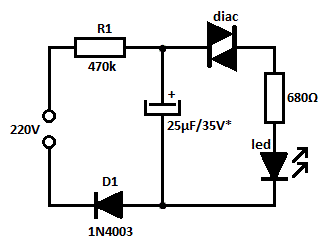
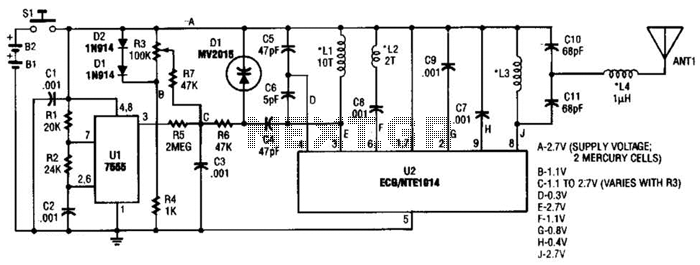
HiFi preamp with tone control
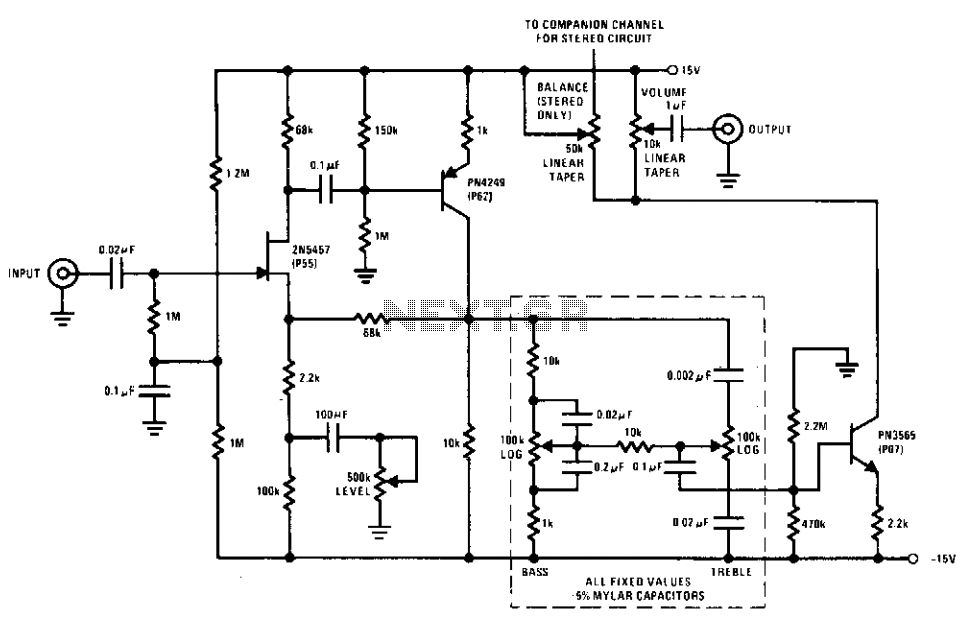
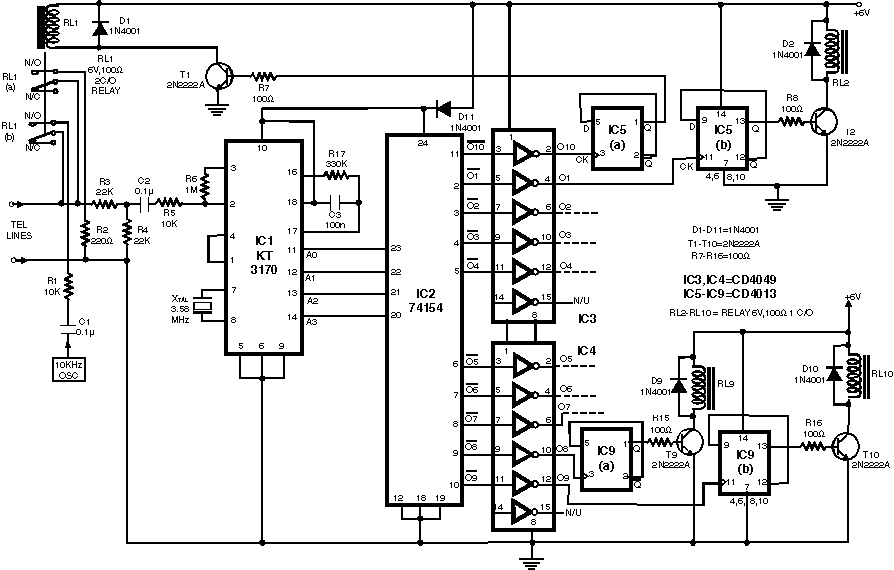
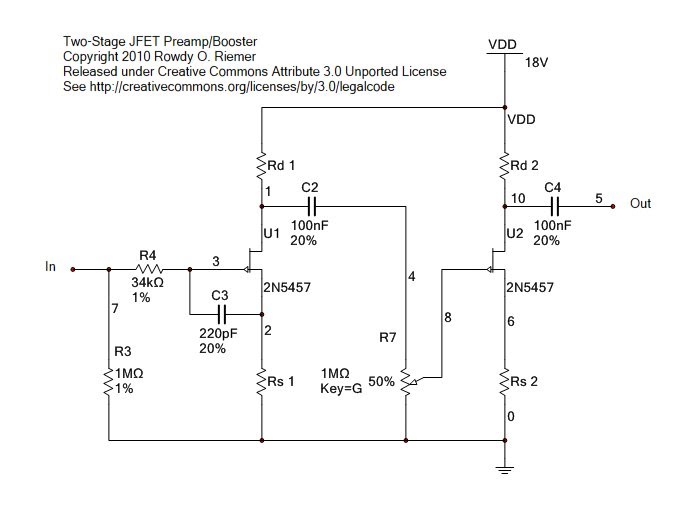
This preamplifier and tone control circuit utilizes a JFET to maximize its performance as a low-noise, high-input impedance device. All device parameters are non-critical, yet the circuit achieves harmonic distortion levels below 0.05% with a signal-to-noise ratio exceeding 85 dB. The tone controls provide 18 dB of cut and boost, while the amplifier delivers a 1-V output for a 100-mV input at maximum level.
The circuit design features a JFET (Junction Field-Effect Transistor) as the primary amplifying element, chosen for its low noise characteristics and high input impedance, making it ideal for processing weak signals without introducing significant distortion. The JFET operates in the linear region, ensuring that the signal integrity is maintained throughout the amplification process.
The tone control section incorporates adjustable resistive and capacitive elements, allowing for precise manipulation of frequency response. The capability to achieve an 18 dB cut or boost enables users to tailor the audio output to their preferences, accommodating various audio sources and listening environments.
The amplifier stage is designed to provide a robust output, capable of delivering 1 V for a 100 mV input signal at maximum gain. This high level of output ensures compatibility with a wide range of audio equipment, facilitating seamless integration into existing audio systems. The low harmonic distortion level of less than 0.05% is indicative of high fidelity performance, ensuring that the audio signal remains clean and true to the original source.
Overall, this preamp and tone control circuit is engineered to deliver exceptional audio quality, characterized by low noise, minimal distortion, and versatile tone shaping capabilities. Its design emphasizes reliability and performance, making it suitable for both professional and consumer audio applications.This preamp and tone control uses the JFET to its best advantage; as a low noise high input impedance device. All device parameters are noncritical, yet the circuit achieves harmonic distortion levels of less than 0.05% with a S/N ratio of over 85 dB.
The tone controls allow 18 dB of cut and boost; the amplifier has a 1-V output for 100-mV input at maximum level. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design features a JFET (Junction Field-Effect Transistor) as the primary amplifying element, chosen for its low noise characteristics and high input impedance, making it ideal for processing weak signals without introducing significant distortion. The JFET operates in the linear region, ensuring that the signal integrity is maintained throughout the amplification process.
The tone control section incorporates adjustable resistive and capacitive elements, allowing for precise manipulation of frequency response. The capability to achieve an 18 dB cut or boost enables users to tailor the audio output to their preferences, accommodating various audio sources and listening environments.
The amplifier stage is designed to provide a robust output, capable of delivering 1 V for a 100 mV input signal at maximum gain. This high level of output ensures compatibility with a wide range of audio equipment, facilitating seamless integration into existing audio systems. The low harmonic distortion level of less than 0.05% is indicative of high fidelity performance, ensuring that the audio signal remains clean and true to the original source.
Overall, this preamp and tone control circuit is engineered to deliver exceptional audio quality, characterized by low noise, minimal distortion, and versatile tone shaping capabilities. Its design emphasizes reliability and performance, making it suitable for both professional and consumer audio applications.This preamp and tone control uses the JFET to its best advantage; as a low noise high input impedance device. All device parameters are noncritical, yet the circuit achieves harmonic distortion levels of less than 0.05% with a S/N ratio of over 85 dB.
The tone controls allow 18 dB of cut and boost; the amplifier has a 1-V output for 100-mV input at maximum level. 🔗 External reference