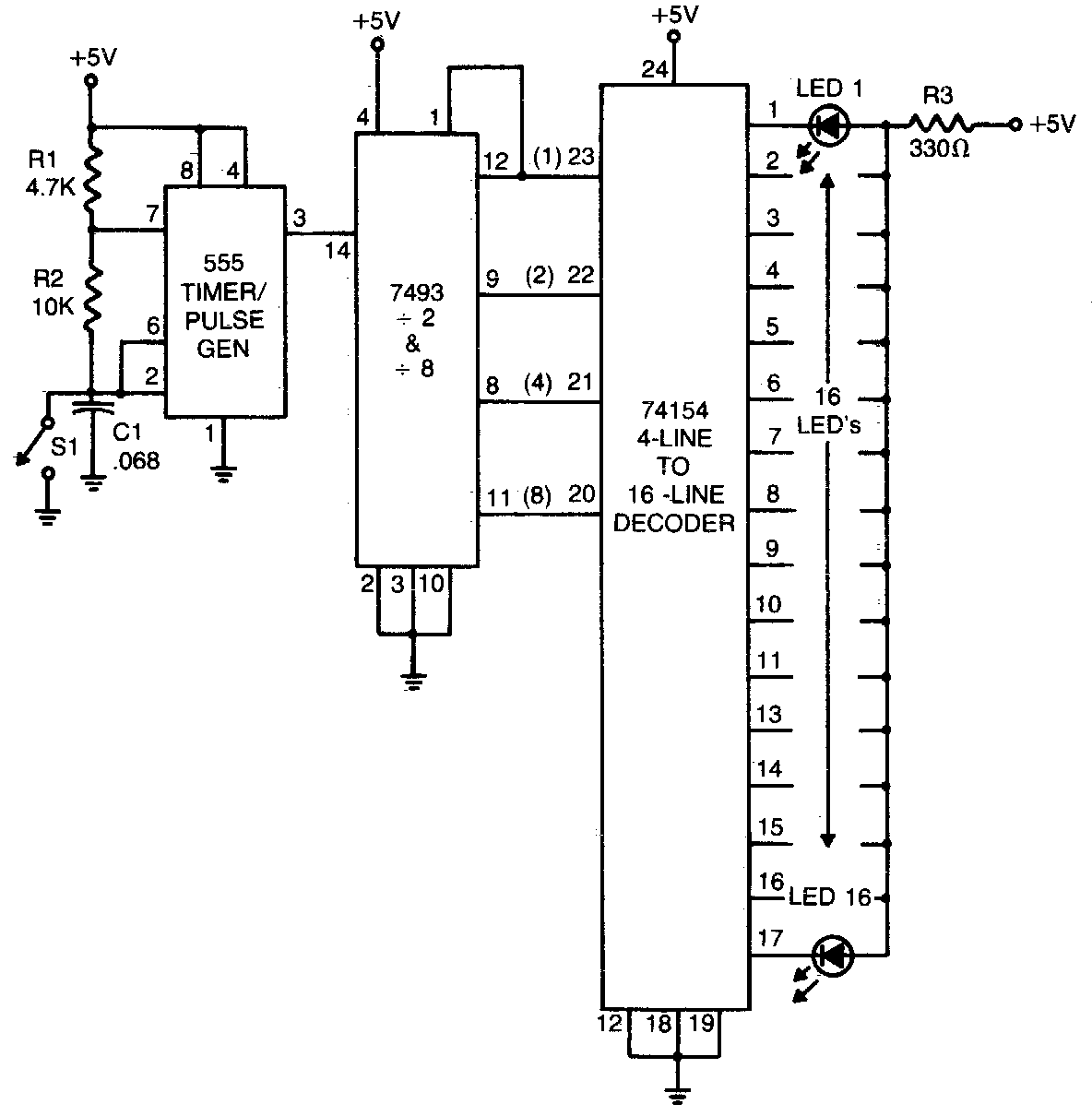
Differential amplifier circuit four connection methods and compare the characteristics of d
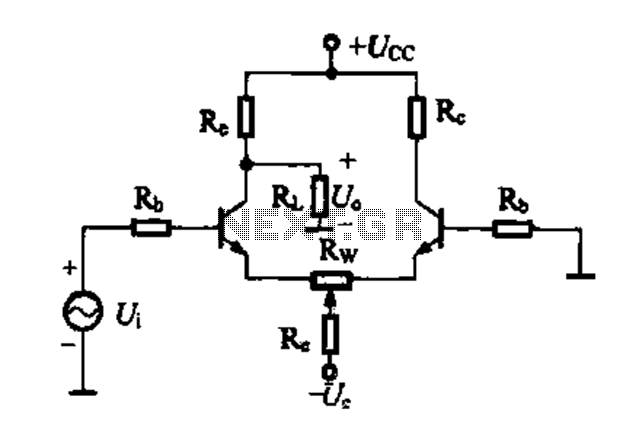
A differential amplifier circuit can be connected in four different ways, allowing for a comparison of their characteristics. The gain of the amplifier is equivalent to that of a single tube, with half the gain providing a high common-mode rejection capability. The inputs and outputs are designed to be suitable for grounding.
A differential amplifier is an electronic device that amplifies the difference between two input voltages while rejecting any signals that are common to both inputs. This feature is particularly useful in noisy environments, as it enhances the desired signal while minimizing interference.
In terms of connection methods, the differential amplifier can be configured in several ways, including:
1. **Single-Ended Input Configuration**: In this method, one input is grounded while the other receives the input signal. This configuration is simple but may not provide optimal common-mode rejection.
2. **Fully Differential Configuration**: Both inputs are utilized, and the output is taken across a load resistor. This method maximizes the differential gain and common-mode rejection, making it ideal for high-precision applications.
3. **Instrumentation Amplifier Configuration**: This configuration uses additional resistors to set the gain and improve the common-mode rejection ratio further. It is particularly useful in applications requiring high accuracy and stability.
4. **Feedback Configuration**: This method employs feedback to stabilize the gain and improve linearity. It can be used to tailor the amplifier's response to specific applications.
The gain of the differential amplifier is defined by the ratio of the feedback and input resistors. High common-mode rejection is achieved through careful selection of these resistors and the layout of the circuit, which minimizes the effects of noise and interference.
The grounding of inputs and outputs is vital as it ensures a reference point for the signals being processed. Proper grounding techniques can significantly enhance the performance of the differential amplifier, leading to improved signal integrity and reduced noise levels.
In summary, the differential amplifier's versatility in connection methods, along with its inherent ability to reject common-mode signals, makes it an essential component in various electronic applications, including sensor interfacing, audio processing, and data acquisition systems.Differential amplifier circuit four connection methods and compare the characteristics of d d. O magnification equal to a single tube of half has a high common mode rejection c apability inputs and outputs are suitable for the case to be grounded
A differential amplifier is an electronic device that amplifies the difference between two input voltages while rejecting any signals that are common to both inputs. This feature is particularly useful in noisy environments, as it enhances the desired signal while minimizing interference.
In terms of connection methods, the differential amplifier can be configured in several ways, including:
1. **Single-Ended Input Configuration**: In this method, one input is grounded while the other receives the input signal. This configuration is simple but may not provide optimal common-mode rejection.
2. **Fully Differential Configuration**: Both inputs are utilized, and the output is taken across a load resistor. This method maximizes the differential gain and common-mode rejection, making it ideal for high-precision applications.
3. **Instrumentation Amplifier Configuration**: This configuration uses additional resistors to set the gain and improve the common-mode rejection ratio further. It is particularly useful in applications requiring high accuracy and stability.
4. **Feedback Configuration**: This method employs feedback to stabilize the gain and improve linearity. It can be used to tailor the amplifier's response to specific applications.
The gain of the differential amplifier is defined by the ratio of the feedback and input resistors. High common-mode rejection is achieved through careful selection of these resistors and the layout of the circuit, which minimizes the effects of noise and interference.
The grounding of inputs and outputs is vital as it ensures a reference point for the signals being processed. Proper grounding techniques can significantly enhance the performance of the differential amplifier, leading to improved signal integrity and reduced noise levels.
In summary, the differential amplifier's versatility in connection methods, along with its inherent ability to reject common-mode signals, makes it an essential component in various electronic applications, including sensor interfacing, audio processing, and data acquisition systems.Differential amplifier circuit four connection methods and compare the characteristics of d d. O magnification equal to a single tube of half has a high common mode rejection c apability inputs and outputs are suitable for the case to be grounded