Overall, this soft turn-on circuit is a practical solution for controlling halogen lamps in various lighting applications. This circuit, produces a soft turn-on for halogen lamp filaments upon powering up. MOSFET used is a BUZ10, which has 0.2 Rm on. Rl, R2, and CI set the turn-on rate and D1 discharges CI at turn-off. 🔗 External reference