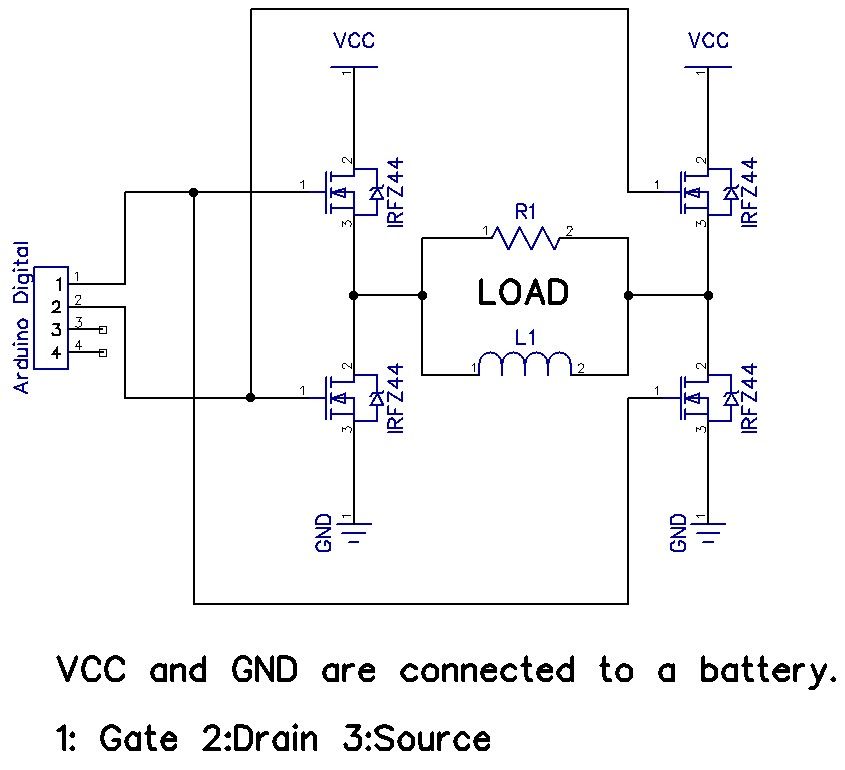
H-Bridge on a Breadboard
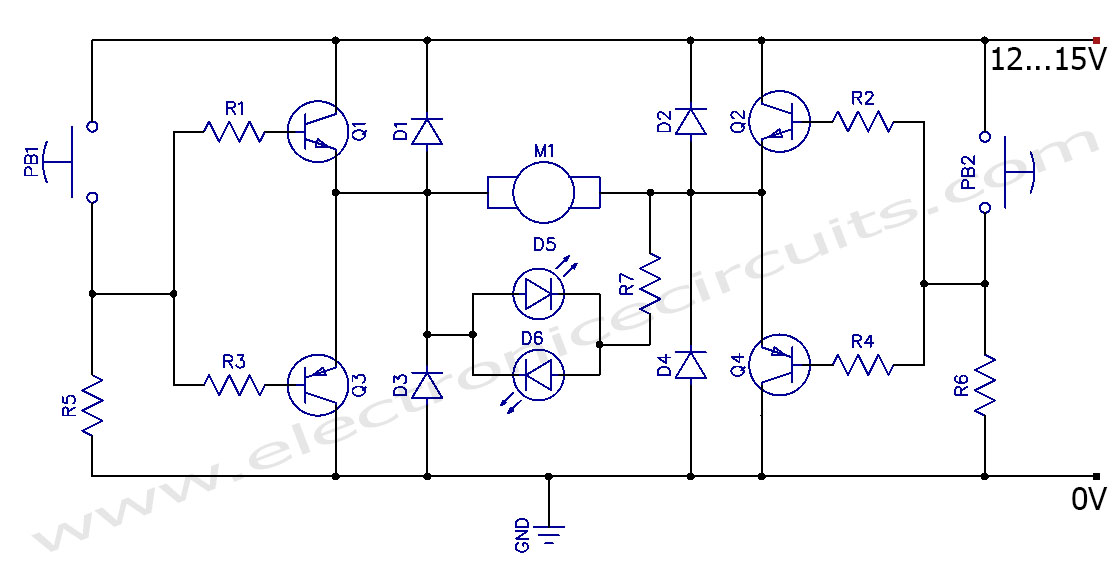
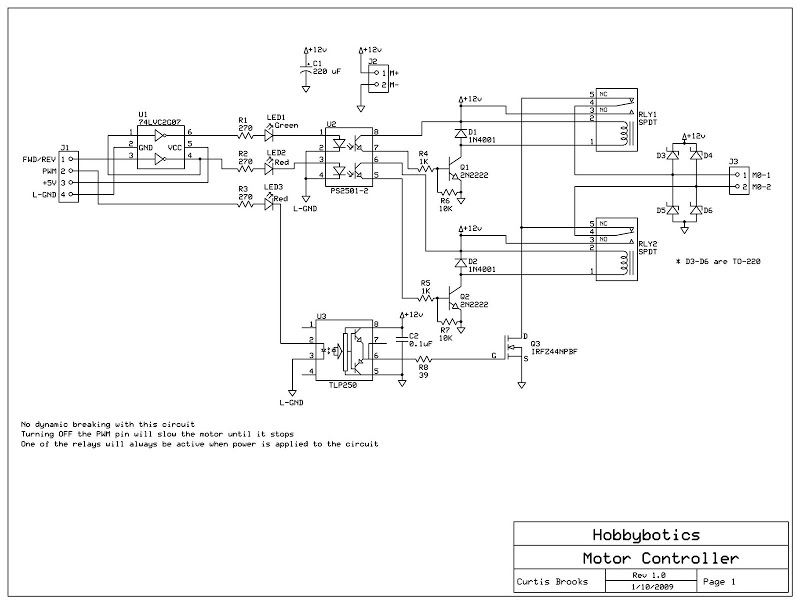
The H-Bridge is a circuit that can drive a motor in both forward and reverse directions. It can be a straightforward circuit that requires only a few components.
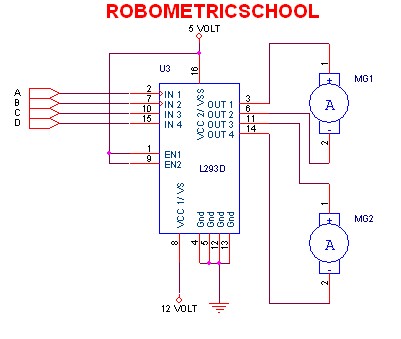
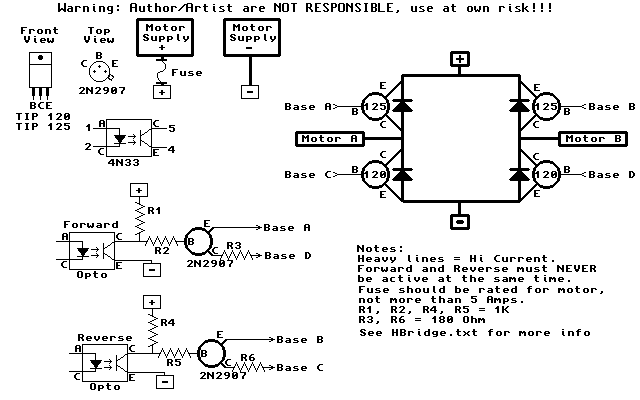
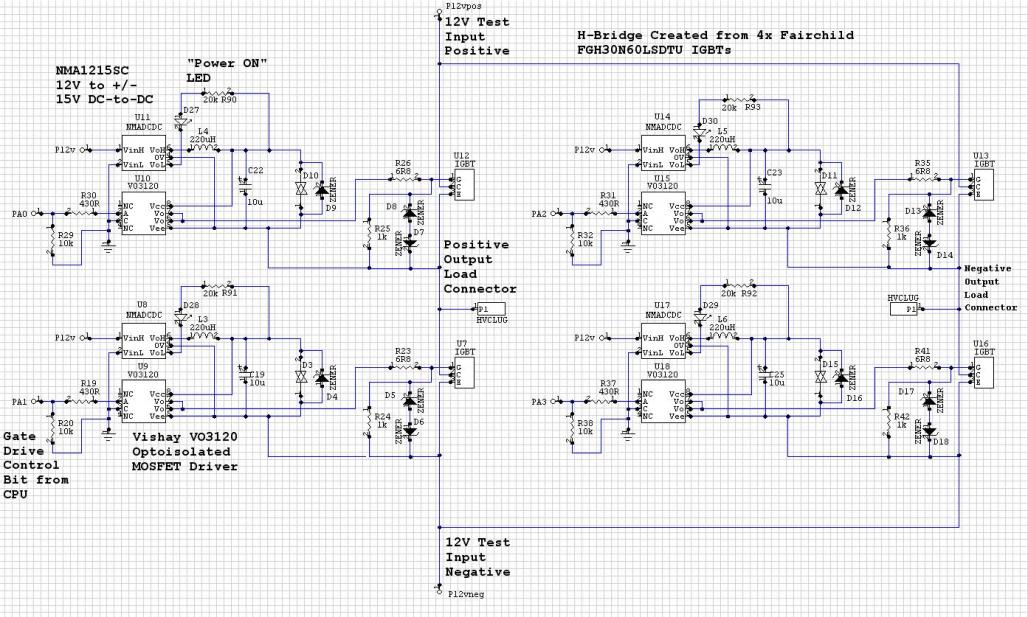
The H-Bridge circuit is a fundamental configuration used in motor control applications, allowing for bidirectional operation of DC motors. It typically consists of four switches, which can be implemented using transistors or MOSFETs. These switches are arranged in an "H" formation, hence the name "H-Bridge."
To drive the motor forward, two switches on one side of the bridge are closed while the other two switches are opened. This creates a voltage potential across the motor terminals in one direction. Conversely, to reverse the motor's direction, the opposite pair of switches is activated, allowing current to flow in the opposite direction through the motor.
Control of the H-Bridge can be achieved using various methods, including microcontrollers, which provide PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals to modulate the speed and direction of the motor. Additionally, diodes are often included in the design to protect the circuit from back EMF generated by the motor during operation, ensuring reliability and longevity of the components.
In more advanced applications, H-Bridges can be integrated into larger systems with feedback mechanisms for precise control of motor speed and position. The simplicity and versatility of the H-Bridge make it a popular choice in robotics, automation, and various consumer electronics where motor control is required.The H-Bridge is a circuit which can drive a motor in forward and reverse. It can be a very simple circuit that requires only a handful of components.. 🔗 External reference
The H-Bridge circuit is a fundamental configuration used in motor control applications, allowing for bidirectional operation of DC motors. It typically consists of four switches, which can be implemented using transistors or MOSFETs. These switches are arranged in an "H" formation, hence the name "H-Bridge."
To drive the motor forward, two switches on one side of the bridge are closed while the other two switches are opened. This creates a voltage potential across the motor terminals in one direction. Conversely, to reverse the motor's direction, the opposite pair of switches is activated, allowing current to flow in the opposite direction through the motor.
Control of the H-Bridge can be achieved using various methods, including microcontrollers, which provide PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals to modulate the speed and direction of the motor. Additionally, diodes are often included in the design to protect the circuit from back EMF generated by the motor during operation, ensuring reliability and longevity of the components.
In more advanced applications, H-Bridges can be integrated into larger systems with feedback mechanisms for precise control of motor speed and position. The simplicity and versatility of the H-Bridge make it a popular choice in robotics, automation, and various consumer electronics where motor control is required.The H-Bridge is a circuit which can drive a motor in forward and reverse. It can be a very simple circuit that requires only a handful of components.. 🔗 External reference