DIGITAL TACHOMETER COUNTER
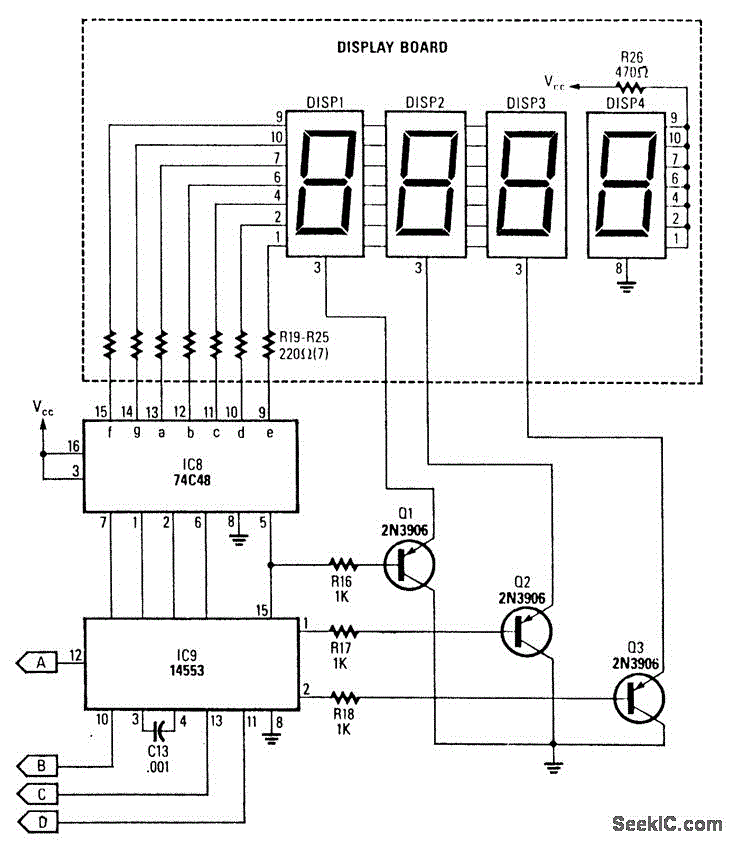
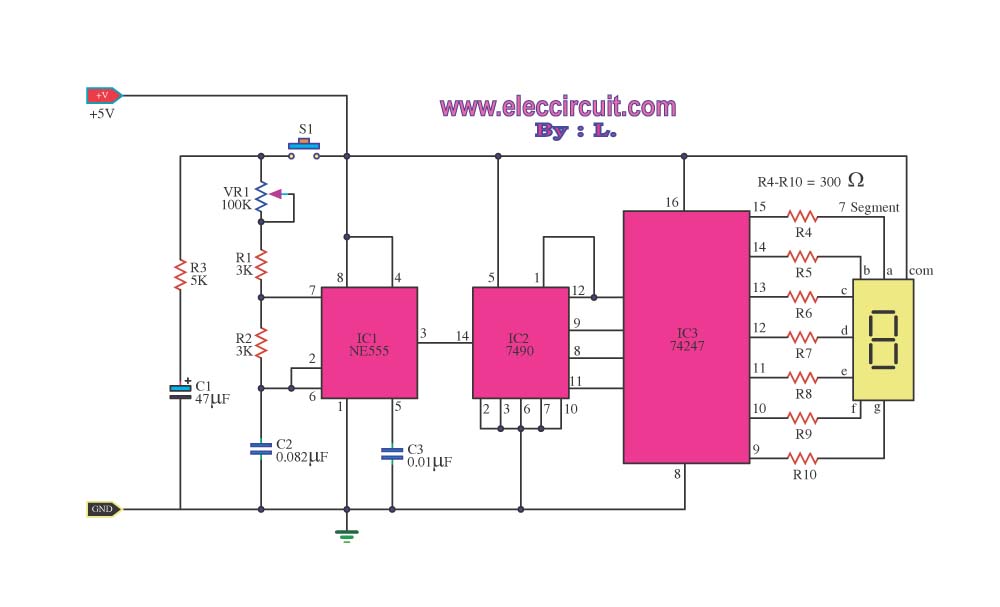
This circuit generates a readout for a digital tachometer. IC9 functions as a 3-digit LED display driver, counter, and latch. IC8 operates the common cathode LEDs, which are activated by transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3. Refer to page 268, Fig. 46-5 for the corresponding project.
The described circuit serves the purpose of displaying rotational speed in a digital format through a tachometer. The primary component, IC9, is responsible for driving a 3-digit LED display, which allows for the visualization of the measured RPM (Revolutions Per Minute). It integrates functionalities of a counter and a latch, enabling it to count pulses from a sensor that detects the rotational speed of a motor or other rotating machinery.
IC8 is utilized to drive the common cathode LED configuration. This configuration means that the cathodes of the LEDs are connected to ground, and the anodes are driven high by the display driver IC. The activation of the LEDs is controlled by transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3, which act as switches. When a pulse is detected by the counter, the corresponding transistor will turn on, allowing current to flow through the specific LED segment, thus illuminating it. This process is essential for displaying the correct digits on the LED screen.
For accurate functioning, the circuit must be calibrated to ensure that the pulse count corresponds correctly to the actual RPM being measured. The layout of the circuit should minimize noise and interference, which could affect the accuracy of the tachometer readings. Proper power supply decoupling and grounding techniques should be employed to ensure stable operation.
Referencing page 268, Fig. 46-5 provides additional insights into the schematic and layout of the project, illustrating how the components interconnect and function together to achieve the desired tachometer readout.This circuit produces a readout for the digital tachometer circuit.IC9 is a 3-digit LED display driver,counter,and latch?IC8 drives the common?cathode LEDs,which are enabled by Q1,Q2,and Q3.See page 268?Fig.46-5 for the matching project?.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit serves the purpose of displaying rotational speed in a digital format through a tachometer. The primary component, IC9, is responsible for driving a 3-digit LED display, which allows for the visualization of the measured RPM (Revolutions Per Minute). It integrates functionalities of a counter and a latch, enabling it to count pulses from a sensor that detects the rotational speed of a motor or other rotating machinery.
IC8 is utilized to drive the common cathode LED configuration. This configuration means that the cathodes of the LEDs are connected to ground, and the anodes are driven high by the display driver IC. The activation of the LEDs is controlled by transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3, which act as switches. When a pulse is detected by the counter, the corresponding transistor will turn on, allowing current to flow through the specific LED segment, thus illuminating it. This process is essential for displaying the correct digits on the LED screen.
For accurate functioning, the circuit must be calibrated to ensure that the pulse count corresponds correctly to the actual RPM being measured. The layout of the circuit should minimize noise and interference, which could affect the accuracy of the tachometer readings. Proper power supply decoupling and grounding techniques should be employed to ensure stable operation.
Referencing page 268, Fig. 46-5 provides additional insights into the schematic and layout of the project, illustrating how the components interconnect and function together to achieve the desired tachometer readout.This circuit produces a readout for the digital tachometer circuit.IC9 is a 3-digit LED display driver,counter,and latch?IC8 drives the common?cathode LEDs,which are enabled by Q1,Q2,and Q3.See page 268?Fig.46-5 for the matching project?.. 🔗 External reference