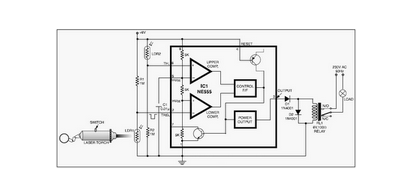
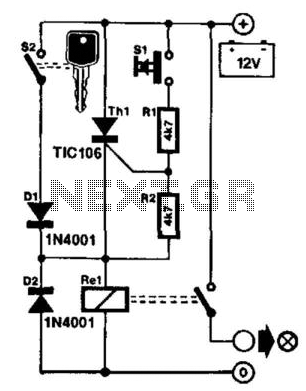
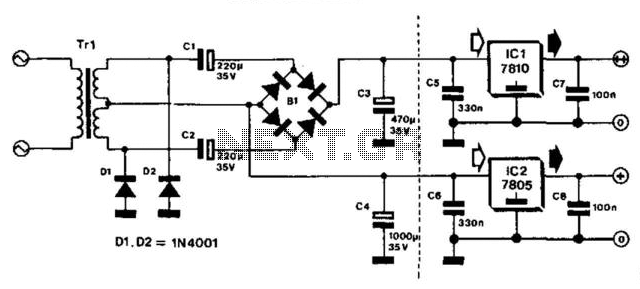
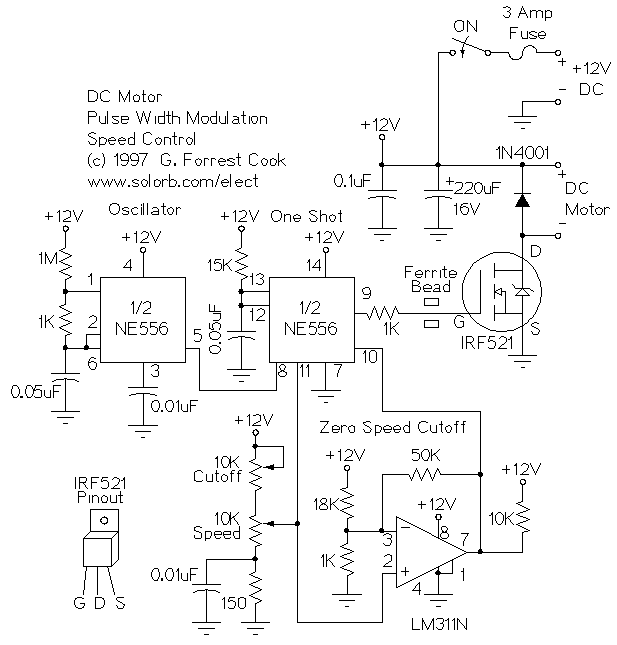
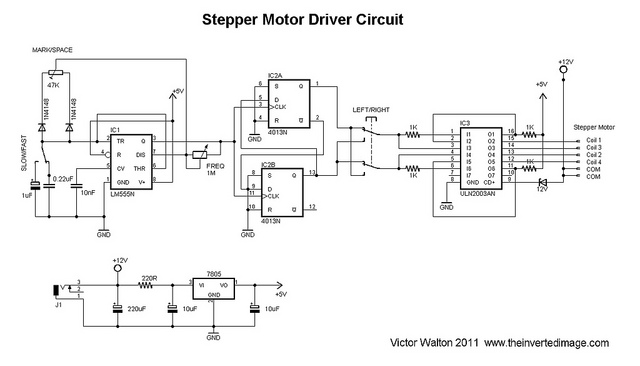
H Bridge Direct Current Motor Control Circuits
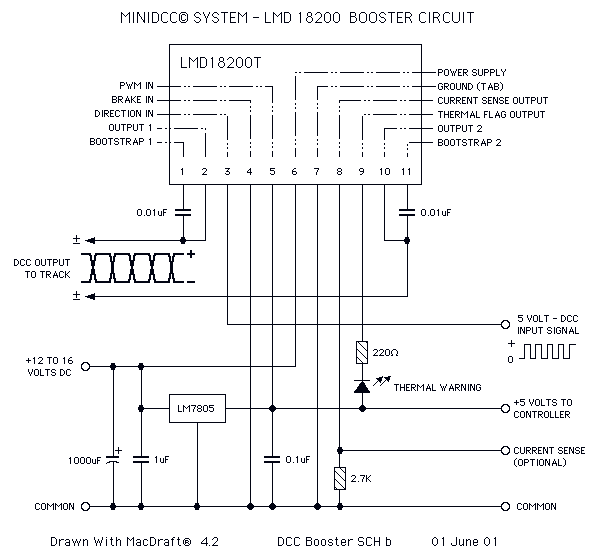
This page features H-Bridge circuits used for controlling direct current motors. Several designs are shown using both CMOS and Bi-Polar power devices. These circuits could be used as the basis for Model Railroad DCC Boosters or PWM motor controllers. The first schematic is for a basic 3 Amp - DCC Booster using the LMD 18200 CMOS, H-Bridge. More: Included in the design is a 5Volt regulator that supplies power to the DCC signal generation and display circuitry. This circuit was designed to be used with the MiniDCC© system. - A DCC (Digital Command Control) do-it-yourself project...
The H-Bridge circuit is a critical component in controlling the direction and speed of DC motors, particularly in applications such as model railroads where precise control is essential. In this schematic, the LMD 18200, a CMOS H-Bridge driver, is utilized, capable of delivering up to 3 Amps of continuous current. This allows for the effective operation of small to medium-sized DC motors, providing the necessary torque and speed control.
The design incorporates a 5V voltage regulator, which is essential for powering the DCC signal generation and display circuitry. This regulator ensures that the control logic operates reliably, as the DCC system requires a stable voltage for proper signal transmission and reception. The integration of the MiniDCC© system indicates that this circuit is tailored for hobbyists looking to implement a DIY DCC solution, enhancing the functionality of model trains through digital control.
The H-Bridge configuration allows for bidirectional control of the motor. By switching the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor terminals, the direction can be reversed. Additionally, PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control can be employed to adjust the speed of the motor, providing a versatile solution for various operational needs in model railroading.
Overall, this H-Bridge circuit design serves as a robust foundation for those interested in developing their own DCC boosters or PWM motor controllers, leveraging both CMOS technology for efficiency and ease of use in hobbyist applications.This page features H-Bridge circuits used for controlling direct current motors. Several designs are shown using both CMOS and Bi-Polar power devices. These circuits could be used as the basis for Model Railroad DCC Boosters or PWM motor controllers. The first schematic is for a basic 3 Amp - DCC Booster using the LMD 18200 CMOS, H-Bridge. Included in the design is a 5Volt regulator that supplies power to the DCC signal generation and display circuitry. This circuit was designed be used with the MiniDCC© system. - A DCC ( Digital Command Control) do-it-yourself project... 🔗 External reference
The H-Bridge circuit is a critical component in controlling the direction and speed of DC motors, particularly in applications such as model railroads where precise control is essential. In this schematic, the LMD 18200, a CMOS H-Bridge driver, is utilized, capable of delivering up to 3 Amps of continuous current. This allows for the effective operation of small to medium-sized DC motors, providing the necessary torque and speed control.
The design incorporates a 5V voltage regulator, which is essential for powering the DCC signal generation and display circuitry. This regulator ensures that the control logic operates reliably, as the DCC system requires a stable voltage for proper signal transmission and reception. The integration of the MiniDCC© system indicates that this circuit is tailored for hobbyists looking to implement a DIY DCC solution, enhancing the functionality of model trains through digital control.
The H-Bridge configuration allows for bidirectional control of the motor. By switching the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor terminals, the direction can be reversed. Additionally, PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control can be employed to adjust the speed of the motor, providing a versatile solution for various operational needs in model railroading.
Overall, this H-Bridge circuit design serves as a robust foundation for those interested in developing their own DCC boosters or PWM motor controllers, leveraging both CMOS technology for efficiency and ease of use in hobbyist applications.This page features H-Bridge circuits used for controlling direct current motors. Several designs are shown using both CMOS and Bi-Polar power devices. These circuits could be used as the basis for Model Railroad DCC Boosters or PWM motor controllers. The first schematic is for a basic 3 Amp - DCC Booster using the LMD 18200 CMOS, H-Bridge. Included in the design is a 5Volt regulator that supplies power to the DCC signal generation and display circuitry. This circuit was designed be used with the MiniDCC© system. - A DCC ( Digital Command Control) do-it-yourself project... 🔗 External reference