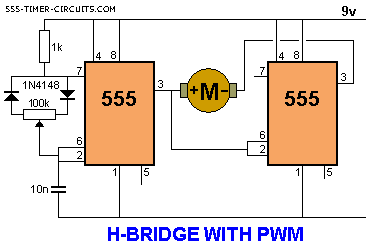
h bridge with pwm
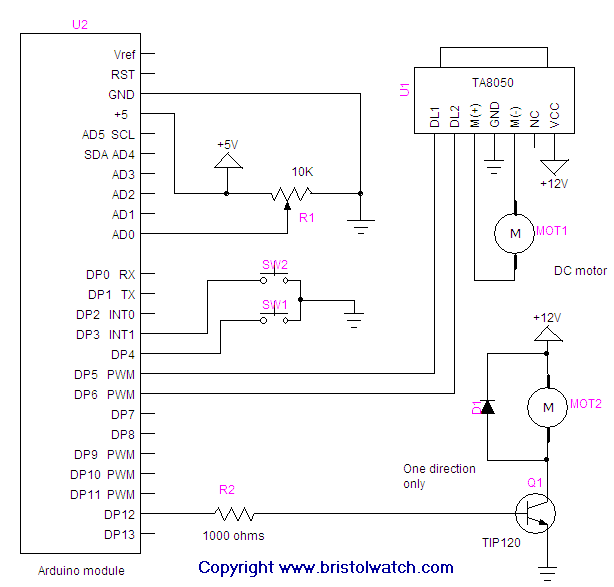
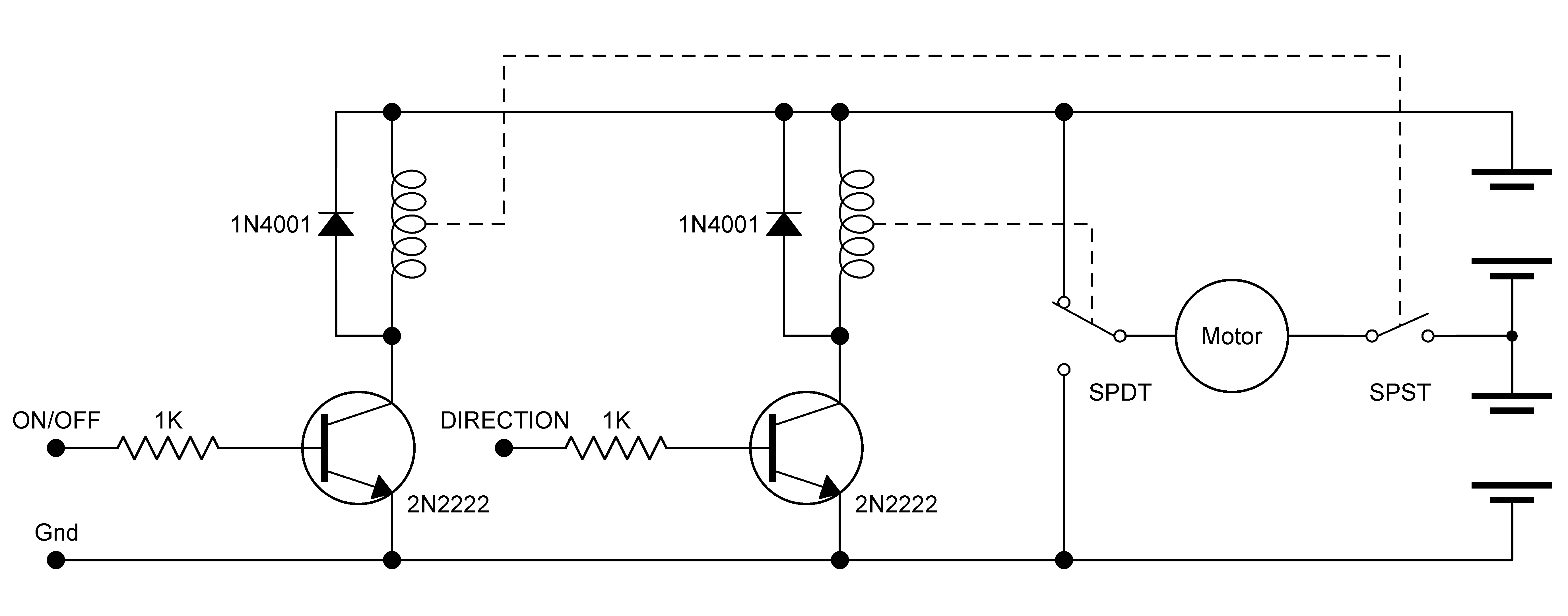
This circuit controls a motor's rotation direction (clockwise or counterclockwise) using a potentiometer and can reduce the speed to zero when the potentiometer is positioned in the middle. The current is limited to 200 mA, and the voltage across the motor remains below 6 V. The circuit demonstrates the principle of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), delivering powerful bursts of current to the motor to achieve varying RPM under load. It also facilitates both forward and reverse RPM through an H-bridge configuration.
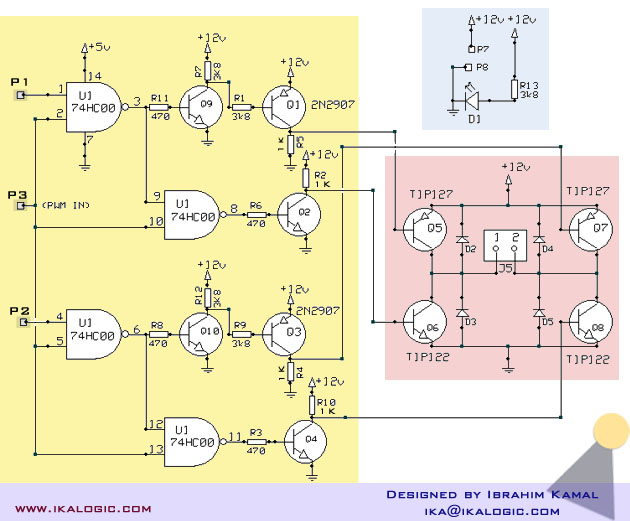
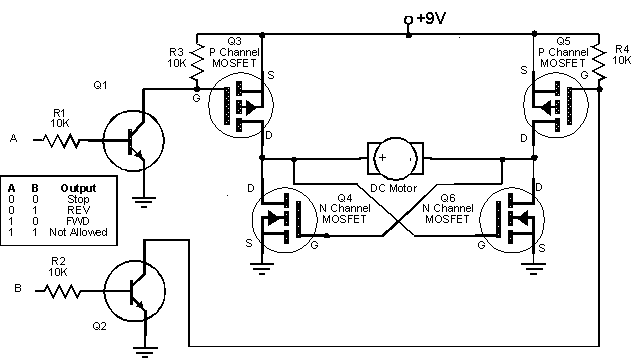
The described circuit employs an H-bridge arrangement, which is essential for controlling the direction of the motor's rotation. The H-bridge consists of four switches (transistors or MOSFETs) arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for the reversal of current through the motor. When the potentiometer is adjusted, it alters the duty cycle of the PWM signal generated by a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM circuit. This signal modulates the average voltage applied to the motor, effectively controlling its speed.
In the mid-position of the potentiometer, the PWM duty cycle approaches zero, resulting in no current flow to the motor and consequently halting its operation. As the potentiometer is turned in one direction, the PWM signal increases, allowing more power to reach the motor, thus increasing its speed in the designated direction. Conversely, turning the potentiometer in the opposite direction decreases the PWM duty cycle, reducing the motor's speed or reversing its direction.
The circuit includes current-limiting features to prevent damage to the motor and the H-bridge components, ensuring that the maximum current does not exceed 200 mA. This is particularly important for small motors that may experience stall conditions under load. Additionally, the use of a voltage rating below 6 V ensures safe operation and compatibility with low-voltage motors.
Overall, this circuit effectively demonstrates the principles of motor control using PWM and H-bridge technology, providing a versatile solution for applications requiring precise speed and direction control.This circuit drives a motor clockwise / anticlockwise via a pot and reduces the speed to zero when the pot is in mid-position. The current is limited to 200mA and the voltage across the motor is less than 6v, but the circuit shows the principle of Pulse Width Modulation (providing powerful bursts of current to the motor to create a high or low RPM
under load) and both forward / reverse RPM via the H-bridge arrangement. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs an H-bridge arrangement, which is essential for controlling the direction of the motor's rotation. The H-bridge consists of four switches (transistors or MOSFETs) arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for the reversal of current through the motor. When the potentiometer is adjusted, it alters the duty cycle of the PWM signal generated by a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM circuit. This signal modulates the average voltage applied to the motor, effectively controlling its speed.
In the mid-position of the potentiometer, the PWM duty cycle approaches zero, resulting in no current flow to the motor and consequently halting its operation. As the potentiometer is turned in one direction, the PWM signal increases, allowing more power to reach the motor, thus increasing its speed in the designated direction. Conversely, turning the potentiometer in the opposite direction decreases the PWM duty cycle, reducing the motor's speed or reversing its direction.
The circuit includes current-limiting features to prevent damage to the motor and the H-bridge components, ensuring that the maximum current does not exceed 200 mA. This is particularly important for small motors that may experience stall conditions under load. Additionally, the use of a voltage rating below 6 V ensures safe operation and compatibility with low-voltage motors.
Overall, this circuit effectively demonstrates the principles of motor control using PWM and H-bridge technology, providing a versatile solution for applications requiring precise speed and direction control.This circuit drives a motor clockwise / anticlockwise via a pot and reduces the speed to zero when the pot is in mid-position. The current is limited to 200mA and the voltage across the motor is less than 6v, but the circuit shows the principle of Pulse Width Modulation (providing powerful bursts of current to the motor to create a high or low RPM
under load) and both forward / reverse RPM via the H-bridge arrangement. 🔗 External reference