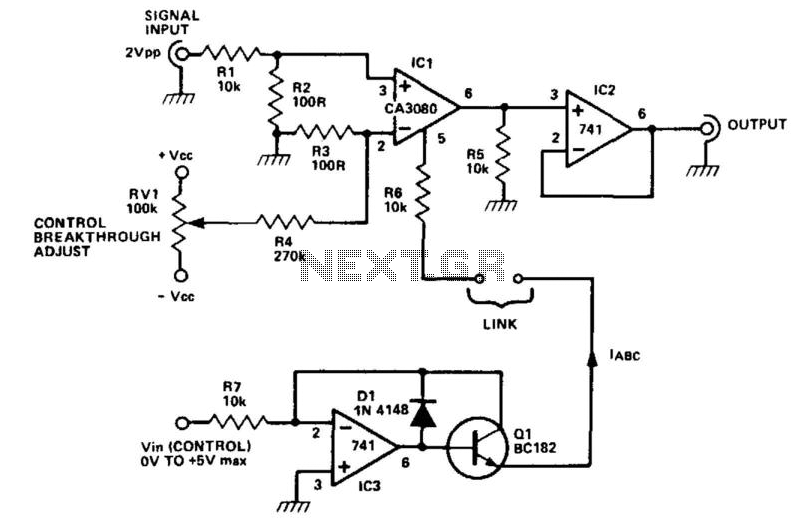
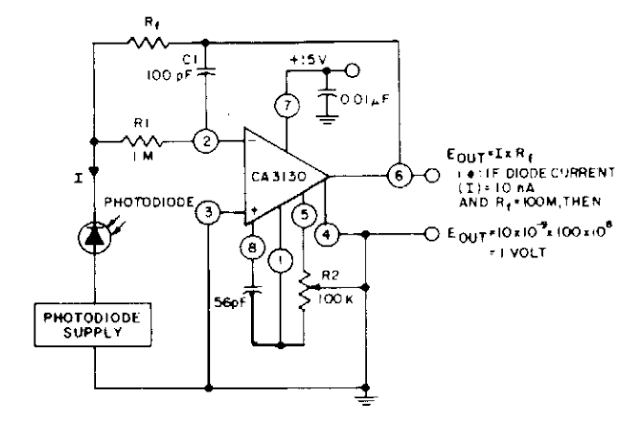
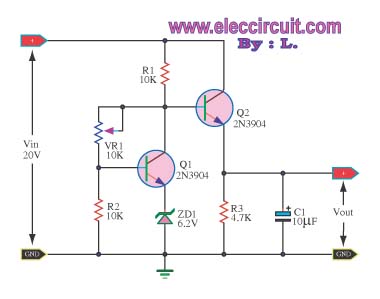
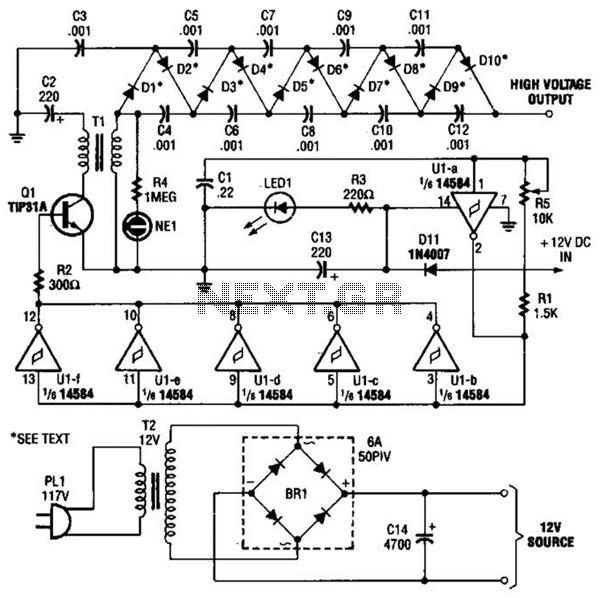
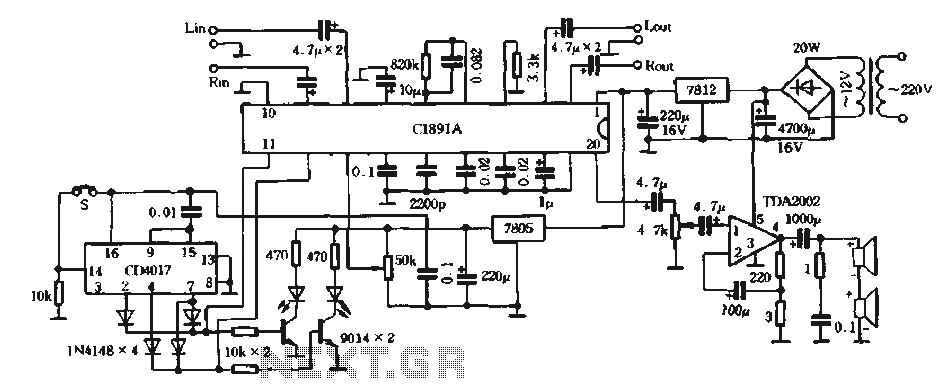
high voltage parallel programmer avr

AVR has two different programming modes called Parallel Programming Mode (Parallel Mode) and Serial Downloading Mode (ISP mode). In Parallel Mode, the programming is done using multiple data lines simultaneously, allowing for faster programming speeds. This mode is typically used for factory programming or in situations where multiple devices need to be programmed at once. In contrast, the ISP mode utilizes a single data line for programming, allowing for in-circuit programming and the ability to update firmware without removing the microcontroller from the circuit. This makes ISP mode particularly useful for development and debugging purposes.
The AVR microcontroller family supports two distinct programming modes: Parallel Programming Mode and Serial Downloading Mode (ISP mode). In Parallel Programming Mode, multiple data lines are engaged simultaneously, facilitating rapid programming of the microcontroller. This mode is advantageous in manufacturing environments where numerous devices require simultaneous programming, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing programming time.
On the other hand, Serial Downloading Mode, commonly referred to as In-System Programming (ISP), employs a single data line for communication. This method allows for programming while the microcontroller remains installed within the circuit, which is beneficial for firmware updates and debugging. The ISP mode is particularly advantageous during the development phase, as it enables developers to modify and upload new firmware without the need for desoldering the microcontroller from the PCB.
Both programming modes are essential for different applications, with Parallel Mode being preferred for high-volume production and ISP mode being ideal for flexible and iterative development processes. Understanding the characteristics and applications of each mode is crucial for optimizing programming strategies in various electronic projects.AVR has two different programming modes called Parallel Programming Mode (Parallel Mode) and Serial Downloading Mode (ISP mode). At the Parallel Mode,.. 🔗 External reference
The AVR microcontroller family supports two distinct programming modes: Parallel Programming Mode and Serial Downloading Mode (ISP mode). In Parallel Programming Mode, multiple data lines are engaged simultaneously, facilitating rapid programming of the microcontroller. This mode is advantageous in manufacturing environments where numerous devices require simultaneous programming, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing programming time.
On the other hand, Serial Downloading Mode, commonly referred to as In-System Programming (ISP), employs a single data line for communication. This method allows for programming while the microcontroller remains installed within the circuit, which is beneficial for firmware updates and debugging. The ISP mode is particularly advantageous during the development phase, as it enables developers to modify and upload new firmware without the need for desoldering the microcontroller from the PCB.
Both programming modes are essential for different applications, with Parallel Mode being preferred for high-volume production and ISP mode being ideal for flexible and iterative development processes. Understanding the characteristics and applications of each mode is crucial for optimizing programming strategies in various electronic projects.AVR has two different programming modes called Parallel Programming Mode (Parallel Mode) and Serial Downloading Mode (ISP mode). At the Parallel Mode,.. 🔗 External reference