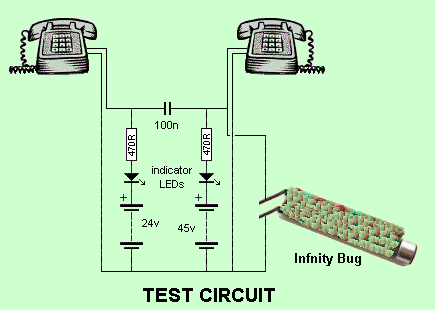
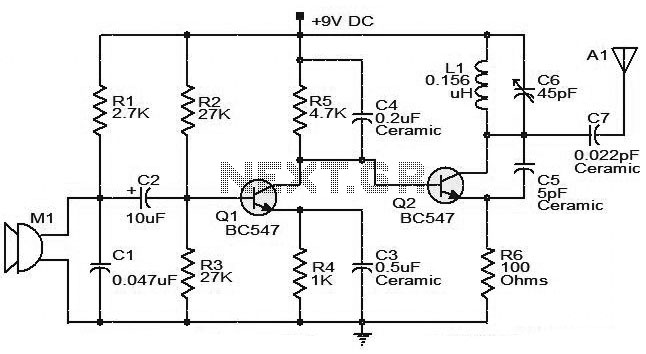
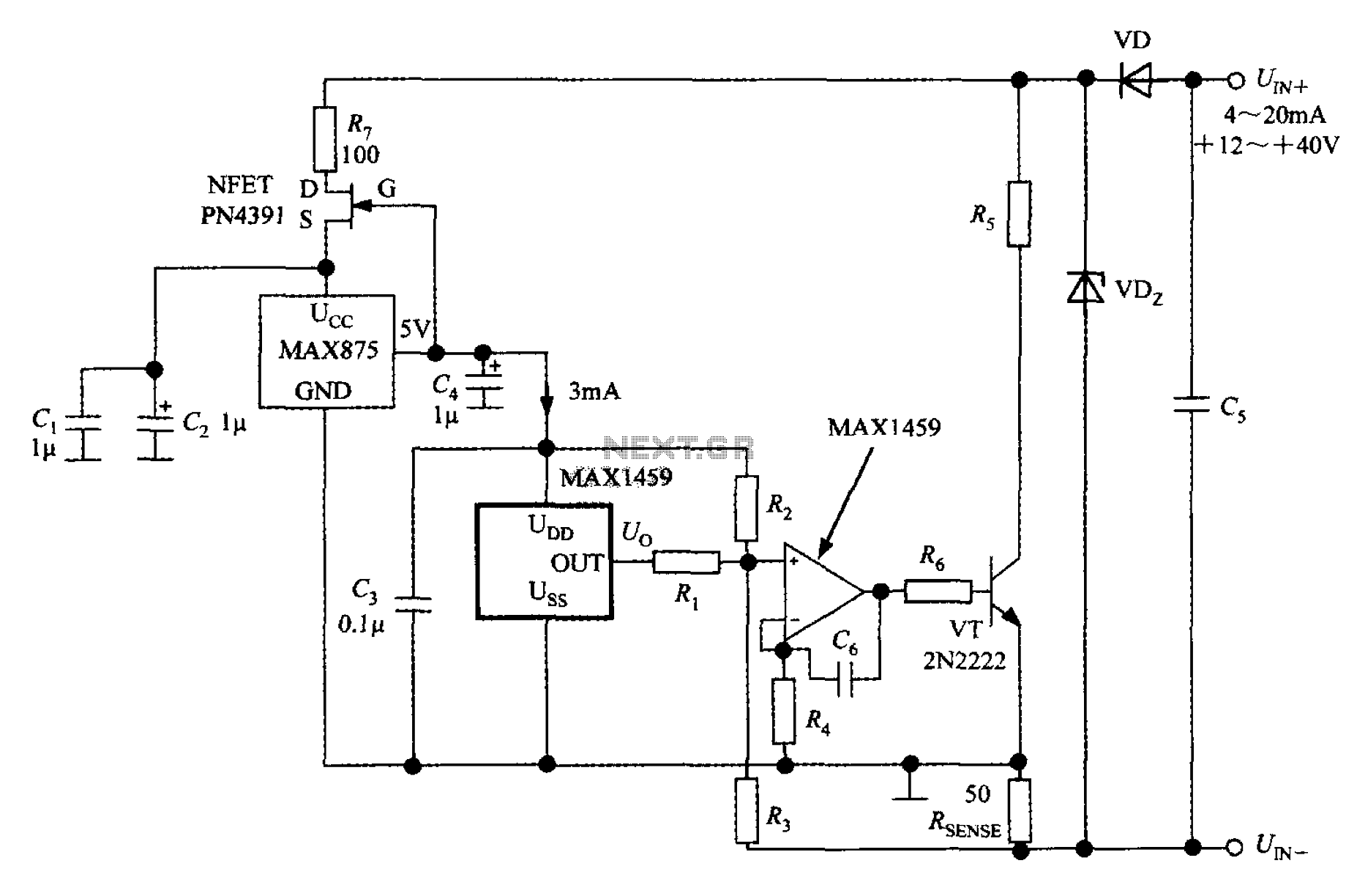
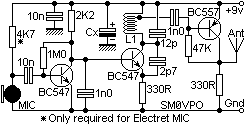
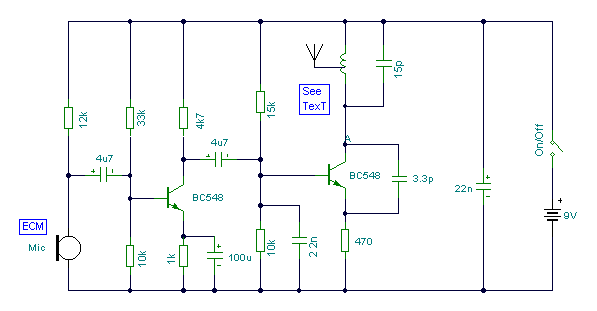
FM surveillance BuG Transmitter
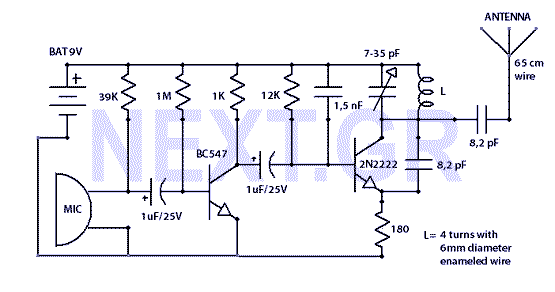
The circuit illustrated is capable of transmitting voice over an exceptionally wide range. Adjust the trimmer to receive the signal on a nearby radio. The frequency range operates between 88 and 108 MHz, with a maximum current consumption of 30 mA. Power can be supplied using a 9-volt battery or by connecting a power supply providing 9 to 12 volts. Source: NEXT.GR.
The described circuit functions as a low-power FM transmitter, suitable for voice transmission within the FM radio band. The operating frequency range of 88 to 108 MHz is standard for commercial FM radio stations, allowing the circuit to be compatible with most FM receivers. The circuit design typically includes a microphone for audio input, an oscillator circuit to modulate the audio signal onto the carrier frequency, and an output stage to amplify the modulated signal for transmission.
To optimize performance, the trimmer capacitor is used to fine-tune the oscillator circuit, ensuring that the transmitted signal is within the desired frequency range. This adjustment is crucial for minimizing interference with other radio signals and maximizing clarity in audio transmission.
The power requirements indicate a low-power design, with a maximum current consumption of 30 mA, making it energy-efficient. The option to use a 9-volt battery or an external power supply ranging from 9 to 12 volts provides flexibility in powering the circuit, catering to various applications and user preferences.
Additional components may include resistors and capacitors for filtering and stability, and an antenna to enhance the transmission range. The overall design should ensure that the circuit is compact and portable, suitable for various environments where voice transmission is needed. Proper assembly and tuning are essential to achieve optimal performance and avoid regulatory issues related to unauthorized transmission in the FM band.The Circuit shown can transmit voice to exceptionally good range. Tune trimmer to hear the signal to your near radio. Frequency range is 88-108 MHz. Max current consumption is 30mA. You can power the bug with a 9Volt Battery, or you can plug a power supply to feed in 9-12 Volts. Source: NEXT.GR.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a low-power FM transmitter, suitable for voice transmission within the FM radio band. The operating frequency range of 88 to 108 MHz is standard for commercial FM radio stations, allowing the circuit to be compatible with most FM receivers. The circuit design typically includes a microphone for audio input, an oscillator circuit to modulate the audio signal onto the carrier frequency, and an output stage to amplify the modulated signal for transmission.
To optimize performance, the trimmer capacitor is used to fine-tune the oscillator circuit, ensuring that the transmitted signal is within the desired frequency range. This adjustment is crucial for minimizing interference with other radio signals and maximizing clarity in audio transmission.
The power requirements indicate a low-power design, with a maximum current consumption of 30 mA, making it energy-efficient. The option to use a 9-volt battery or an external power supply ranging from 9 to 12 volts provides flexibility in powering the circuit, catering to various applications and user preferences.
Additional components may include resistors and capacitors for filtering and stability, and an antenna to enhance the transmission range. The overall design should ensure that the circuit is compact and portable, suitable for various environments where voice transmission is needed. Proper assembly and tuning are essential to achieve optimal performance and avoid regulatory issues related to unauthorized transmission in the FM band.The Circuit shown can transmit voice to exceptionally good range. Tune trimmer to hear the signal to your near radio. Frequency range is 88-108 MHz. Max current consumption is 30mA. You can power the bug with a 9Volt Battery, or you can plug a power supply to feed in 9-12 Volts. Source: NEXT.GR.. 🔗 External reference