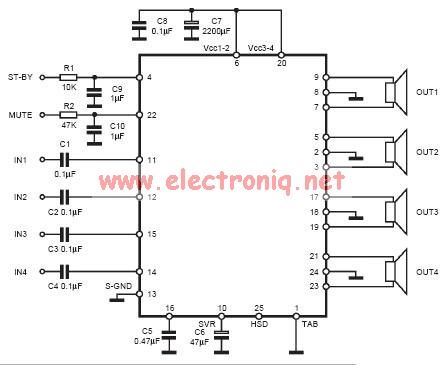
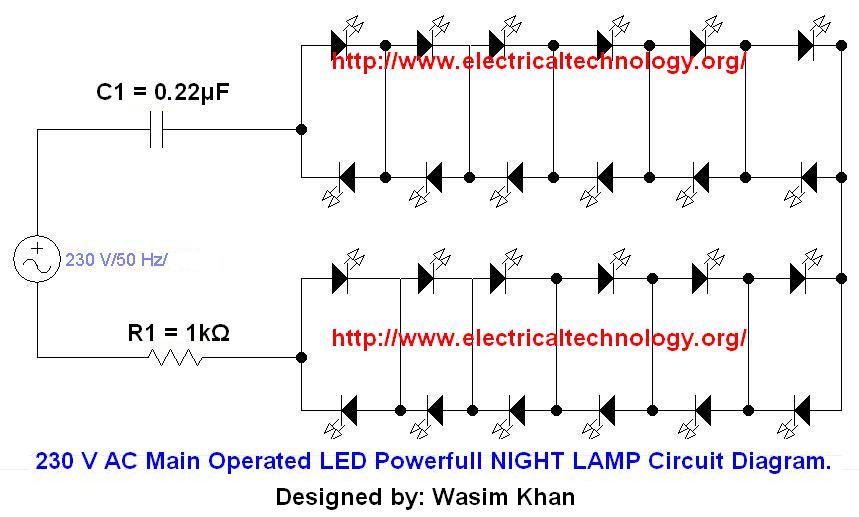
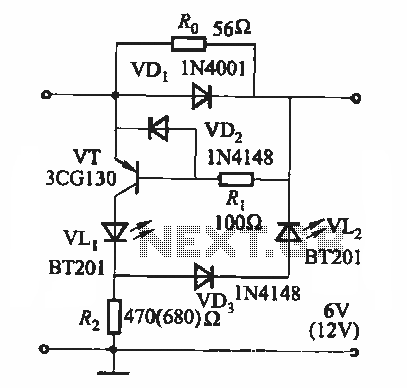
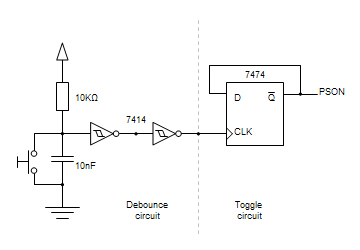
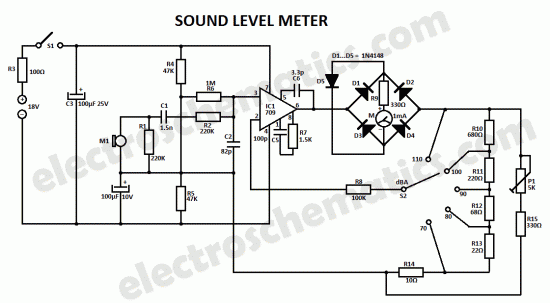
Four lights flash circuit
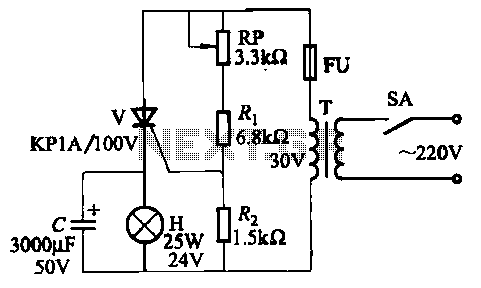
The circuit employs thyristor control. The flash frequency is determined by resistors Ri, RP, Rz, and capacitor C. By adjusting the electrical locator RP, the flash frequency can be varied from 0.5 Hz to several Hz.
The described circuit utilizes a thyristor as the primary control element, which allows for efficient switching of the load by controlling the timing of the conduction phase. The flash frequency is influenced by the values of the resistors (Ri, RP, Rz) and the capacitor (C) in the timing circuit.
In this configuration, Ri sets a baseline resistance that influences the charging time of capacitor C. The capacitor's charge and discharge cycles establish the timing intervals, thereby determining the flash frequency. The resistor RP acts as an adjustable element; by varying its resistance, the time constant of the RC network can be modified, leading to changes in the frequency of the flashing output.
Rz may be included for additional stabilization or to set a minimum flash frequency, ensuring that the circuit operates within a specified range. The overall design allows for flexibility in operation, enabling the user to fine-tune the flash frequency to suit specific applications, such as in visual signaling or decorative lighting.
The thyristor's ability to handle high power makes this circuit suitable for applications where high current or voltage is required, while the RC timing network provides a straightforward method of frequency modulation. Proper attention must be given to the selection of components to ensure reliable operation and to achieve the desired frequency range.It uses thyristor control. Flash frequency is determined by Ri, RP, Rz and C. Adjusting the electrical locator RP, can change the flash frequency 0.5Hz to several Hz.
The described circuit utilizes a thyristor as the primary control element, which allows for efficient switching of the load by controlling the timing of the conduction phase. The flash frequency is influenced by the values of the resistors (Ri, RP, Rz) and the capacitor (C) in the timing circuit.
In this configuration, Ri sets a baseline resistance that influences the charging time of capacitor C. The capacitor's charge and discharge cycles establish the timing intervals, thereby determining the flash frequency. The resistor RP acts as an adjustable element; by varying its resistance, the time constant of the RC network can be modified, leading to changes in the frequency of the flashing output.
Rz may be included for additional stabilization or to set a minimum flash frequency, ensuring that the circuit operates within a specified range. The overall design allows for flexibility in operation, enabling the user to fine-tune the flash frequency to suit specific applications, such as in visual signaling or decorative lighting.
The thyristor's ability to handle high power makes this circuit suitable for applications where high current or voltage is required, while the RC timing network provides a straightforward method of frequency modulation. Proper attention must be given to the selection of components to ensure reliable operation and to achieve the desired frequency range.It uses thyristor control. Flash frequency is determined by Ri, RP, Rz and C. Adjusting the electrical locator RP, can change the flash frequency 0.5Hz to several Hz.