gear display
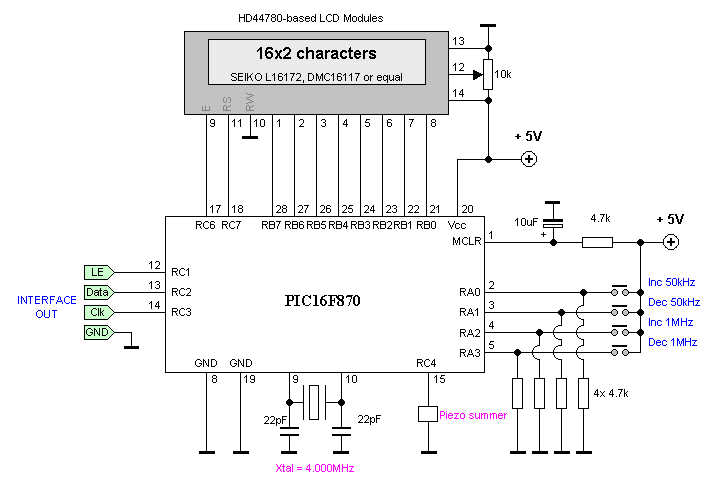
A universal digital gear display that can be installed on any motorbike. This is a low-cost solution based on simple TTL digital technology without software programming.
The universal digital gear display is designed for easy installation on a variety of motorbike models, providing riders with a clear indication of the current gear engaged. The device utilizes basic Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL) technology, which is known for its reliability and cost-effectiveness. The absence of complex software programming simplifies the setup process, making it accessible for users without extensive technical knowledge.
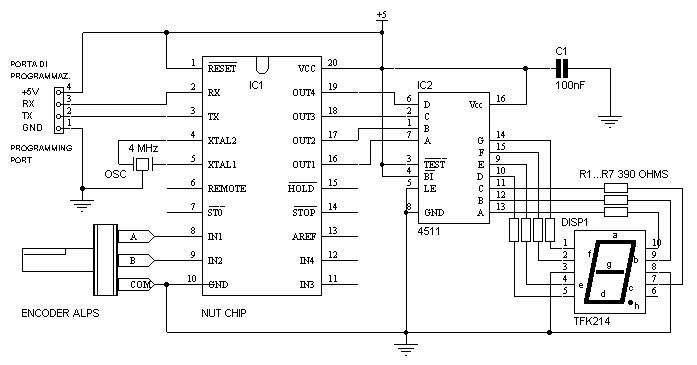
The schematic for this gear display includes several key components. A microcontroller, capable of interpreting signals from the motorbike's gear selector, serves as the central processing unit. The microcontroller is connected to a series of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that visually represent each gear.
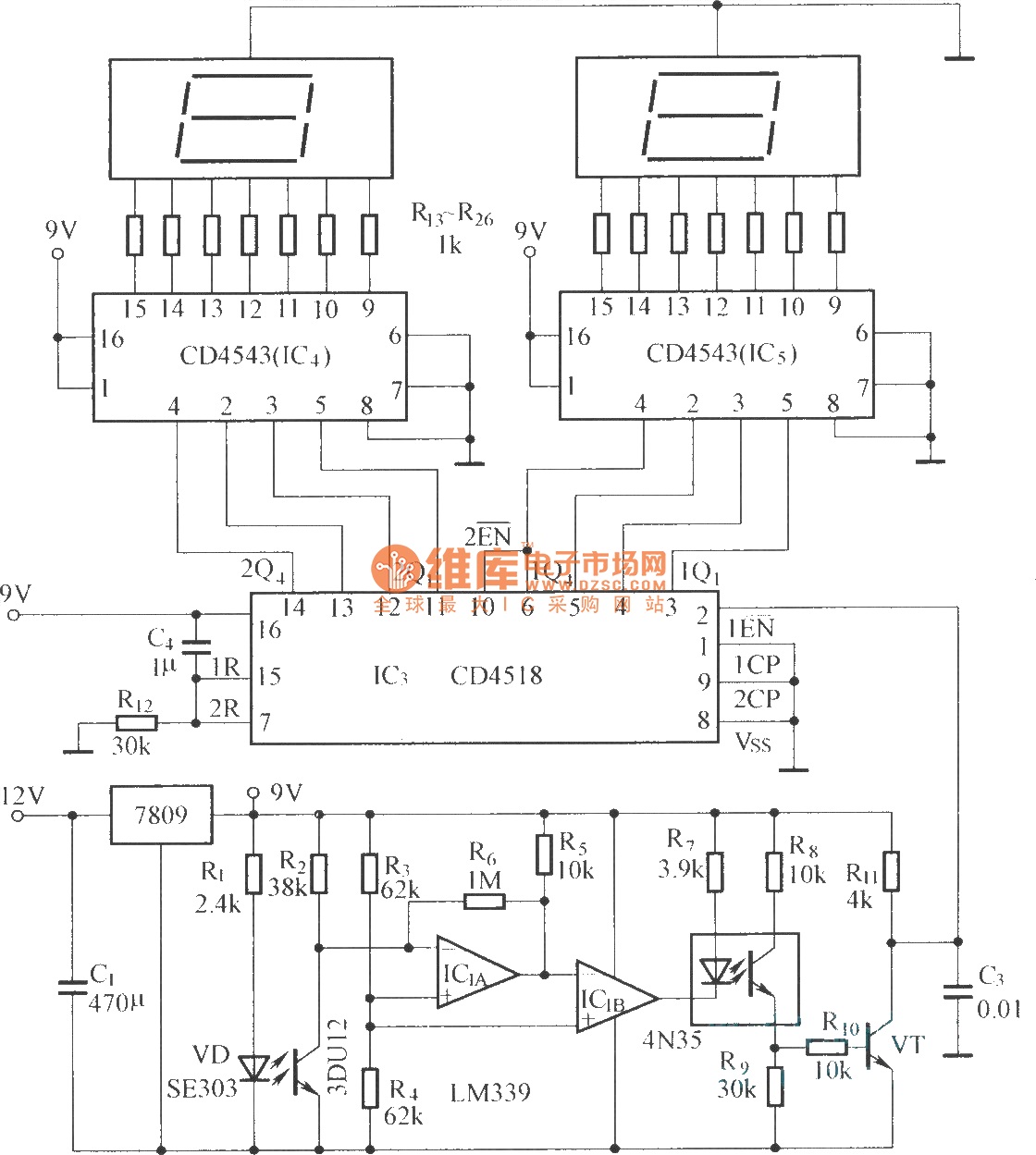
To enhance functionality, the circuit may incorporate a voltage regulator to ensure stable operation across varying input voltages from the motorbike's electrical system. Additionally, a series of resistors and capacitors may be included to filter signals and prevent noise interference, ensuring accurate gear detection.
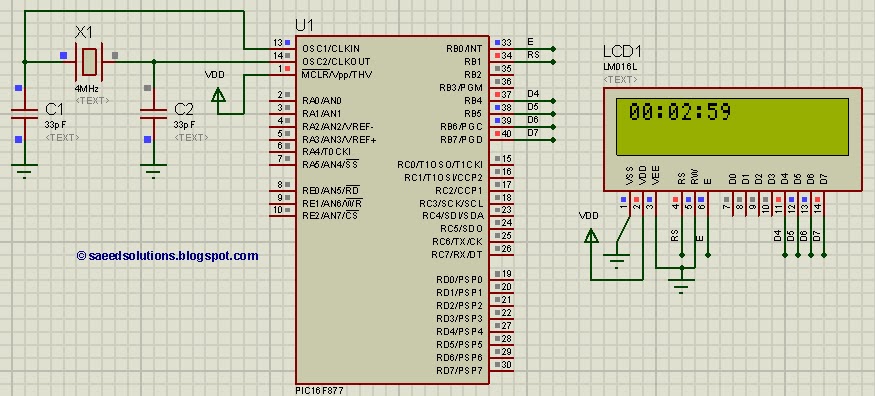
The user interface consists of a simple display panel mounted on the motorbike's dashboard, allowing for easy visibility while riding. This design prioritizes user safety and convenience, ensuring that the rider can quickly ascertain the gear status without distraction.
In summary, this universal digital gear display represents a practical solution for motorbike enthusiasts seeking an efficient and economical method for gear indication, leveraging straightforward TTL technology to deliver reliable performance.A universal digital gear display that can be installed on any motorbike. A low cost solution based on simple TTL digital technology without software programming.. 🔗 External reference
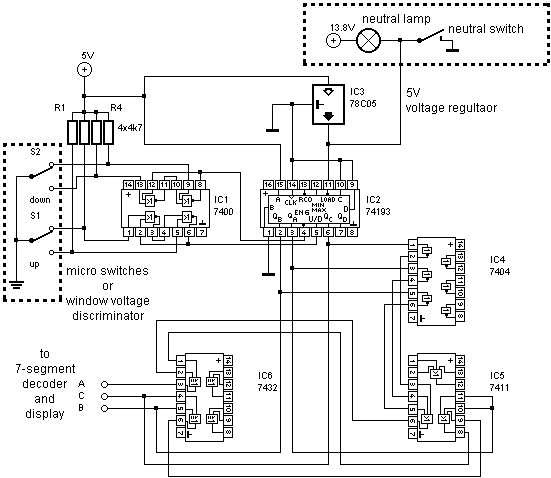
The universal digital gear display is designed for easy installation on a variety of motorbike models, providing riders with a clear indication of the current gear engaged. The device utilizes basic Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL) technology, which is known for its reliability and cost-effectiveness. The absence of complex software programming simplifies the setup process, making it accessible for users without extensive technical knowledge.
The schematic for this gear display includes several key components. A microcontroller, capable of interpreting signals from the motorbike's gear selector, serves as the central processing unit. The microcontroller is connected to a series of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that visually represent each gear.
To enhance functionality, the circuit may incorporate a voltage regulator to ensure stable operation across varying input voltages from the motorbike's electrical system. Additionally, a series of resistors and capacitors may be included to filter signals and prevent noise interference, ensuring accurate gear detection.
The user interface consists of a simple display panel mounted on the motorbike's dashboard, allowing for easy visibility while riding. This design prioritizes user safety and convenience, ensuring that the rider can quickly ascertain the gear status without distraction.
In summary, this universal digital gear display represents a practical solution for motorbike enthusiasts seeking an efficient and economical method for gear indication, leveraging straightforward TTL technology to deliver reliable performance.A universal digital gear display that can be installed on any motorbike. A low cost solution based on simple TTL digital technology without software programming.. 🔗 External reference