Forward and reverse operation of the dynamic braking circuit 2
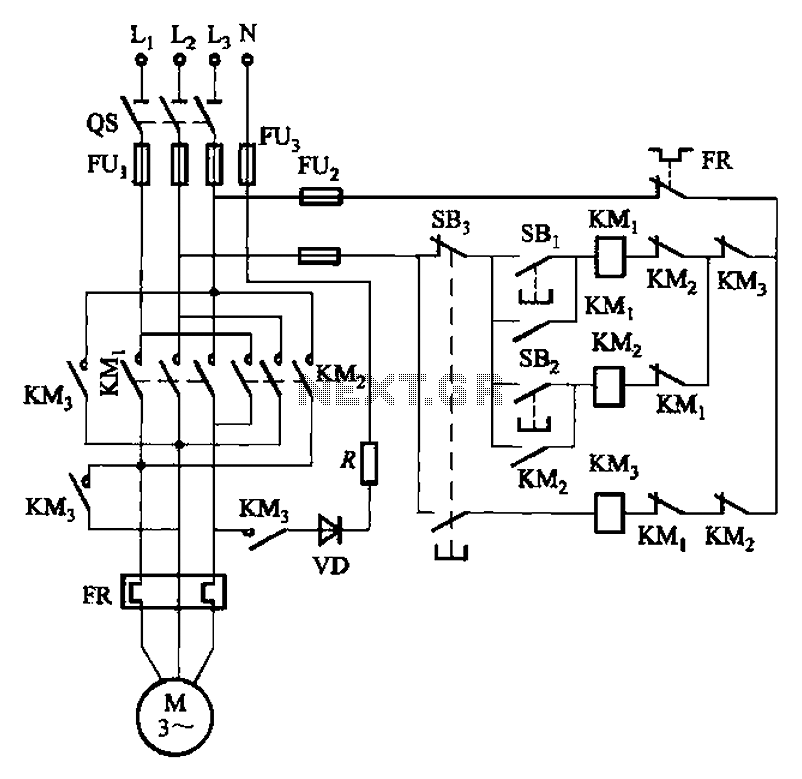
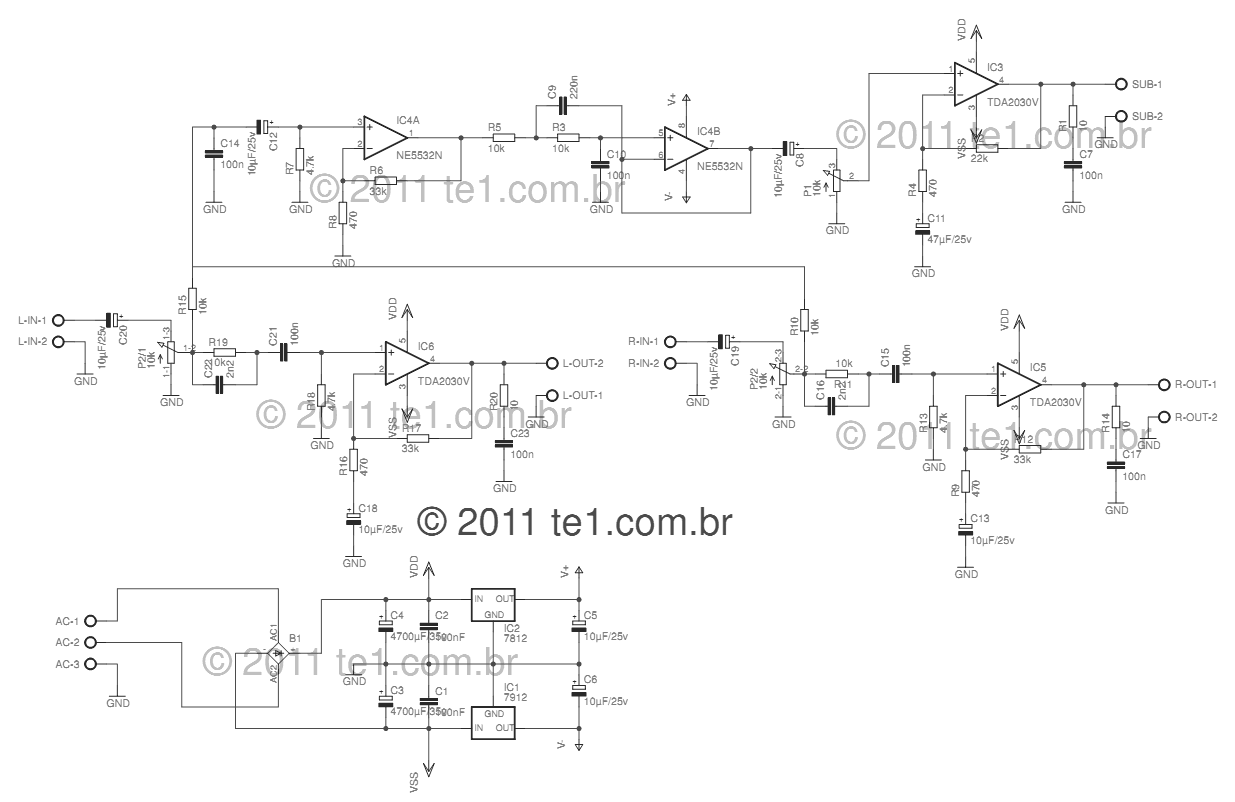
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-145 employs a rectifier diode brake for neutral grounding in a three-phase, four-wire power supply system.
This circuit design incorporates a rectifier diode brake, which plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of a three-phase power supply system. The primary function of the rectifier diode is to convert alternating current (AC) from the power supply into direct current (DC), which is essential for maintaining a stable voltage level and preventing fluctuations that could damage connected equipment.
In a three-phase, four-wire system, the neutral wire serves as a return path for unbalanced loads, allowing for the effective distribution of power across the three phases. The rectifier diode brake is strategically connected to the neutral point to ground the system, which helps in stabilizing the voltage levels and provides a reference point for the system. This grounding mechanism is vital for protecting the circuit from overvoltage conditions and ensuring that any fault currents are safely diverted to the ground, thereby minimizing the risk of electrical shock or equipment damage.
The circuit's configuration may include additional components such as capacitors for filtering, resistors for current limiting, and possibly fuses for overcurrent protection. These elements work in conjunction to enhance the overall performance and safety of the power supply system. Proper sizing and rating of the rectifier diode are essential to handle the expected load currents and to ensure efficient operation without overheating or failure.
Overall, the implementation of a rectifier diode brake in a three-phase, four-wire power supply system is a critical aspect of electrical engineering that contributes to the efficient and safe operation of industrial and commercial electrical systems.1The circuit shown in Figure 3-145. The line uses a rectifier diode rectifier brake for neutral grounding of the three-phase four-wire power supply system.
This circuit design incorporates a rectifier diode brake, which plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of a three-phase power supply system. The primary function of the rectifier diode is to convert alternating current (AC) from the power supply into direct current (DC), which is essential for maintaining a stable voltage level and preventing fluctuations that could damage connected equipment.
In a three-phase, four-wire system, the neutral wire serves as a return path for unbalanced loads, allowing for the effective distribution of power across the three phases. The rectifier diode brake is strategically connected to the neutral point to ground the system, which helps in stabilizing the voltage levels and provides a reference point for the system. This grounding mechanism is vital for protecting the circuit from overvoltage conditions and ensuring that any fault currents are safely diverted to the ground, thereby minimizing the risk of electrical shock or equipment damage.
The circuit's configuration may include additional components such as capacitors for filtering, resistors for current limiting, and possibly fuses for overcurrent protection. These elements work in conjunction to enhance the overall performance and safety of the power supply system. Proper sizing and rating of the rectifier diode are essential to handle the expected load currents and to ensure efficient operation without overheating or failure.
Overall, the implementation of a rectifier diode brake in a three-phase, four-wire power supply system is a critical aspect of electrical engineering that contributes to the efficient and safe operation of industrial and commercial electrical systems.1The circuit shown in Figure 3-145. The line uses a rectifier diode rectifier brake for neutral grounding of the three-phase four-wire power supply system.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713