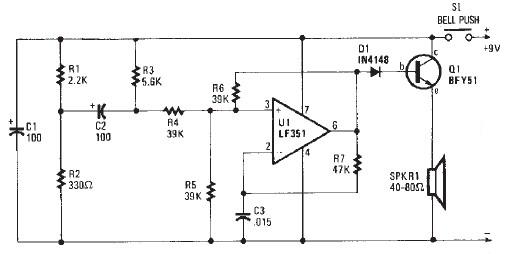
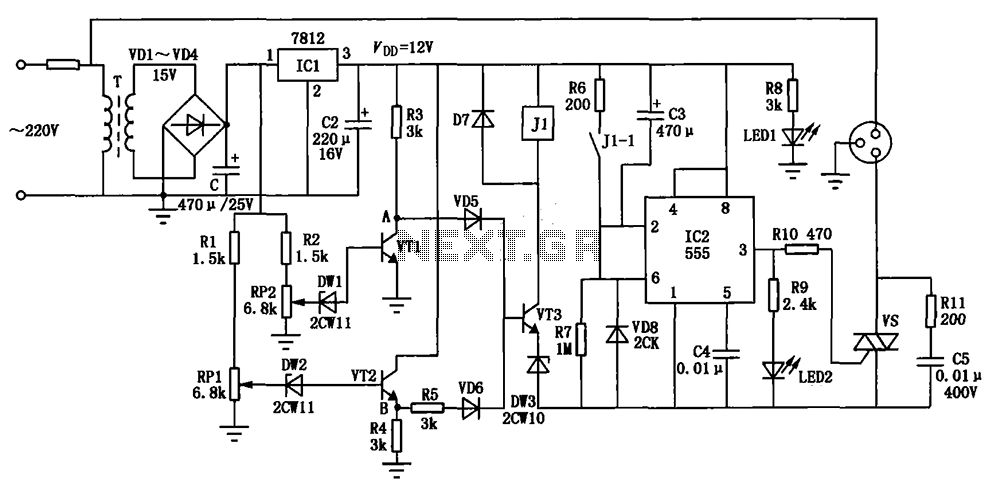
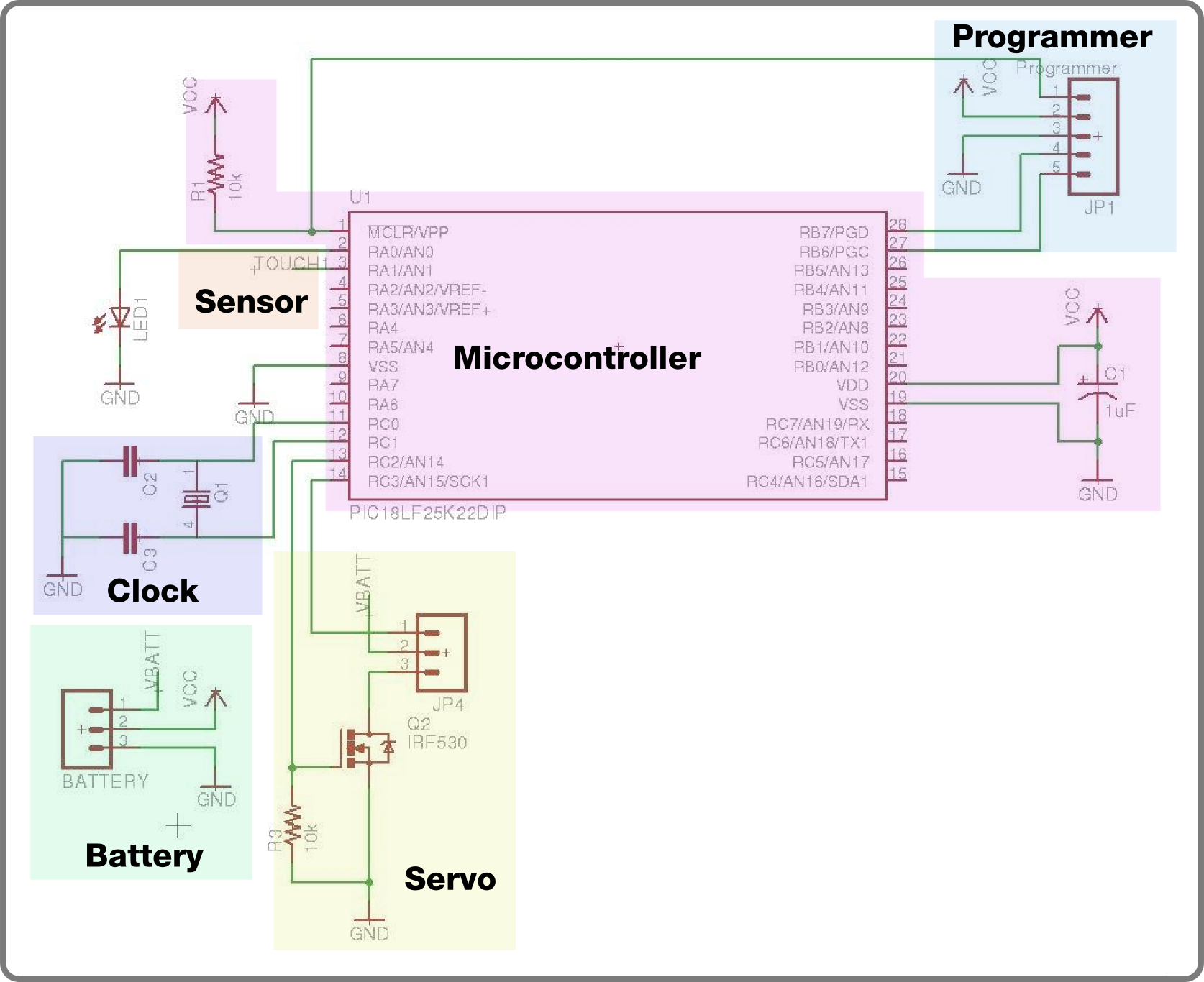
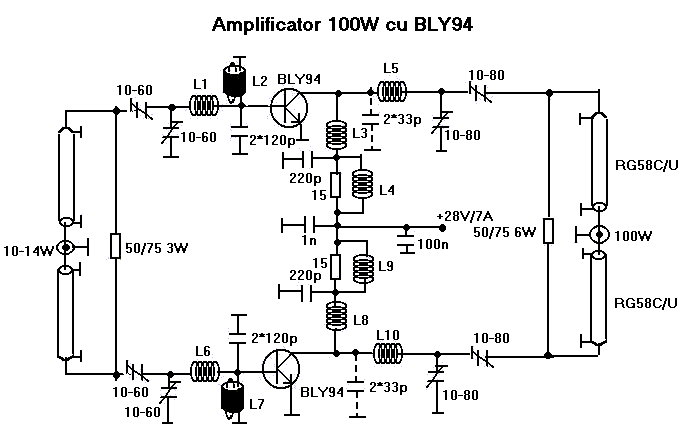
Differential amplifier circuit four connection methods and features comparison b
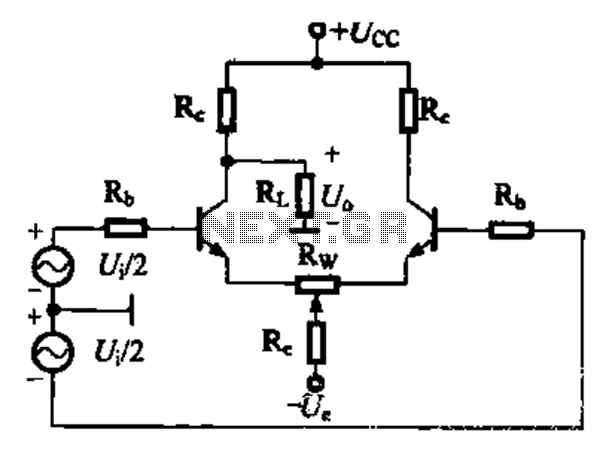
A comparison of four connection methods and features of a differential amplifier circuit is presented. The circuit demonstrates a magnification of a single tube with half the earnings, effectively countering common-mode negative feedback effects. The Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) remains high, suitable for converting differential signals into single-ended signals under tube-like conditions.
The differential amplifier is a crucial component in analog signal processing, designed to amplify the difference between two input voltages while rejecting any signals that are common to both inputs. This characteristic is essential in applications such as instrumentation, audio processing, and sensor signal conditioning.
The circuit can be configured in several ways, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. The four primary connection methods typically include:
1. **Direct Coupling**: This method connects the inputs directly to the amplifier without any capacitive coupling. It allows for a wide frequency response but may introduce DC offset issues.
2. **Capacitive Coupling**: In this configuration, capacitors are used to block DC components while allowing AC signals to pass. This is beneficial in applications where DC offset is a concern, but it may limit low-frequency response.
3. **Transformer Coupling**: Utilizing transformers to couple the input signals can provide excellent isolation and help in impedance matching. However, this method may introduce additional complexity and cost.
4. **Feedback Resistor Network**: This method employs a network of resistors to set the gain of the amplifier and improve linearity. It can effectively control the bandwidth and stability of the amplifier but requires careful design to avoid introducing noise.
The differential amplifier's ability to maintain a high Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) is critical. CMRR quantifies the amplifier's ability to reject common-mode signals, which are noise or interference present on both inputs. A high CMRR indicates that the amplifier can effectively amplify the desired differential signal while minimizing the effect of unwanted common-mode signals.
In summary, the differential amplifier circuit's design and configuration play a pivotal role in its performance. By selecting the appropriate connection method, engineers can optimize the circuit for specific applications, ensuring high fidelity and reliable operation in various electronic systems.Differential amplifier circuit four connection methods and features comparison b b.0 magnification of a single tube of half earnings due anti-common-mode negative feed-effects, CMRR is still great adapted to the differential signal into a single-ended signal tube-like conditions
The differential amplifier is a crucial component in analog signal processing, designed to amplify the difference between two input voltages while rejecting any signals that are common to both inputs. This characteristic is essential in applications such as instrumentation, audio processing, and sensor signal conditioning.
The circuit can be configured in several ways, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. The four primary connection methods typically include:
1. **Direct Coupling**: This method connects the inputs directly to the amplifier without any capacitive coupling. It allows for a wide frequency response but may introduce DC offset issues.
2. **Capacitive Coupling**: In this configuration, capacitors are used to block DC components while allowing AC signals to pass. This is beneficial in applications where DC offset is a concern, but it may limit low-frequency response.
3. **Transformer Coupling**: Utilizing transformers to couple the input signals can provide excellent isolation and help in impedance matching. However, this method may introduce additional complexity and cost.
4. **Feedback Resistor Network**: This method employs a network of resistors to set the gain of the amplifier and improve linearity. It can effectively control the bandwidth and stability of the amplifier but requires careful design to avoid introducing noise.
The differential amplifier's ability to maintain a high Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) is critical. CMRR quantifies the amplifier's ability to reject common-mode signals, which are noise or interference present on both inputs. A high CMRR indicates that the amplifier can effectively amplify the desired differential signal while minimizing the effect of unwanted common-mode signals.
In summary, the differential amplifier circuit's design and configuration play a pivotal role in its performance. By selecting the appropriate connection method, engineers can optimize the circuit for specific applications, ensuring high fidelity and reliable operation in various electronic systems.Differential amplifier circuit four connection methods and features comparison b b.0 magnification of a single tube of half earnings due anti-common-mode negative feed-effects, CMRR is still great adapted to the differential signal into a single-ended signal tube-like conditions
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713