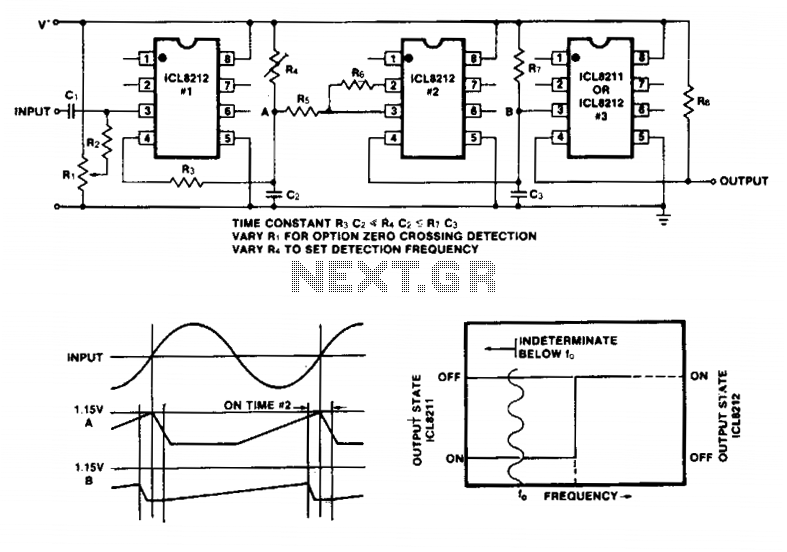
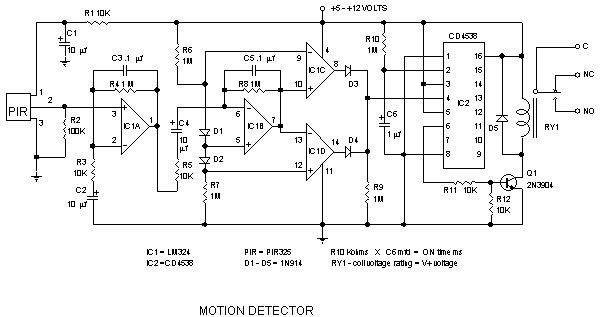
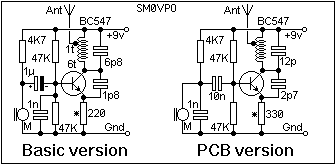
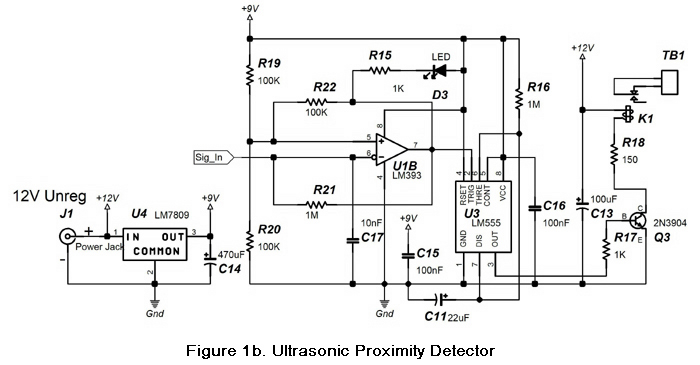
FM Bug Detector Kit
This device is designed for individuals concerned about surveillance. An essential tool for any operative is an Electronic Bug Detector, as it helps identify hidden listening devices.
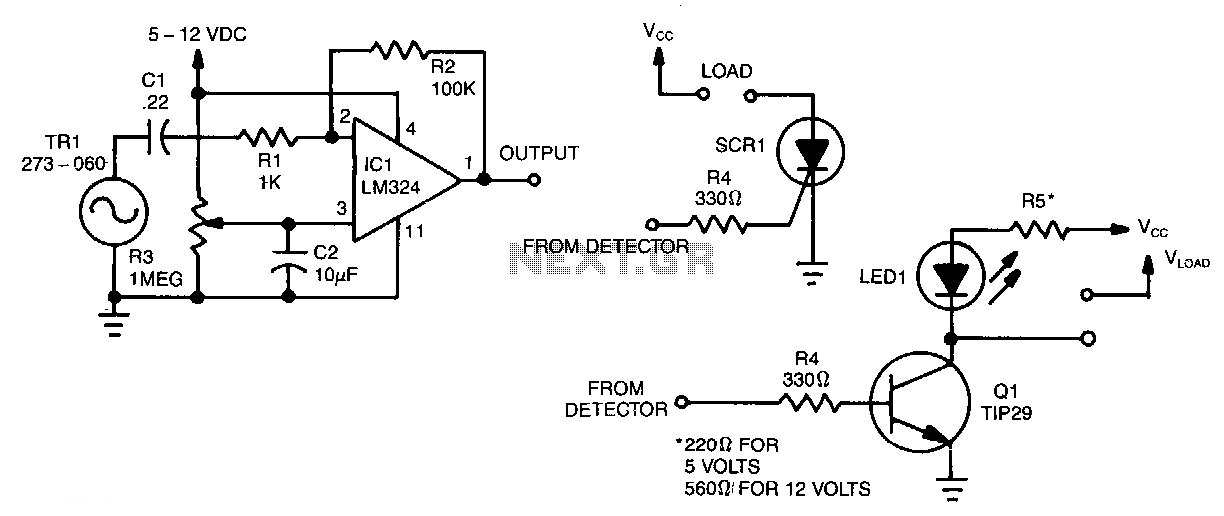
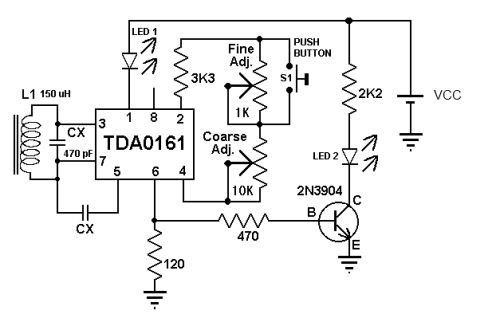
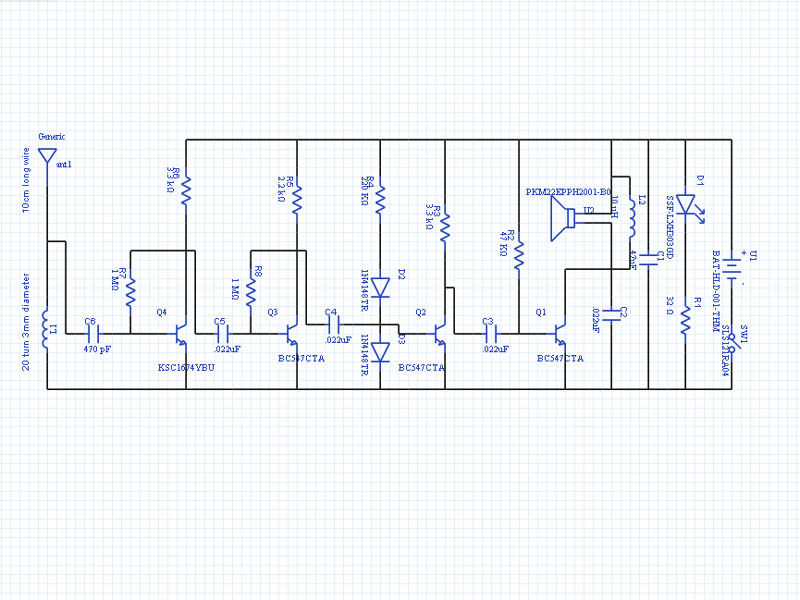
The Electronic Bug Detector serves as a critical instrument for privacy protection in environments where unauthorized surveillance may occur. It typically operates by detecting radio frequency (RF) signals emitted by wireless listening devices, hidden cameras, and other surveillance equipment. The device can be equipped with various features, including adjustable sensitivity settings, a visual display for signal strength, and audio alerts to indicate the presence of detected signals.
In terms of circuitry, the core of the bug detector typically includes a radio frequency receiver capable of tuning into a range of frequencies where common surveillance devices operate. The receiver is usually coupled with a microcontroller that processes the incoming signals and determines their strength. The output can be visualized through an LED array or an LCD screen, providing users with real-time feedback on the detected signals.
Power supply considerations are also critical; most bug detectors operate on batteries, making portability essential. The choice of components such as low-noise amplifiers and filters can enhance the detector's performance, allowing it to distinguish between legitimate RF sources and potential threats.
Overall, the Electronic Bug Detector is a sophisticated device that combines various electronic components to ensure users can maintain their privacy and security in an increasingly surveilled world.This is for all the spies/paranoid people out there. An essential piece of equipment for any spy is an Electronic Bug Detector. You never know what go.. 🔗 External reference
The Electronic Bug Detector serves as a critical instrument for privacy protection in environments where unauthorized surveillance may occur. It typically operates by detecting radio frequency (RF) signals emitted by wireless listening devices, hidden cameras, and other surveillance equipment. The device can be equipped with various features, including adjustable sensitivity settings, a visual display for signal strength, and audio alerts to indicate the presence of detected signals.
In terms of circuitry, the core of the bug detector typically includes a radio frequency receiver capable of tuning into a range of frequencies where common surveillance devices operate. The receiver is usually coupled with a microcontroller that processes the incoming signals and determines their strength. The output can be visualized through an LED array or an LCD screen, providing users with real-time feedback on the detected signals.
Power supply considerations are also critical; most bug detectors operate on batteries, making portability essential. The choice of components such as low-noise amplifiers and filters can enhance the detector's performance, allowing it to distinguish between legitimate RF sources and potential threats.
Overall, the Electronic Bug Detector is a sophisticated device that combines various electronic components to ensure users can maintain their privacy and security in an increasingly surveilled world.This is for all the spies/paranoid people out there. An essential piece of equipment for any spy is an Electronic Bug Detector. You never know what go.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713