Transistor Circuits
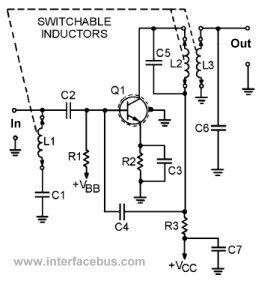
This page presents several transistor circuits that are not commonly found on other pages due to the absence of a specific topic. These circuits, however, illustrate particular points but lack detailed descriptions. An example of an RF amplifier circuit using a transistor is provided below. The transistor is labeled as TUT, which stands for Transistor Under Test. The schematic aims to demonstrate the additional components necessary in an RF circuit. It is important to note that the transistor case is grounded, and a metal shield is utilized on the printed wiring board. Although the meaning of the dashed grounded lines is not explicitly defined, many transistor cases feature an uncommitted metal case or tab that can serve for grounding or heat dissipation. C5 is a Feed-through Capacitor employed to suppress electromagnetic interference (EMI) between inter-panel connections. The subsequent circuit example is also an RF circuit, with the transistor designated as DUT, meaning Device Under Test, as the circuit is configured to evaluate the operating characteristics of the transistor. The circuit exhibits a significant use of variable capacitors or trimmer capacitors, which typically indicates an RF application. Coaxial connectors are illustrated as 50-ohm inputs and outputs, indicated by the cycle around the dot. The next circuit represents another RF circuit, this time illustrating a VHF transistor amplifier. The distinction here is the presence of a shielded screen surrounding the transistor case and the switchable inductors that are ganged together. The following circuit is another RF FET amplifier, utilizing a four-lead package, with the fourth lead connected to the transistor case, which is then grounded. Again, 50-ohm coax connectors are depicted.
The circuits described encompass various configurations and components essential for RF applications. The RF amplifier circuit featuring the TUT transistor demonstrates the significance of grounding and shielding in minimizing interference and enhancing performance. The grounding of the transistor case, along with the use of a metal shield on the printed circuit board, forms a critical part of the design to ensure stability and reliability in RF signal transmission.
In the circuit with the DUT transistor, the use of variable or trimmer capacitors indicates a focus on tuning and optimizing the circuit for specific frequency responses, which is paramount in RF applications. The coaxial connectors facilitate the connection of RF signals while maintaining impedance matching, which is vital for minimizing signal reflections and losses.
The VHF transistor amplifier circuit builds on these principles by incorporating additional shielding and ganged inductors, which allow for dynamic tuning of the circuit's response characteristics. The design of the FET amplifier with a four-lead package further emphasizes the importance of grounding for thermal management and signal integrity in high-frequency operations.
Overall, the collection of circuits serves to illustrate the complexities and requirements of designing effective RF amplifiers, highlighting the interplay of various components and configurations to achieve desired operational characteristics.This page lists a few transistor circuits not found on other pages because no topic exists. However the circuits do serve to make some specific point, but do not come with a description. An example of an RF amplifier circuit using a transistor is shown below. The transistor is identified as TUT which stands for Transistor Under Test. The point of the schematic is to show the additional components required in an RF circuit. Also note that the case of the transistor is grounded and there appears to be metal shield being used on the printed wiring board. Although there is no clear-cut definition of what the dashed grounded lines means. Many transistor cases have an un-committed metal case or tab that may be used for either grounding or heat dissipation.
Note that C5 is a Feed-through Capacitor used to suppress EMI between inter-panel connections. The next circuit example below is also an RF circuit. In this case the transistor is labeled as DUT for Device Under Test, because the circuit is a setup to test operating characteristics of the transistor. Note the heavy use of variable capacitors, or trimmer capacitors normally implying an RF circuit. Coaxial connectors are shown as 50 ohm inputs and outputs, depicted by the cycle around the dot. The next circuit is also another RF circuit except this time it depicts an actual VHF transistor amplifier.
The difference here is the shielded screen around the transistor case, and the switchable inductors [which are ganged together]. This next circuit is another RF FET amplifier. This particular example uses a four lead package with the fourth lead being connected to the transistor case, which is than grounded.
Again 50 coax connectors are shown. 🔗 External reference
The circuits described encompass various configurations and components essential for RF applications. The RF amplifier circuit featuring the TUT transistor demonstrates the significance of grounding and shielding in minimizing interference and enhancing performance. The grounding of the transistor case, along with the use of a metal shield on the printed circuit board, forms a critical part of the design to ensure stability and reliability in RF signal transmission.
In the circuit with the DUT transistor, the use of variable or trimmer capacitors indicates a focus on tuning and optimizing the circuit for specific frequency responses, which is paramount in RF applications. The coaxial connectors facilitate the connection of RF signals while maintaining impedance matching, which is vital for minimizing signal reflections and losses.
The VHF transistor amplifier circuit builds on these principles by incorporating additional shielding and ganged inductors, which allow for dynamic tuning of the circuit's response characteristics. The design of the FET amplifier with a four-lead package further emphasizes the importance of grounding for thermal management and signal integrity in high-frequency operations.
Overall, the collection of circuits serves to illustrate the complexities and requirements of designing effective RF amplifiers, highlighting the interplay of various components and configurations to achieve desired operational characteristics.This page lists a few transistor circuits not found on other pages because no topic exists. However the circuits do serve to make some specific point, but do not come with a description. An example of an RF amplifier circuit using a transistor is shown below. The transistor is identified as TUT which stands for Transistor Under Test. The point of the schematic is to show the additional components required in an RF circuit. Also note that the case of the transistor is grounded and there appears to be metal shield being used on the printed wiring board. Although there is no clear-cut definition of what the dashed grounded lines means. Many transistor cases have an un-committed metal case or tab that may be used for either grounding or heat dissipation.
Note that C5 is a Feed-through Capacitor used to suppress EMI between inter-panel connections. The next circuit example below is also an RF circuit. In this case the transistor is labeled as DUT for Device Under Test, because the circuit is a setup to test operating characteristics of the transistor. Note the heavy use of variable capacitors, or trimmer capacitors normally implying an RF circuit. Coaxial connectors are shown as 50 ohm inputs and outputs, depicted by the cycle around the dot. The next circuit is also another RF circuit except this time it depicts an actual VHF transistor amplifier.
The difference here is the shielded screen around the transistor case, and the switchable inductors [which are ganged together]. This next circuit is another RF FET amplifier. This particular example uses a four lead package with the fourth lead being connected to the transistor case, which is than grounded.
Again 50 coax connectors are shown. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713