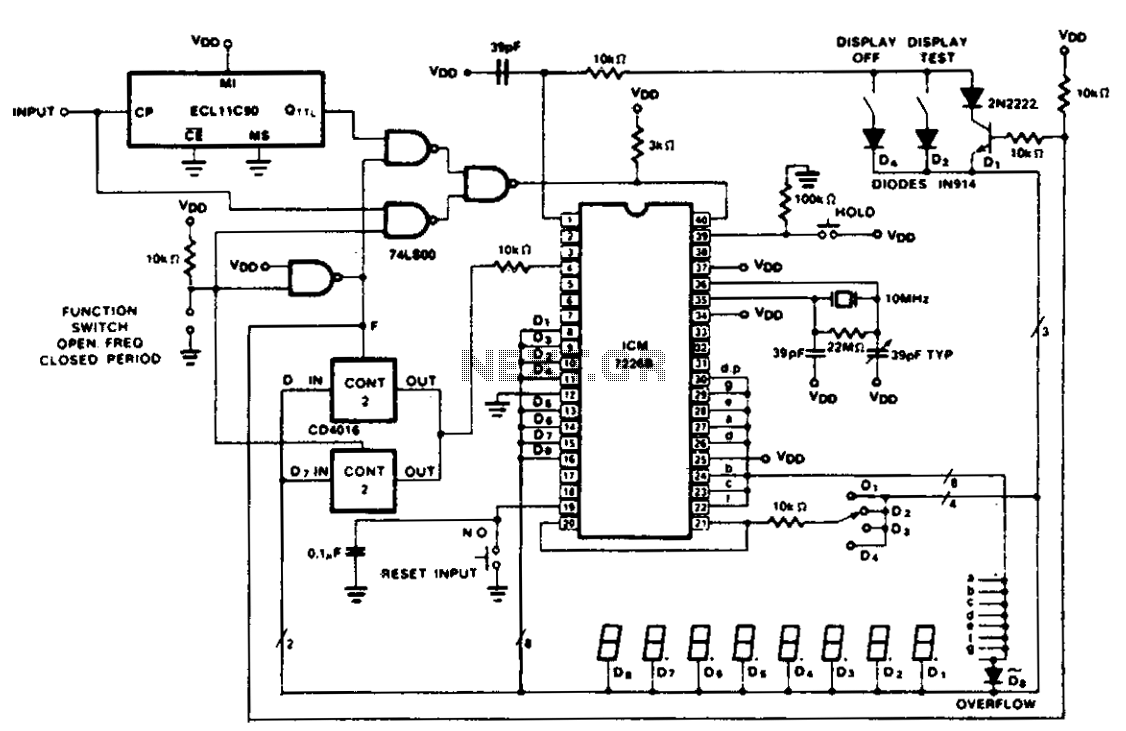
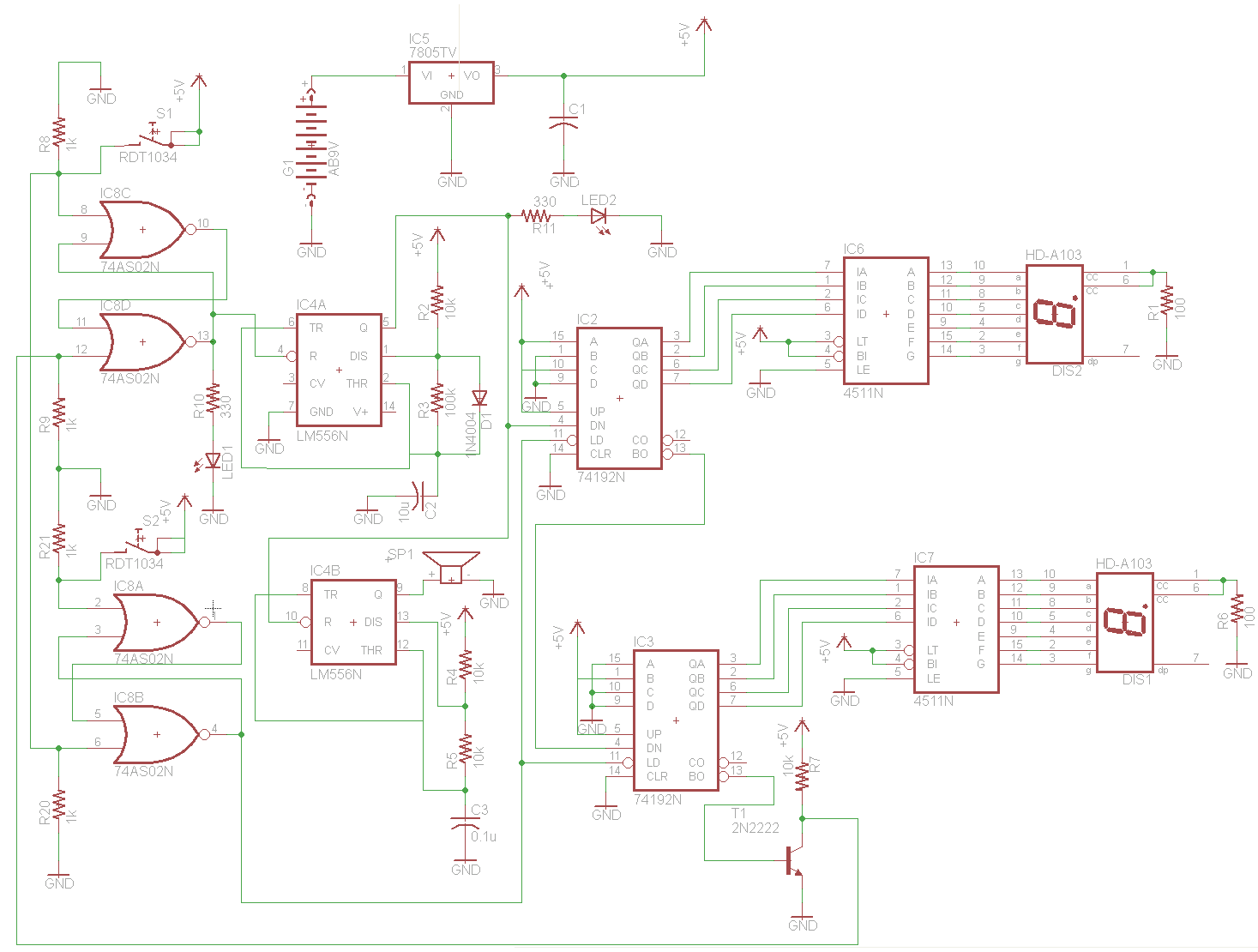
Digital 7 Segment Pulse Counter
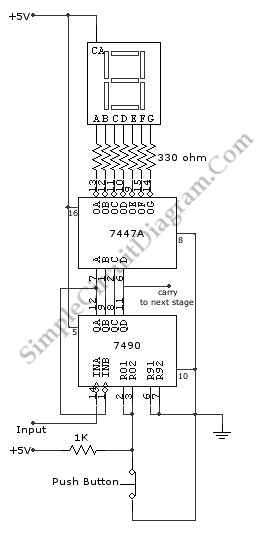
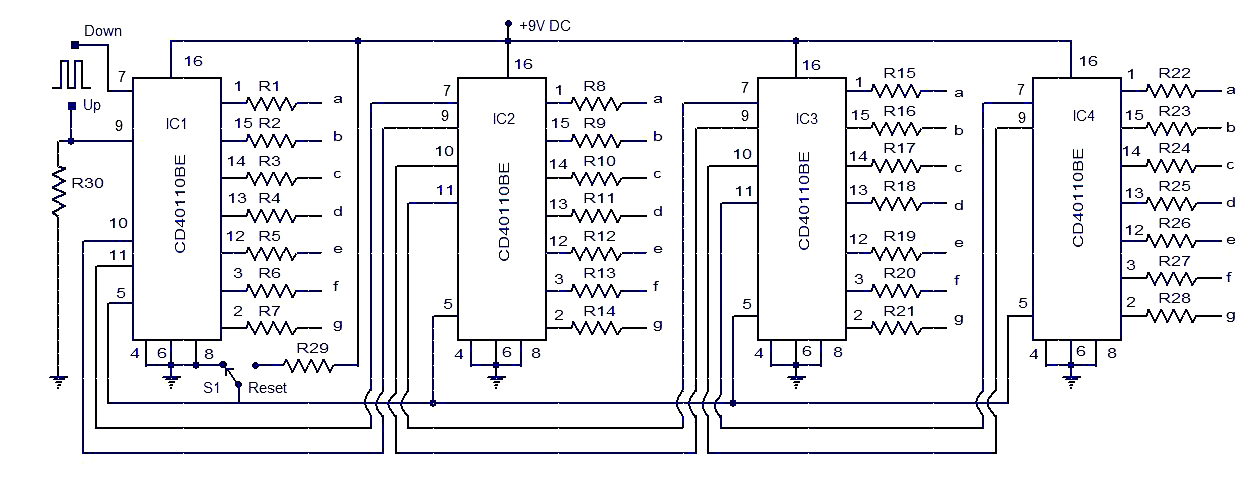
A pulse counter can be constructed using a 7490 decade counter and a 7557A timer. This circuit is capable of counting from zero to nine. Pins 3 and 2 of all 7490s must be interconnected.
The circuit utilizes the 7490 decade counter, which is a versatile IC designed to count pulses in a decimal format. It can count from 0 to 9, providing a straightforward solution for applications requiring basic counting functionality. The 7557A timer, on the other hand, serves as a dual timer and can be configured in monostable or astable mode, allowing for precise timing intervals or pulse generation to drive the counting process.
To construct the pulse counter, the 7490 IC should be connected in such a way that its output can be utilized to display the counted value. The interconnection of pins 3 and 2 is crucial as it allows for the proper functioning of the counter. Pin 3 typically serves as the carry-out pin, while pin 2 is used for enabling the counting operation. By connecting these pins across multiple 7490 ICs, it is possible to cascade them for counting beyond the single IC's limit, although in this specific application, only a single IC is utilized for counting up to nine.
The 7557A timer can be configured to generate clock pulses at a desired frequency, which will serve as the input to the 7490 counter. The output of the 7490 can then be fed into a display mechanism, such as a 7-segment display or an LED array, to visually represent the counted values. Additional components, such as resistors and capacitors, may be required to set the timing characteristics of the 7557A, ensuring that the pulse rate is suitable for the counting application.
Overall, this pulse counter circuit offers a simple yet effective solution for counting applications, leveraging the capabilities of the 7490 and 7557A integrated circuits to achieve reliable and accurate counting from zero to nine.A pulse counter can be built by using 7490 decode counter and 7557A. This circuit can count from zero to 9. Pins 3 and 2 of all 7490`s must be connected.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes the 7490 decade counter, which is a versatile IC designed to count pulses in a decimal format. It can count from 0 to 9, providing a straightforward solution for applications requiring basic counting functionality. The 7557A timer, on the other hand, serves as a dual timer and can be configured in monostable or astable mode, allowing for precise timing intervals or pulse generation to drive the counting process.
To construct the pulse counter, the 7490 IC should be connected in such a way that its output can be utilized to display the counted value. The interconnection of pins 3 and 2 is crucial as it allows for the proper functioning of the counter. Pin 3 typically serves as the carry-out pin, while pin 2 is used for enabling the counting operation. By connecting these pins across multiple 7490 ICs, it is possible to cascade them for counting beyond the single IC's limit, although in this specific application, only a single IC is utilized for counting up to nine.
The 7557A timer can be configured to generate clock pulses at a desired frequency, which will serve as the input to the 7490 counter. The output of the 7490 can then be fed into a display mechanism, such as a 7-segment display or an LED array, to visually represent the counted values. Additional components, such as resistors and capacitors, may be required to set the timing characteristics of the 7557A, ensuring that the pulse rate is suitable for the counting application.
Overall, this pulse counter circuit offers a simple yet effective solution for counting applications, leveraging the capabilities of the 7490 and 7557A integrated circuits to achieve reliable and accurate counting from zero to nine.A pulse counter can be built by using 7490 decode counter and 7557A. This circuit can count from zero to 9. Pins 3 and 2 of all 7490`s must be connected.. 🔗 External reference