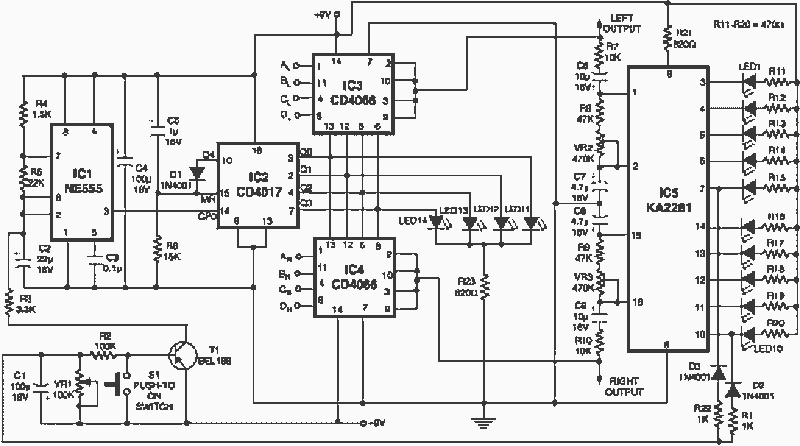
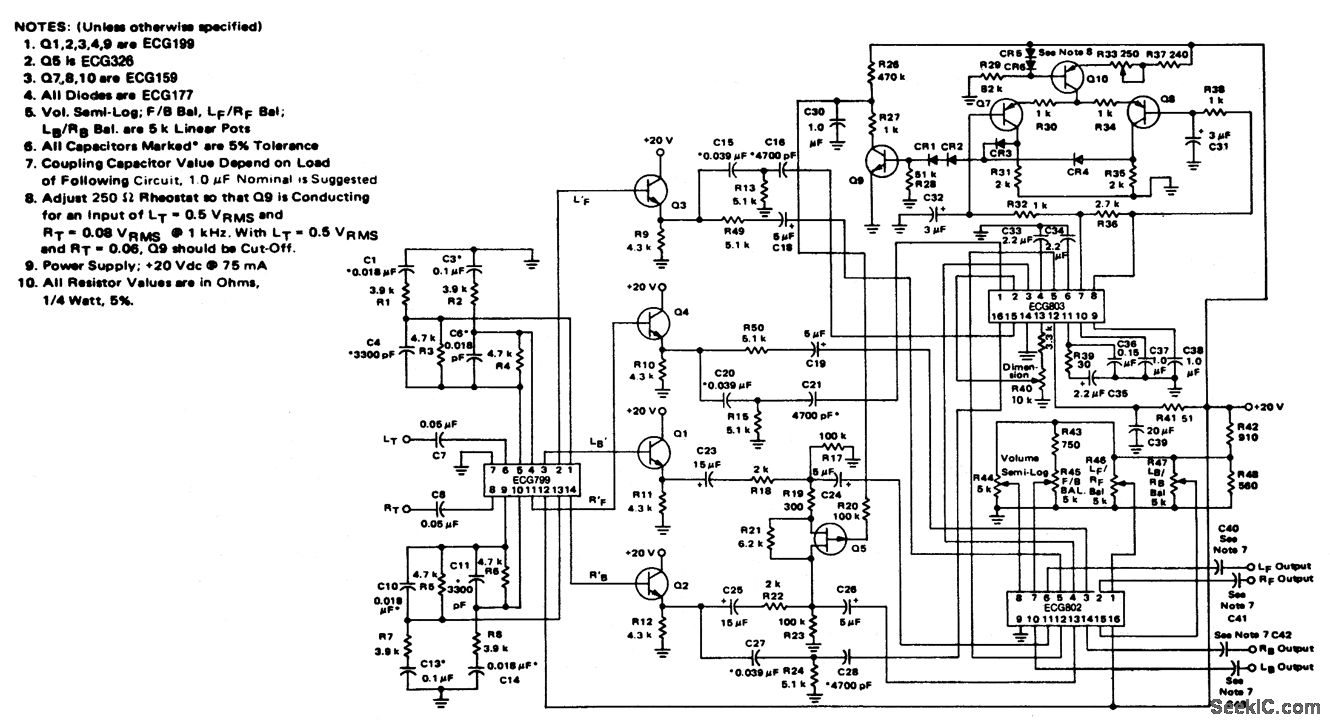
Four channel synthesizer
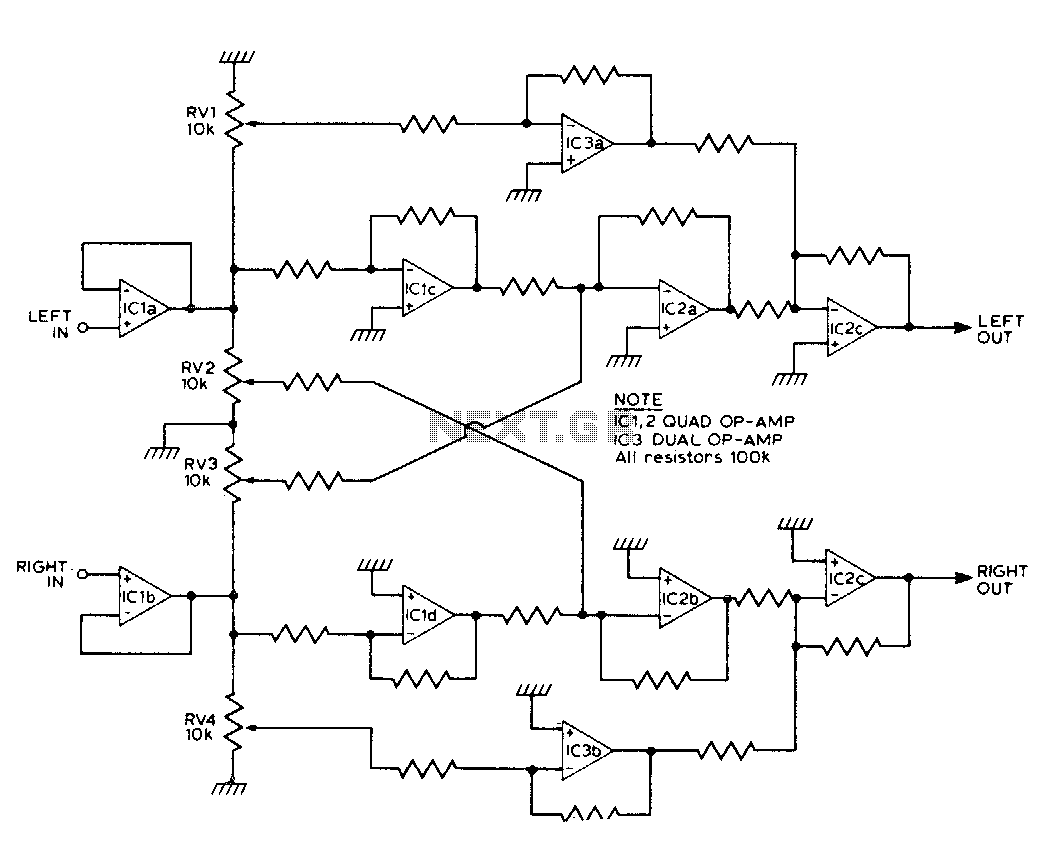
This circuit synthesizes two rear channels for quadraphonic sound when provided with a stereo signal. The rear output for the left channel is created by combining the left channel input, which is 180 degrees out of phase, with a portion of the right channel (also out of phase). Similarly, the right rear output is generated in a comparable manner.
The quadraphonic sound synthesis circuit operates by utilizing phase manipulation to create a spatial audio experience. The left rear channel is derived from the left stereo input, which is inverted (180 degrees phase shift) to create a distinct auditory effect. This inversion is crucial as it allows for the cancellation of direct sound waves while enhancing the spatial characteristics of the audio.
In addition to the inverted left channel, a portion of the right channel is mixed in, also inverted, to provide a balanced auditory experience that enhances the perception of depth and surrounding sound. This mixing typically involves a variable resistor or a mixing circuit, allowing the user to adjust the level of the right channel input contributing to the left rear output.
The right rear channel is synthesized using a similar approach, where the right channel input is inverted and combined with a portion of the left channel input, also inverted. This symmetrical processing ensures that both rear channels maintain a coherent audio image, creating an immersive listening environment.
The circuit may incorporate operational amplifiers to achieve the necessary phase shifts and mixing. These amplifiers can be configured in inverting and non-inverting modes to facilitate the required signal processing. Additionally, passive components such as resistors and capacitors may be utilized for filtering and gain control, ensuring that the output signals are well-matched and free from distortion.
Overall, this quadraphonic sound synthesis circuit effectively transforms a standard stereo signal into a four-channel output, enhancing the auditory experience through strategic phase manipulation and mixing techniques.This circuit will synthesize two rear channels for quadraphonic sound when fed with a stereo signal. The rear output for the left channel, is a combination of the left channel input 180 out of phase, added to a proportion of the right hand channel (also out of phase) The right hand rear output is obtained in a similar way.
The quadraphonic sound synthesis circuit operates by utilizing phase manipulation to create a spatial audio experience. The left rear channel is derived from the left stereo input, which is inverted (180 degrees phase shift) to create a distinct auditory effect. This inversion is crucial as it allows for the cancellation of direct sound waves while enhancing the spatial characteristics of the audio.
In addition to the inverted left channel, a portion of the right channel is mixed in, also inverted, to provide a balanced auditory experience that enhances the perception of depth and surrounding sound. This mixing typically involves a variable resistor or a mixing circuit, allowing the user to adjust the level of the right channel input contributing to the left rear output.
The right rear channel is synthesized using a similar approach, where the right channel input is inverted and combined with a portion of the left channel input, also inverted. This symmetrical processing ensures that both rear channels maintain a coherent audio image, creating an immersive listening environment.
The circuit may incorporate operational amplifiers to achieve the necessary phase shifts and mixing. These amplifiers can be configured in inverting and non-inverting modes to facilitate the required signal processing. Additionally, passive components such as resistors and capacitors may be utilized for filtering and gain control, ensuring that the output signals are well-matched and free from distortion.
Overall, this quadraphonic sound synthesis circuit effectively transforms a standard stereo signal into a four-channel output, enhancing the auditory experience through strategic phase manipulation and mixing techniques.This circuit will synthesize two rear channels for quadraphonic sound when fed with a stereo signal. The rear output for the left channel, is a combination of the left channel input 180 out of phase, added to a proportion of the right hand channel (also out of phase) The right hand rear output is obtained in a similar way.