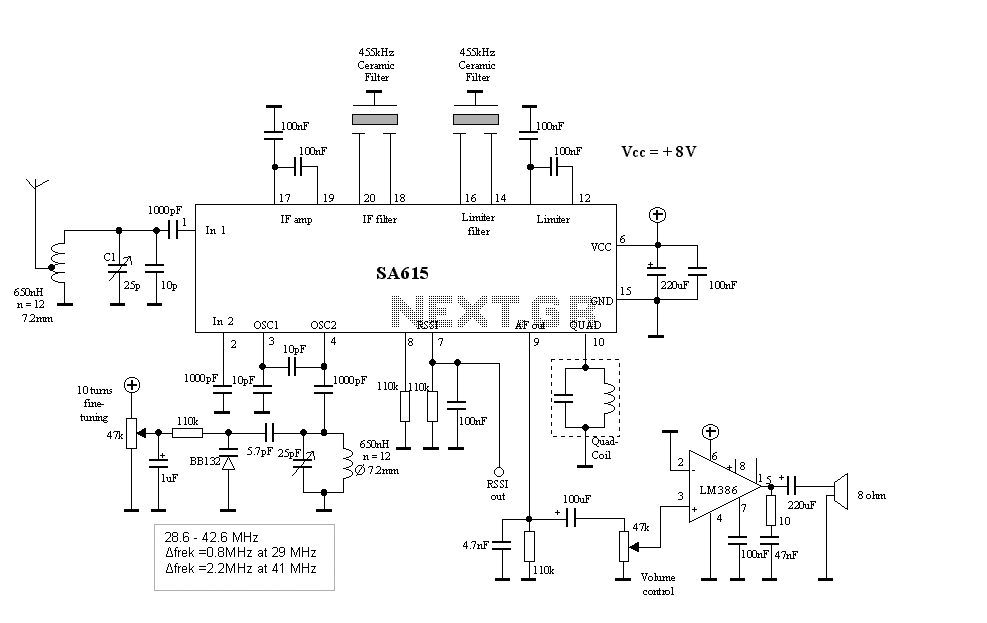
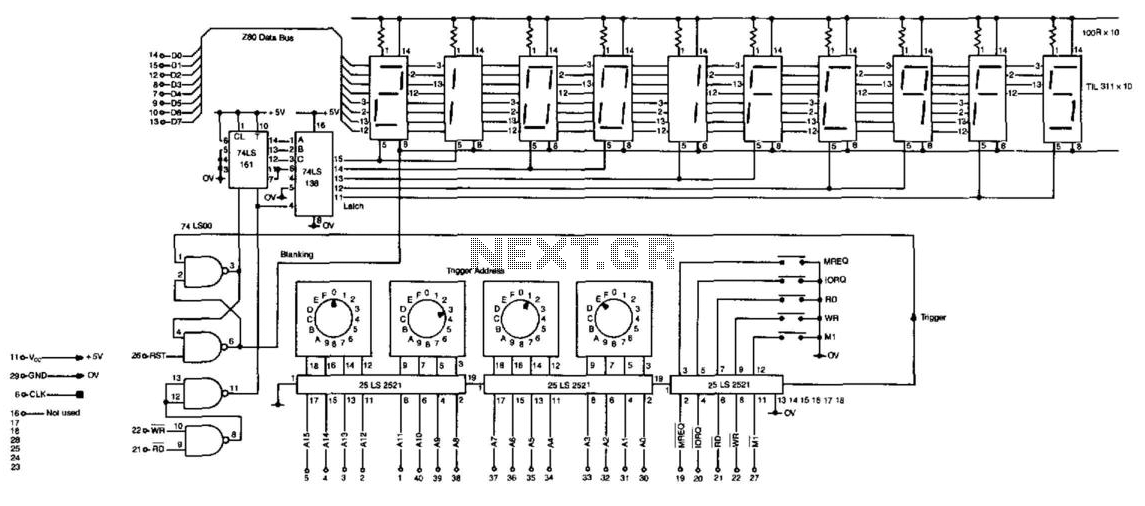
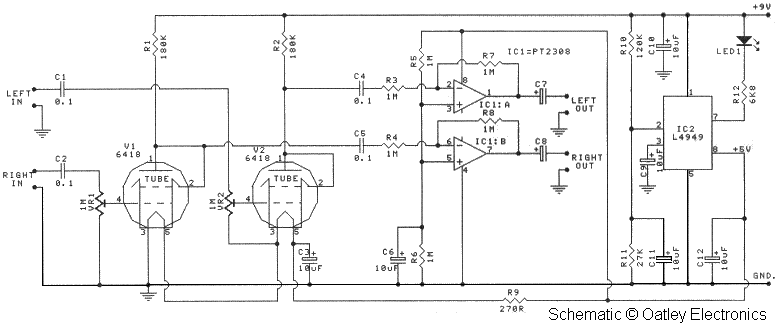
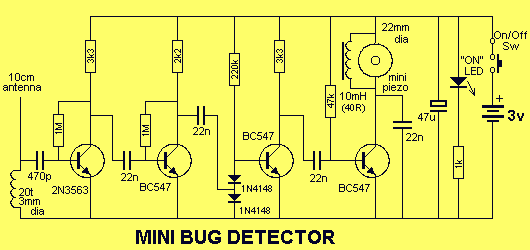
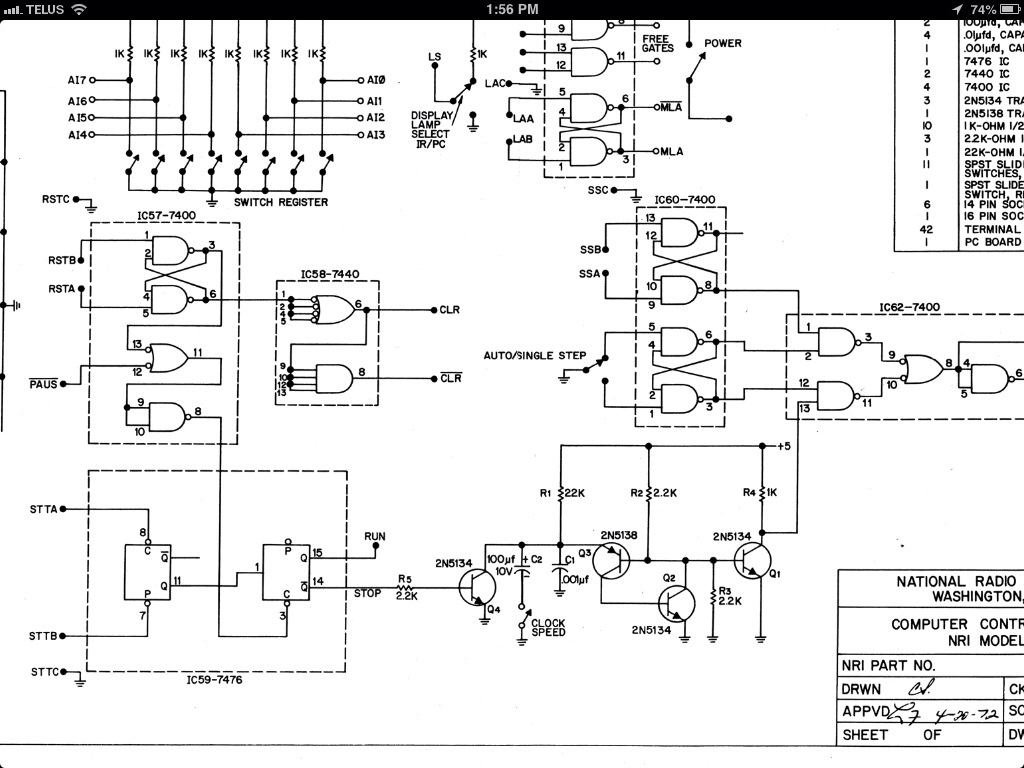
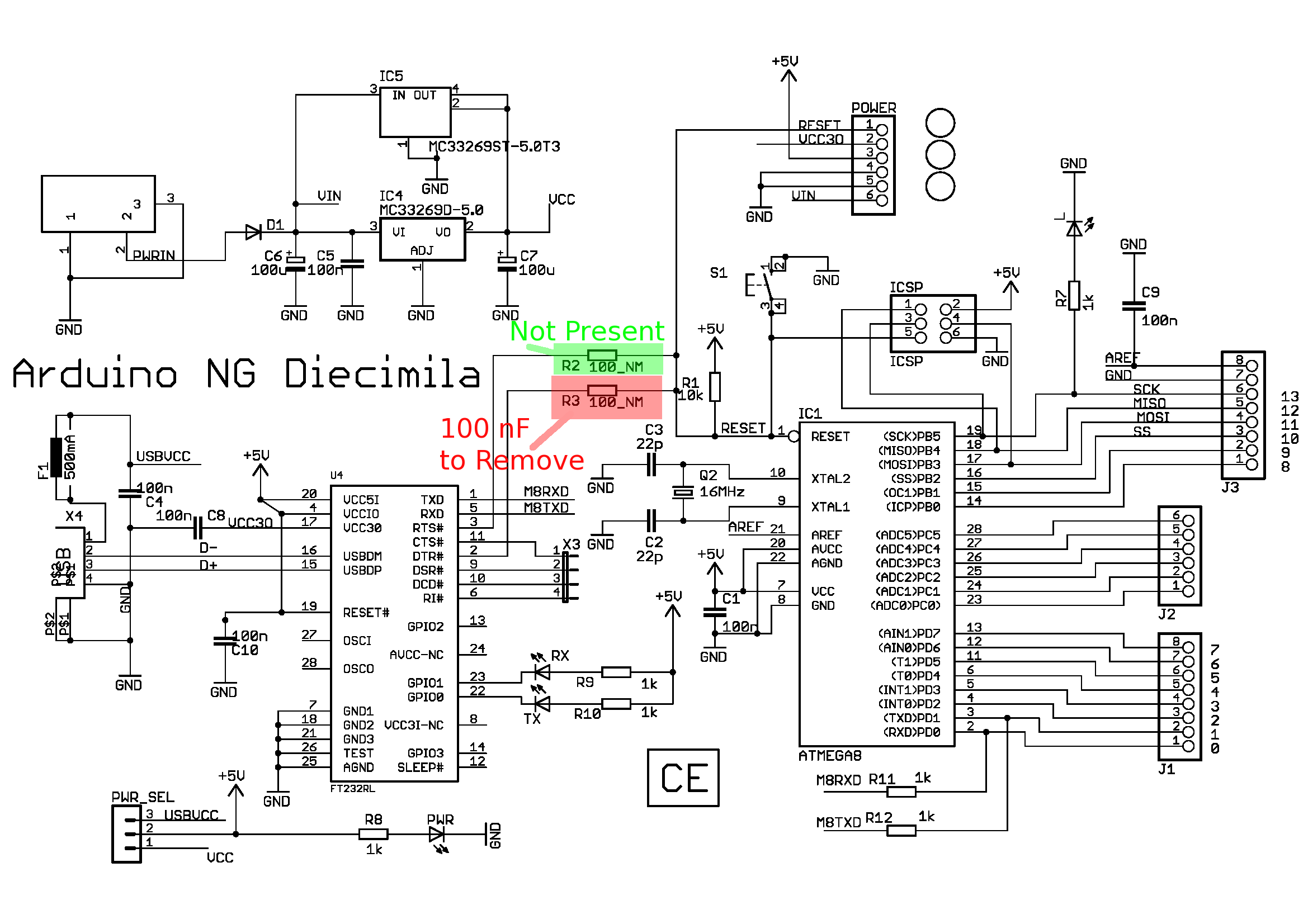
FM Listening Bug Kit
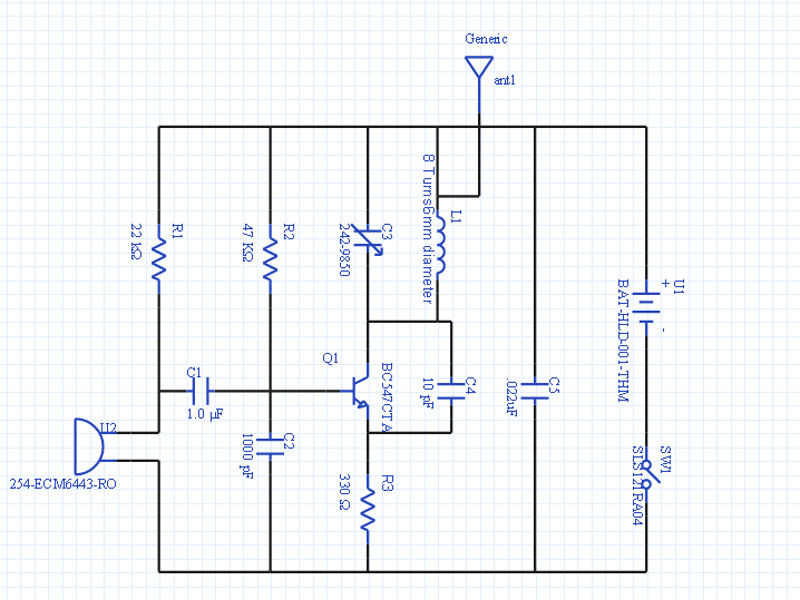
The schematic below illustrates a simple circuit that is straightforward to construct. One aspect that is not clearly represented in the schematic is the location of certain components.
This circuit design comprises a basic arrangement of electronic components, typically including resistors, capacitors, and possibly diodes or transistors, depending on the specific application. The simplicity of the circuit allows for ease of assembly, making it suitable for beginners or for educational purposes in electronics.
Key components may include a power source, such as a battery or power supply, which provides the necessary voltage and current for operation. Resistors are often used to limit current flow, while capacitors can be utilized for smoothing voltage fluctuations or for timing applications. If diodes are included, they may serve to protect the circuit from reverse polarity or to rectify AC signals into DC.
The schematic should clearly indicate the connections between these components, often represented by lines that denote electrical pathways. Each component will be labeled with its respective value, such as resistance in ohms for resistors or capacitance in farads for capacitors, ensuring that the builder can accurately replicate the circuit.
Additionally, it is crucial to pay attention to the orientation of polarized components, such as electrolytic capacitors and diodes, as incorrect placement can lead to circuit failure. The layout should facilitate a logical flow of current, ensuring that all components are connected in a manner that fulfills the intended function of the circuit.
Proper assembly techniques, such as soldering connections cleanly and securely, will contribute to the reliability and longevity of the circuit. Testing the circuit with a multimeter before powering it on can help identify any potential issues in the assembly process, ensuring that the final product operates as designed.As you can see in the schematic below this is a very simple circuit and will be an easy build. On thing the Schematic doesn`t convey very well is wher.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit design comprises a basic arrangement of electronic components, typically including resistors, capacitors, and possibly diodes or transistors, depending on the specific application. The simplicity of the circuit allows for ease of assembly, making it suitable for beginners or for educational purposes in electronics.
Key components may include a power source, such as a battery or power supply, which provides the necessary voltage and current for operation. Resistors are often used to limit current flow, while capacitors can be utilized for smoothing voltage fluctuations or for timing applications. If diodes are included, they may serve to protect the circuit from reverse polarity or to rectify AC signals into DC.
The schematic should clearly indicate the connections between these components, often represented by lines that denote electrical pathways. Each component will be labeled with its respective value, such as resistance in ohms for resistors or capacitance in farads for capacitors, ensuring that the builder can accurately replicate the circuit.
Additionally, it is crucial to pay attention to the orientation of polarized components, such as electrolytic capacitors and diodes, as incorrect placement can lead to circuit failure. The layout should facilitate a logical flow of current, ensuring that all components are connected in a manner that fulfills the intended function of the circuit.
Proper assembly techniques, such as soldering connections cleanly and securely, will contribute to the reliability and longevity of the circuit. Testing the circuit with a multimeter before powering it on can help identify any potential issues in the assembly process, ensuring that the final product operates as designed.As you can see in the schematic below this is a very simple circuit and will be an easy build. On thing the Schematic doesn`t convey very well is wher.. 🔗 External reference