Fet curve tracer
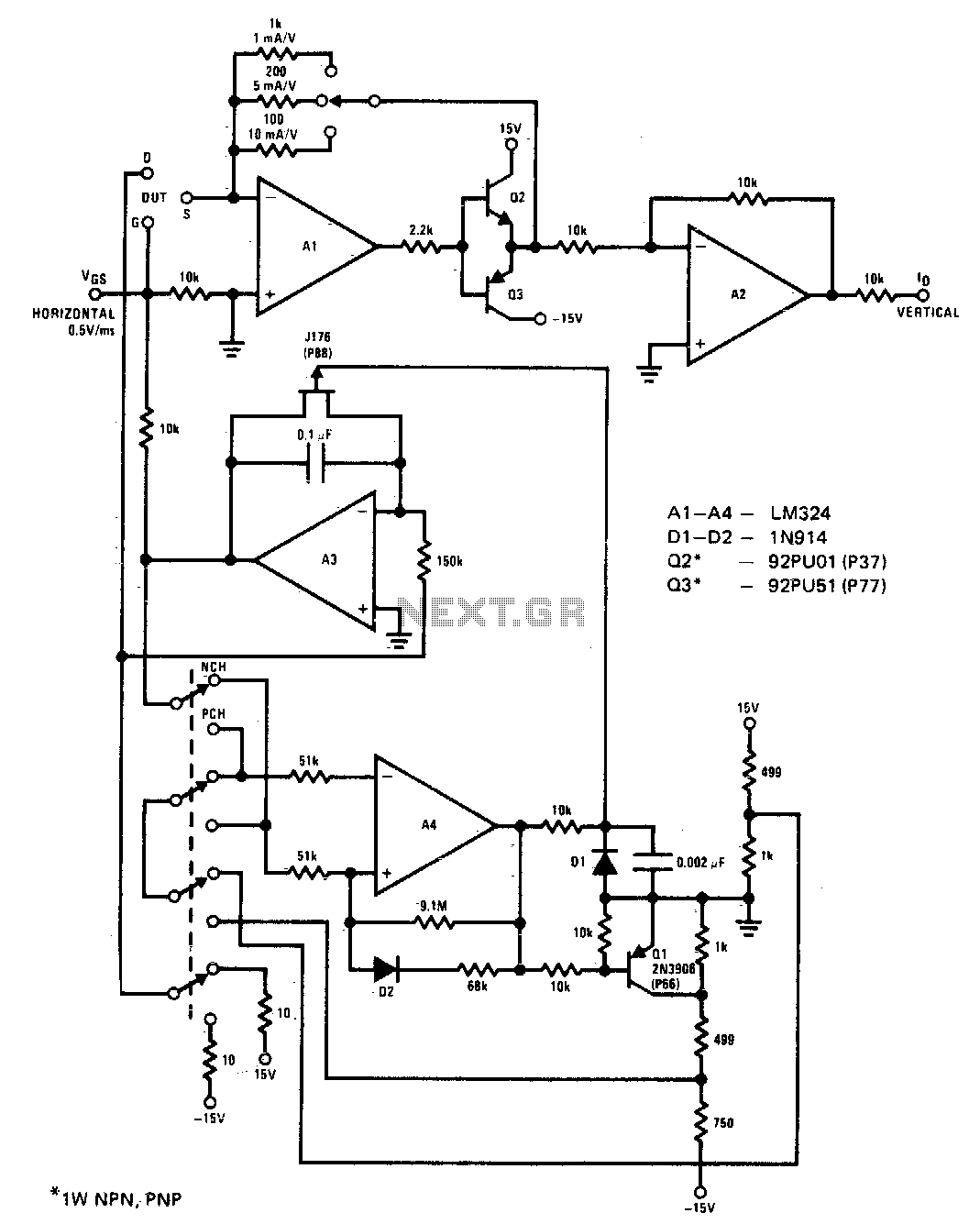
The circuit displays drain current versus gate voltage for both P-channel and N-channel JFETs at a constant drain voltage.
The described circuit is designed to analyze the characteristics of Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFETs), specifically focusing on the relationship between the drain current (Id) and the gate voltage (Vg) for both P-channel and N-channel types. This analysis is crucial for understanding the operational behavior of JFETs within various electronic applications.
In the circuit, the drain current is monitored while maintaining a constant drain-source voltage (Vds). The gate voltage is varied to observe how it impacts the drain current. For N-channel JFETs, as the gate voltage is decreased (more negative), the depletion region widens, leading to a reduction in the channel conductivity, which in turn decreases the drain current. Conversely, for P-channel JFETs, increasing the gate voltage (more positive) results in a similar effect, reducing the drain current.
The circuit typically includes a power supply to provide the necessary Vds, a variable resistor or potentiometer to adjust the gate voltage, and an ammeter or current sensing resistor to measure the drain current. The output can be graphed to create a characteristic curve, illustrating the Id versus Vg relationship for both types of JFETs. This curve is essential for determining the operating region of the transistors and for designing circuits that utilize them effectively.
In summary, the circuit serves as a fundamental tool for studying the electrical characteristics of JFETs, aiding in the design and implementation of more complex electronic systems.The circuit displays drain current versus gate voltage for both P and N-channel JFETS at a constant drain voltge.
The described circuit is designed to analyze the characteristics of Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFETs), specifically focusing on the relationship between the drain current (Id) and the gate voltage (Vg) for both P-channel and N-channel types. This analysis is crucial for understanding the operational behavior of JFETs within various electronic applications.
In the circuit, the drain current is monitored while maintaining a constant drain-source voltage (Vds). The gate voltage is varied to observe how it impacts the drain current. For N-channel JFETs, as the gate voltage is decreased (more negative), the depletion region widens, leading to a reduction in the channel conductivity, which in turn decreases the drain current. Conversely, for P-channel JFETs, increasing the gate voltage (more positive) results in a similar effect, reducing the drain current.
The circuit typically includes a power supply to provide the necessary Vds, a variable resistor or potentiometer to adjust the gate voltage, and an ammeter or current sensing resistor to measure the drain current. The output can be graphed to create a characteristic curve, illustrating the Id versus Vg relationship for both types of JFETs. This curve is essential for determining the operating region of the transistors and for designing circuits that utilize them effectively.
In summary, the circuit serves as a fundamental tool for studying the electrical characteristics of JFETs, aiding in the design and implementation of more complex electronic systems.The circuit displays drain current versus gate voltage for both P and N-channel JFETS at a constant drain voltge.