GPS Jammer
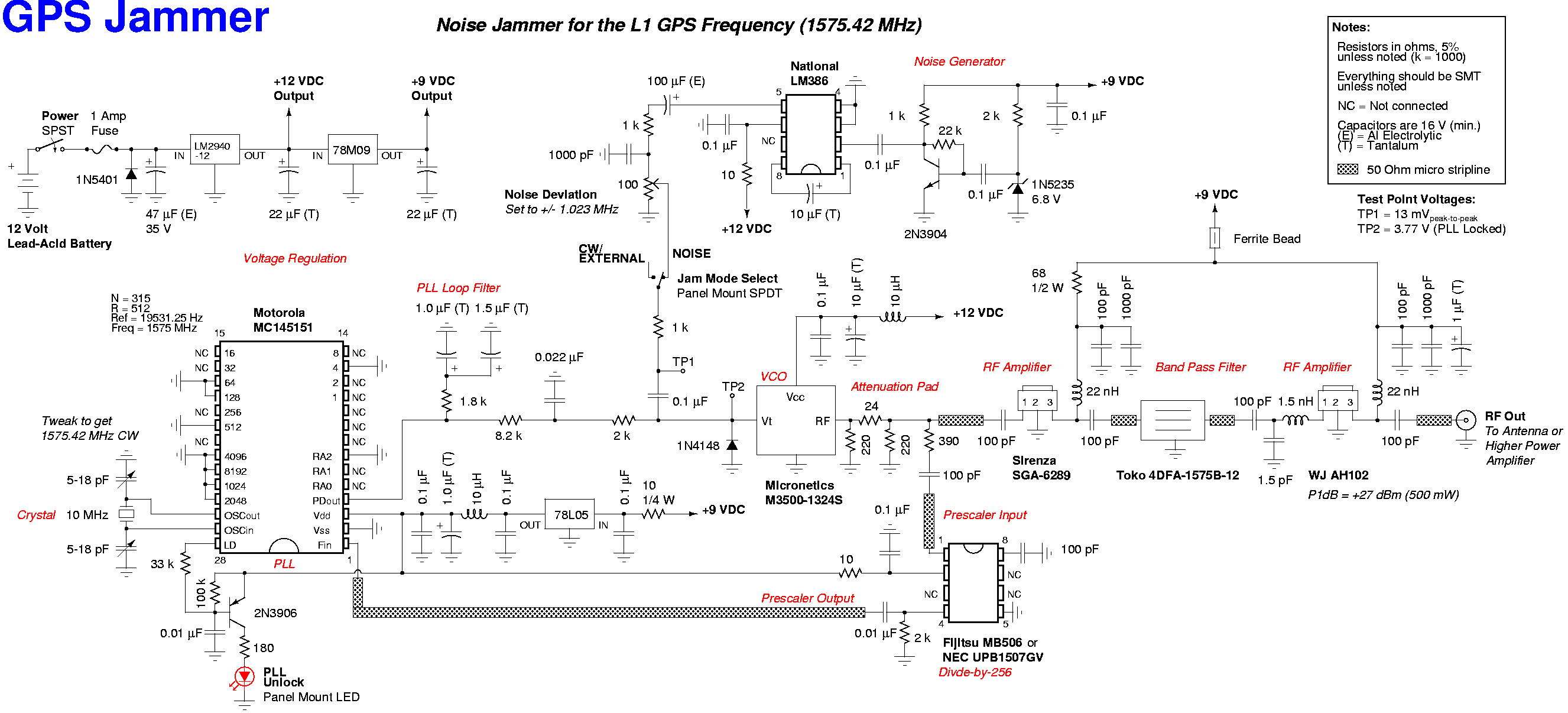
A low-cost device to temporarily disable the reception of the civilian coarse acquisition (C/A) code used for the standard positioning service (SPS) on the Global Positioning System (GPS/NAVSTAR) L1 frequency of 1575.42 MHz. This is accomplished by transmitting a narrowband Gaussian noise signal, with a deviation of +/- 1.023 MHz, on the L1 GPS frequency itself. This technique is more complex than a simple continuous wave (CW) jammer but tends to be more effective against spread spectrum-based radio receivers. This device will not affect the precise positioning service (PPS) transmitted on the GPS L2 frequency of 1227.6 MHz and has minimal effect on the P-code also carried on the L1 frequency. There may be issues if a specific GPS receiver requires acquiring the P(Y)-code through the C/A-code for proper operation. Additionally, this device will not work against the upcoming GPS L5 frequency of 1176.45 MHz or the Russian GLONASS or European Galileo systems. It can be adapted to jam the new civilian C/A-code signal that will also be transmitted on the GPS L2 frequency. The proliferation of inexpensive GPS-based navigation and hidden tracking devices has made it necessary for individuals to engage in electronic warfare. Numerous companies now sell hidden GPS tracking devices that can be mounted inside or underneath vehicles, transmitting location data via cellular networks for extended periods without battery changes or legal oversight. Rental companies have been known to use GPS devices to monitor vehicle use, leading to unexpected fees for renters. Law enforcement agencies utilize GPS tracking bracelets for house arrest monitoring and automatic vehicle location (AVL) systems for dispatching. Various sectors, including cellular phone companies, trucking firms, private investigators, and child safety systems, are heavily involved in GPS tracking technologies. The question remains whether individuals want their locations to be publicly known.
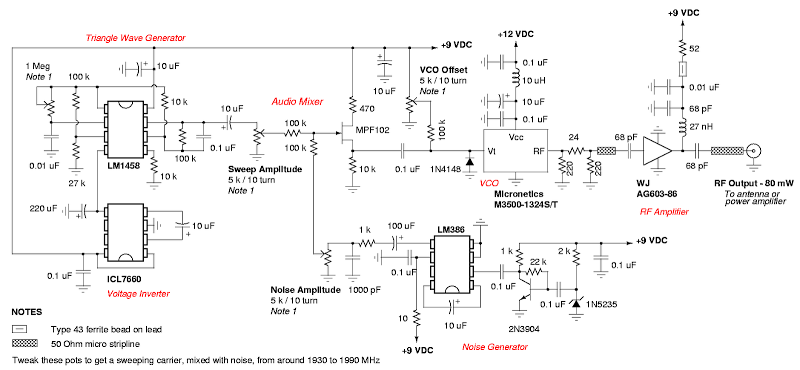
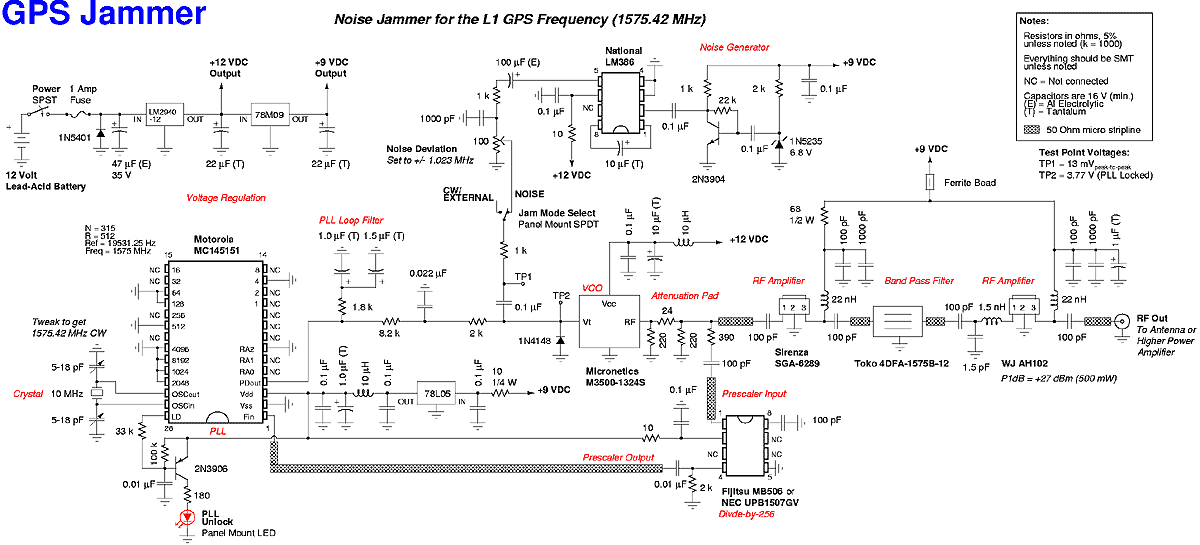
The jammer device is composed of several major sections, detailed in the accompanying schematic diagram. The primary oscillator components include a Motorola MC145151 phase-locked loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer chip, a Micronetics M3500-1324S voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) module, and a Fujitsu MB506 divide-by-256 prescaler chip. The VCO outputs a portion of its radio frequency (RF) signal into the prescaler chip, where it is divided by 256, converting a 1575 MHz signal into a 6.15234375 MHz signal. This output is then fed into one input of the PLL chip, while the other input receives a reference frequency derived from a 10 MHz quartz crystal. The PLL divides this crystal reference frequency down by 512 to achieve 19531.25 Hz. The prescaler output frequency of 6.15234375 MHz is also divided down 315 times by the PLL chip, resulting in the same final frequency of 19531.25 Hz, which serves as the new PLL internal reference frequency. Consequently, the high-frequency 1575 MHz microwave signal is transformed into a manageable audio frequency for the PLL chip and its supporting components. The PLL chip internally compares the phase of the 19531.25 Hz signal from the VCO side with that from the crystal side, producing high or low voltage outputs based on this phase comparison. This configuration enables the device to effectively disrupt the reception of C/A codes by generating a noise signal that complicates the filtering processes of spread spectrum receivers, thereby enhancing the jamming effectiveness.A low cost device to temporarily disable the reception of the civilian coarse acquisition (C/A) code used for the standard positioning service (SPS) on the Global Positioning System (GPS/NAVSTAR) L1 frequency of 1575. 42 MHz. This is accomplished by transmitting a narrowband Gaussian noise signal, with a deviation of +/- 1. 023 MHz, on the L1 GPS fr equency itself. This technique is a little more complicated than a simple continuous wave (CW) jammer, but tends to be more effective (i. e. harder to filter) against spread spectrum based radio receivers. This device will have no effect on the precise positioning service (PPS) which is transmitted on the GPS L2 frequency of 1227.
6 MHz and little effect on the P-code which is also carried on the L1 frequency. There may be a problem if your particular GPS receiver needs to acquire the P(Y)-code through the C/A-code before proper operation. This device will also not work against the new upcoming GPS L5 frequency of 1176. 45 MHz or the Russian GLONASS or European Galileo systems. It can be adapted to jam the new civilian C/A-code signal which is going to also be transmitted on the GPS L2 frequency.
The onslaught of cheap GPS based navigation (or hidden tracking devices) over the past few years has made it necessary for the typical citizen to take up the fine art of electronic warfare. Several companies[Note 1] now sell "hidden" GPS based tracking devices which mount inside or underneath your vehicle.
Some transmit the coordinates, via cellular phone, of your vehicle`s present and/or past locations for weeks at a time without battery changes or court orders! Vehicle rental companies have been known to use GPS tracking devices to verify you don`t speed or abuse their rental vehicles.
The unsuspecting renter is often faced with these hidden abuse "fees" after returning the rental vehicle. Law enforcement agencies are dumb enough to keep track of house arrest prisoners with simple GPS based tracking bracelets[Note 2].
Some even use GPS for automatic vehicle location (AVL) on their squad cars to allow the dispatchers to send in the closest unit to a particular call or to know an officer`s location in case of an emergency situation where they can`t use their radio. Cellular phone companies, trucking companies, private investigators, toll-roads, aircraft, those "protect your child" systems and many more services are all fully involved with the use of GPS based tracking.
The problem is, do you really want everyone to know where you are This will be a brief description of each of the major sections which compromise the entire jammer device. Refer to the included schematic diagram as you read along. You should also refer to the component`s datasheets for even more detailed information. The jammer`s main oscillator components consist of a Motorola MC145151 phase-locked loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer chip, a Micronetics M3500-1324S voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) module and a Fujitsu MB506 divide-by-256 prescaler chip.
The VCO feeds a portion of its radio frequency (RF) output signal into the prescaler chip, where it is divided by 256. A 1575 MHz signal would be turned into a 6. 15234375 MHz signal. This is then fed into one side of the PLL chip. The other side of the PLL is fed with a reference frequency which is derived from a 10 MHz quartz crystal.
This crystal reference frequency is divided down 512 times by the PLL to reach 19531. 25 Hz. The 6. 15234375 MHz prescaler output frequency is also further divided down 315 times by the PLL chip for a final frequency of 19531. 25 Hz. This will be the new PLL internal reference frequency. That big bad 1575 MHz microwave signal now looks like a simple audio frequency to the PLL chip and the supporting components.
The PLL chip internally compares the phase of the 19531. 25 Hz VCO side signal to the phase of the 19531. 25 Hz crystal side signal. The PLL chip outputs high or low voltag 🔗 External reference
The jammer device is composed of several major sections, detailed in the accompanying schematic diagram. The primary oscillator components include a Motorola MC145151 phase-locked loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer chip, a Micronetics M3500-1324S voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) module, and a Fujitsu MB506 divide-by-256 prescaler chip. The VCO outputs a portion of its radio frequency (RF) signal into the prescaler chip, where it is divided by 256, converting a 1575 MHz signal into a 6.15234375 MHz signal. This output is then fed into one input of the PLL chip, while the other input receives a reference frequency derived from a 10 MHz quartz crystal. The PLL divides this crystal reference frequency down by 512 to achieve 19531.25 Hz. The prescaler output frequency of 6.15234375 MHz is also divided down 315 times by the PLL chip, resulting in the same final frequency of 19531.25 Hz, which serves as the new PLL internal reference frequency. Consequently, the high-frequency 1575 MHz microwave signal is transformed into a manageable audio frequency for the PLL chip and its supporting components. The PLL chip internally compares the phase of the 19531.25 Hz signal from the VCO side with that from the crystal side, producing high or low voltage outputs based on this phase comparison. This configuration enables the device to effectively disrupt the reception of C/A codes by generating a noise signal that complicates the filtering processes of spread spectrum receivers, thereby enhancing the jamming effectiveness.A low cost device to temporarily disable the reception of the civilian coarse acquisition (C/A) code used for the standard positioning service (SPS) on the Global Positioning System (GPS/NAVSTAR) L1 frequency of 1575. 42 MHz. This is accomplished by transmitting a narrowband Gaussian noise signal, with a deviation of +/- 1. 023 MHz, on the L1 GPS fr equency itself. This technique is a little more complicated than a simple continuous wave (CW) jammer, but tends to be more effective (i. e. harder to filter) against spread spectrum based radio receivers. This device will have no effect on the precise positioning service (PPS) which is transmitted on the GPS L2 frequency of 1227.
6 MHz and little effect on the P-code which is also carried on the L1 frequency. There may be a problem if your particular GPS receiver needs to acquire the P(Y)-code through the C/A-code before proper operation. This device will also not work against the new upcoming GPS L5 frequency of 1176. 45 MHz or the Russian GLONASS or European Galileo systems. It can be adapted to jam the new civilian C/A-code signal which is going to also be transmitted on the GPS L2 frequency.
The onslaught of cheap GPS based navigation (or hidden tracking devices) over the past few years has made it necessary for the typical citizen to take up the fine art of electronic warfare. Several companies[Note 1] now sell "hidden" GPS based tracking devices which mount inside or underneath your vehicle.
Some transmit the coordinates, via cellular phone, of your vehicle`s present and/or past locations for weeks at a time without battery changes or court orders! Vehicle rental companies have been known to use GPS tracking devices to verify you don`t speed or abuse their rental vehicles.
The unsuspecting renter is often faced with these hidden abuse "fees" after returning the rental vehicle. Law enforcement agencies are dumb enough to keep track of house arrest prisoners with simple GPS based tracking bracelets[Note 2].
Some even use GPS for automatic vehicle location (AVL) on their squad cars to allow the dispatchers to send in the closest unit to a particular call or to know an officer`s location in case of an emergency situation where they can`t use their radio. Cellular phone companies, trucking companies, private investigators, toll-roads, aircraft, those "protect your child" systems and many more services are all fully involved with the use of GPS based tracking.
The problem is, do you really want everyone to know where you are This will be a brief description of each of the major sections which compromise the entire jammer device. Refer to the included schematic diagram as you read along. You should also refer to the component`s datasheets for even more detailed information. The jammer`s main oscillator components consist of a Motorola MC145151 phase-locked loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer chip, a Micronetics M3500-1324S voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) module and a Fujitsu MB506 divide-by-256 prescaler chip.
The VCO feeds a portion of its radio frequency (RF) output signal into the prescaler chip, where it is divided by 256. A 1575 MHz signal would be turned into a 6. 15234375 MHz signal. This is then fed into one side of the PLL chip. The other side of the PLL is fed with a reference frequency which is derived from a 10 MHz quartz crystal.
This crystal reference frequency is divided down 512 times by the PLL to reach 19531. 25 Hz. The 6. 15234375 MHz prescaler output frequency is also further divided down 315 times by the PLL chip for a final frequency of 19531. 25 Hz. This will be the new PLL internal reference frequency. That big bad 1575 MHz microwave signal now looks like a simple audio frequency to the PLL chip and the supporting components.
The PLL chip internally compares the phase of the 19531. 25 Hz VCO side signal to the phase of the 19531. 25 Hz crystal side signal. The PLL chip outputs high or low voltag 🔗 External reference