High Performance Sawtooth Generator
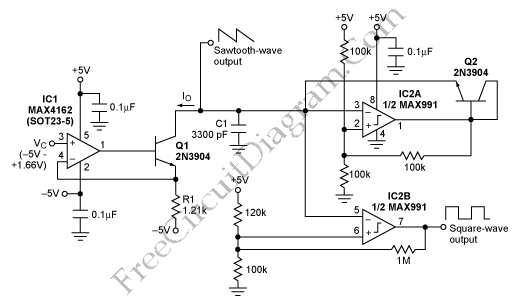
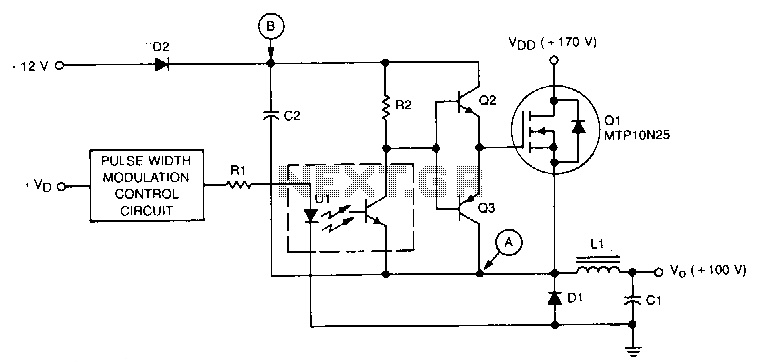
This is a simple sawtooth generator circuit. The advantages of this circuit include low cost and the ability to produce an auxiliary square wave at the same frequency. This circuit can be utilized to sweep the frequency of another generator. The circuit comprises a voltage-controlled current source formed by IC1, R1, and Q1. Capacitor C1 is discharged by current Io until its voltage falls below 1.66V. Once this occurs, the output swings to 5V, triggering the IC2A comparator. Capacitor C1 is then charged by current through the diode-connected transistor Q2 until its voltage reaches 3.33V, causing the IC2A output to return to ground. The output frequency can be adjusted by modifying the values of C1 and R1, within the limitations imposed by the slew rate and settling time of comparator IC2A. The operational frequency range is determined by the linearity of the generator.
The sawtooth generator circuit operates by utilizing a combination of active and passive components to create a linear ramp voltage that periodically resets. The core of the circuit consists of an operational amplifier configured as a comparator, which is essential for generating the sawtooth waveform. The voltage-controlled current source, formed by the integrated circuit (IC1), resistor (R1), and transistor (Q1), regulates the charge and discharge cycles of the capacitor (C1).
During the discharge phase, when the voltage across C1 drops below 1.66V, the output of the comparator (IC2A) transitions high to 5V, initiating the charging phase. The charging of C1 is facilitated through the diode-connected transistor (Q2), which allows current to flow into C1, raising its voltage until it reaches 3.33V. At this point, the comparator output switches low, effectively resetting the cycle.
The frequency of the output waveform is primarily influenced by the values of C1 and R1. By adjusting these components, the output frequency (fOUT) can be set to a desired level, allowing for a wide range of operational frequencies. However, the maximum achievable frequency is constrained by the slew rate and settling time of the comparator IC2A, which affects how quickly the circuit can respond to changes in voltage.
This sawtooth generator circuit is particularly useful in applications requiring a repetitive waveform, such as in signal processing, modulation, and as a timing reference for other electronic circuits. Its simplicity and low cost make it an attractive solution for various electronic design projects.This is a simple sawtooth generator circuit. The advantages of this circuit are low cost and produces an auxiliary square wave at the same frequency. This circuit can be used to sweep the frequency of another generator. Here is the circuit : A voltage-controlled current source is formed by IC1 with R1 and Q1. The C1 is discharged by current Io unt il it`s voltage is less than 1. 66V. It will swing its output to 5V and trips the IC2A comparator. The C1 is charged by current through the diode-connected transistor (Q2) until its voltage reaches 3. 33V, so the IC2A output to swing back to ground. The output frequency is determined by : We can set the fOUT as high as desired by adjusting the values of C1and R1, subject to the limitations of comparator IC2A`s slew settling and rate time.
The frequency range over which it can operate determined by generator`s linearity. [Source: maxim-ic. com] We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems. We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference
The sawtooth generator circuit operates by utilizing a combination of active and passive components to create a linear ramp voltage that periodically resets. The core of the circuit consists of an operational amplifier configured as a comparator, which is essential for generating the sawtooth waveform. The voltage-controlled current source, formed by the integrated circuit (IC1), resistor (R1), and transistor (Q1), regulates the charge and discharge cycles of the capacitor (C1).
During the discharge phase, when the voltage across C1 drops below 1.66V, the output of the comparator (IC2A) transitions high to 5V, initiating the charging phase. The charging of C1 is facilitated through the diode-connected transistor (Q2), which allows current to flow into C1, raising its voltage until it reaches 3.33V. At this point, the comparator output switches low, effectively resetting the cycle.
The frequency of the output waveform is primarily influenced by the values of C1 and R1. By adjusting these components, the output frequency (fOUT) can be set to a desired level, allowing for a wide range of operational frequencies. However, the maximum achievable frequency is constrained by the slew rate and settling time of the comparator IC2A, which affects how quickly the circuit can respond to changes in voltage.
This sawtooth generator circuit is particularly useful in applications requiring a repetitive waveform, such as in signal processing, modulation, and as a timing reference for other electronic circuits. Its simplicity and low cost make it an attractive solution for various electronic design projects.This is a simple sawtooth generator circuit. The advantages of this circuit are low cost and produces an auxiliary square wave at the same frequency. This circuit can be used to sweep the frequency of another generator. Here is the circuit : A voltage-controlled current source is formed by IC1 with R1 and Q1. The C1 is discharged by current Io unt il it`s voltage is less than 1. 66V. It will swing its output to 5V and trips the IC2A comparator. The C1 is charged by current through the diode-connected transistor (Q2) until its voltage reaches 3. 33V, so the IC2A output to swing back to ground. The output frequency is determined by : We can set the fOUT as high as desired by adjusting the values of C1and R1, subject to the limitations of comparator IC2A`s slew settling and rate time.
The frequency range over which it can operate determined by generator`s linearity. [Source: maxim-ic. com] We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems. We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference