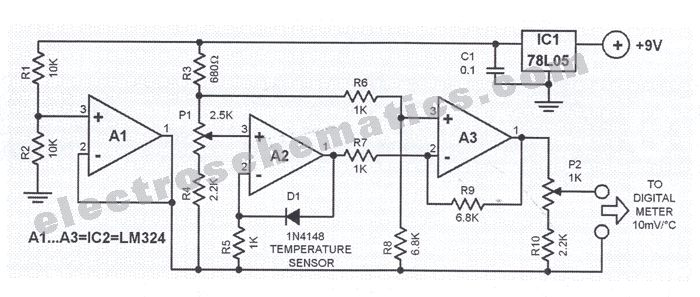
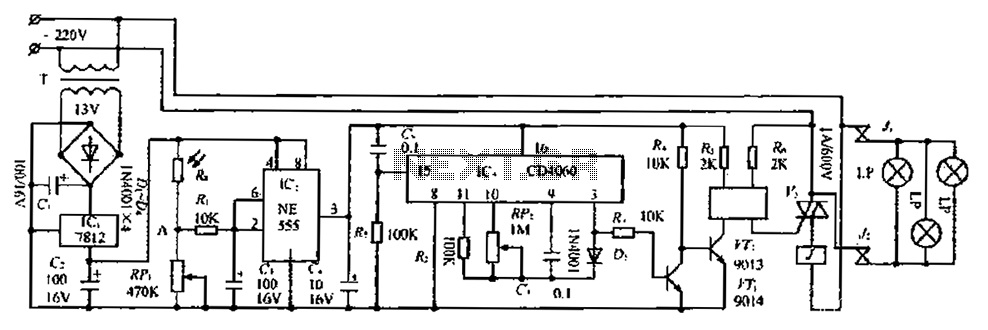
From power fluctuations of one single-junction transistor trigger circuit
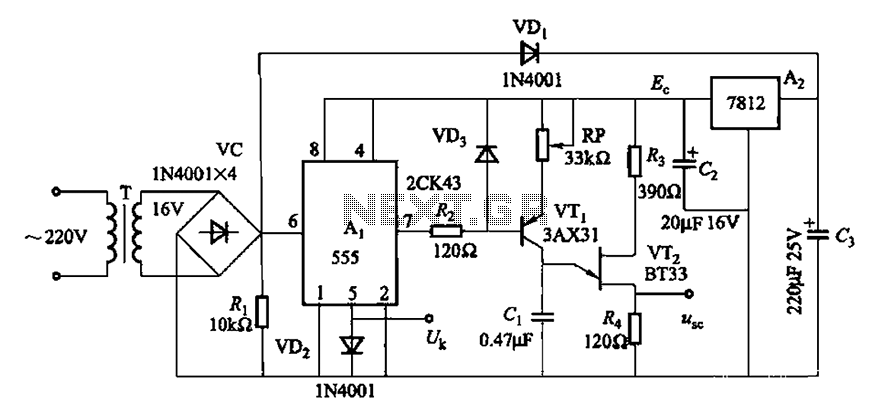
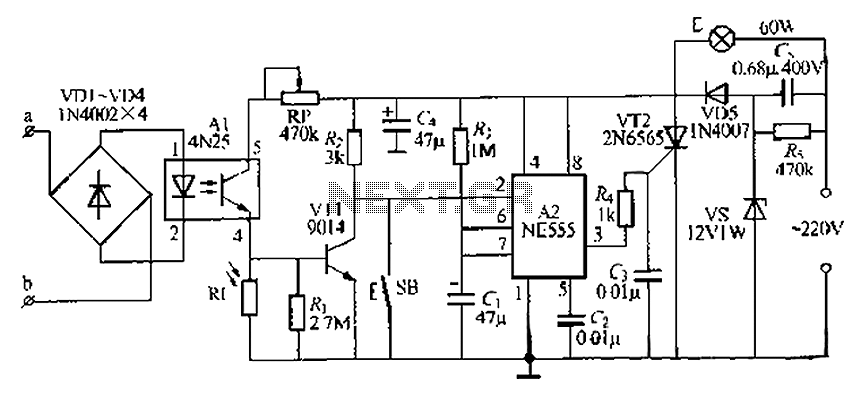
Both circuits can synchronize trapezoidal wave voltage, which is converted into intermittent small rectangular pulses. Its working principle involves periodic operation in synchronization with the grid frequency of the zero-volt switching voltage of the DC chopper. Due to the low threshold voltage of the comparator, the impact of voltage fluctuations on the intermittent sync pulse width is minimal. Consequently, this significantly reduces the phase shift angle's effect on network voltage fluctuations while also expanding the phase shift range. The circuit, as shown in Figure 16-10, utilizes a 555 integrated circuit as a comparator for single inverter voltage. Additionally, a 7812 three-terminal integrated voltage regulator is employed to provide a stable power supply. An adjustment potentiometer (RP) allows for changes to the output pulse's phase shift angle.
The described circuit operates by converting trapezoidal wave voltage into a series of small rectangular pulses that can be synchronized with an external power grid. The synchronization is achieved through a DC chopper, which operates at zero-voltage switching, reducing switching losses and improving efficiency. The 555 timer IC is configured in a comparator mode, which ensures that the output pulses maintain a consistent width despite fluctuations in input voltage.
The use of a low threshold voltage comparator minimizes the influence of voltage variations, allowing the circuit to maintain stable operation even under changing conditions. This design feature not only enhances the reliability of the circuit but also broadens the operational range of phase shifts, which is critical in applications where precise timing is essential.
The circuit's power supply stability is ensured by the 7812 voltage regulator, which outputs a fixed 12V, providing a reliable voltage source for the 555 timer and other components. The inclusion of an adjustment potentiometer (RP) enables fine-tuning of the output pulse width, allowing for precise control over the phase shift angle. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in applications requiring synchronization with varying grid frequencies.
Overall, the circuit design effectively addresses the challenges associated with voltage fluctuations and phase shift management, making it suitable for various electronic applications where synchronization with grid power is crucial. Both circuits can trapezoidal wave voltage synchronous Here is converted into intermittent small rectangular pulse. Its working principle is to make periodic operating in synch ronization with the grid frequency of the zero volt switching voltage of the DC chopper. As a result of the low threshold voltage than the comparator, the impact of voltage fluctuations intermittent sync pulse width is minimal. Therefore, it makes the phase shift angle powered affect network voltage fluctuations greatly reduced, but also expanded phase shift range.
Circuit shown in Figure 16-10. It uses 555 IC Ai limit for single inverter voltage comparator; using 7812 three terminal integrated voltage regulator A2 fixed to provide a stable power supply. Adjustment potentiometer RP, can change the output pulse to e phase shift angle.
The described circuit operates by converting trapezoidal wave voltage into a series of small rectangular pulses that can be synchronized with an external power grid. The synchronization is achieved through a DC chopper, which operates at zero-voltage switching, reducing switching losses and improving efficiency. The 555 timer IC is configured in a comparator mode, which ensures that the output pulses maintain a consistent width despite fluctuations in input voltage.
The use of a low threshold voltage comparator minimizes the influence of voltage variations, allowing the circuit to maintain stable operation even under changing conditions. This design feature not only enhances the reliability of the circuit but also broadens the operational range of phase shifts, which is critical in applications where precise timing is essential.
The circuit's power supply stability is ensured by the 7812 voltage regulator, which outputs a fixed 12V, providing a reliable voltage source for the 555 timer and other components. The inclusion of an adjustment potentiometer (RP) enables fine-tuning of the output pulse width, allowing for precise control over the phase shift angle. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in applications requiring synchronization with varying grid frequencies.
Overall, the circuit design effectively addresses the challenges associated with voltage fluctuations and phase shift management, making it suitable for various electronic applications where synchronization with grid power is crucial. Both circuits can trapezoidal wave voltage synchronous Here is converted into intermittent small rectangular pulse. Its working principle is to make periodic operating in synch ronization with the grid frequency of the zero volt switching voltage of the DC chopper. As a result of the low threshold voltage than the comparator, the impact of voltage fluctuations intermittent sync pulse width is minimal. Therefore, it makes the phase shift angle powered affect network voltage fluctuations greatly reduced, but also expanded phase shift range.
Circuit shown in Figure 16-10. It uses 555 IC Ai limit for single inverter voltage comparator; using 7812 three terminal integrated voltage regulator A2 fixed to provide a stable power supply. Adjustment potentiometer RP, can change the output pulse to e phase shift angle.