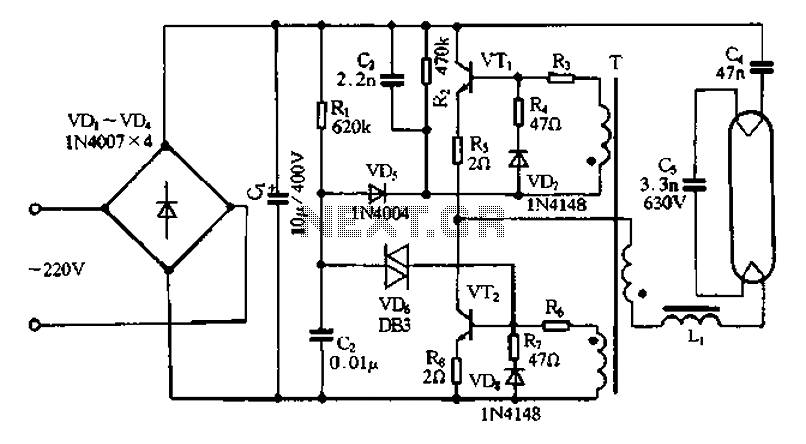
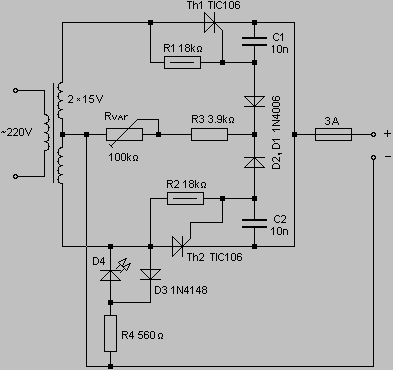
Half-wave rectifier
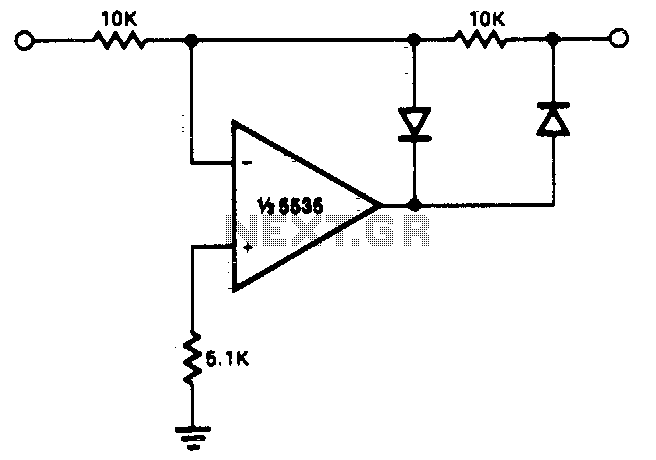
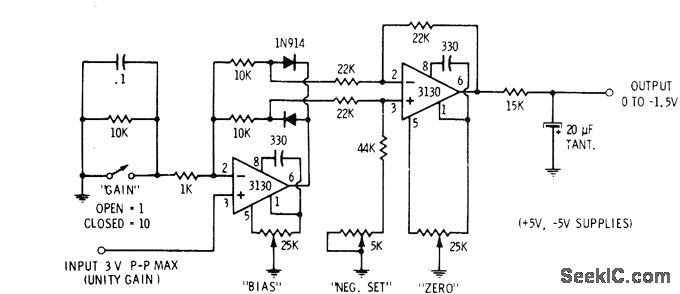
This circuit allows for precise half-wave rectification of the incoming signal. It exhibits a gain of 0 for positive signals and a gain of -1 for negative signals. By reversing the orientation of both diodes, the output polarity can be inverted. While the circuit delivers an accurate output, the output impedance varies with the input polarity, which may necessitate buffering. Additionally, the output must transition through two diode forward voltage drops when the input polarity changes. The NE5535 operational amplifier is capable of functioning effectively up to 10 kHz with less than 5% distortion.
The half-wave rectifier circuit described utilizes two diodes arranged in such a way that they allow current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. The operational amplifier, NE5535, is employed to enhance the performance of the rectifier, ensuring that the output signal is amplified as per the defined gain characteristics. The gain of 0 for positive signals indicates that these signals will not pass through the circuit, while negative signals will be inverted and amplified by a factor of -1, resulting in a mirrored output.
In applications where the output impedance is a concern, additional buffering stages may be implemented. This could involve the use of a voltage follower configuration, which utilizes an operational amplifier to provide a high input impedance and a low output impedance, effectively isolating the rectifier circuit from the load. This buffering ensures that the load does not affect the performance of the rectifier, particularly when dealing with varying input signal characteristics.
The necessity for the output to slew through two diode drops is a critical consideration, as it impacts the response time of the circuit when the input polarity changes. This characteristic is particularly relevant in high-frequency applications, where rapid signal changes are common. The NE5535's capability to operate effectively at frequencies up to 10 kHz with minimal distortion makes it suitable for a range of audio and signal processing applications, where fidelity and accuracy are paramount.
In summary, this half-wave rectification circuit is designed to provide precise signal processing with specific gain characteristics and considerations for output impedance and frequency response, making it a valuable component in various electronic applications.This circuit provides for accurate half wave rectification of the incoming signal. For positive signals, the gain is 0; for negative signals, the gain is — 1. By reversing both diodes, the polarity can be inverted. This circuit provides an accurate output, but the output impedance differs for the two input polarities and buffering may be needed The output must slew through two diode drops when the input polarity reverses. The NE5535 device will work up to 10 kHz with less ttan 5% distortion. 🔗 External reference
The half-wave rectifier circuit described utilizes two diodes arranged in such a way that they allow current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. The operational amplifier, NE5535, is employed to enhance the performance of the rectifier, ensuring that the output signal is amplified as per the defined gain characteristics. The gain of 0 for positive signals indicates that these signals will not pass through the circuit, while negative signals will be inverted and amplified by a factor of -1, resulting in a mirrored output.
In applications where the output impedance is a concern, additional buffering stages may be implemented. This could involve the use of a voltage follower configuration, which utilizes an operational amplifier to provide a high input impedance and a low output impedance, effectively isolating the rectifier circuit from the load. This buffering ensures that the load does not affect the performance of the rectifier, particularly when dealing with varying input signal characteristics.
The necessity for the output to slew through two diode drops is a critical consideration, as it impacts the response time of the circuit when the input polarity changes. This characteristic is particularly relevant in high-frequency applications, where rapid signal changes are common. The NE5535's capability to operate effectively at frequencies up to 10 kHz with minimal distortion makes it suitable for a range of audio and signal processing applications, where fidelity and accuracy are paramount.
In summary, this half-wave rectification circuit is designed to provide precise signal processing with specific gain characteristics and considerations for output impedance and frequency response, making it a valuable component in various electronic applications.This circuit provides for accurate half wave rectification of the incoming signal. For positive signals, the gain is 0; for negative signals, the gain is — 1. By reversing both diodes, the polarity can be inverted. This circuit provides an accurate output, but the output impedance differs for the two input polarities and buffering may be needed The output must slew through two diode drops when the input polarity reverses. The NE5535 device will work up to 10 kHz with less ttan 5% distortion. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713