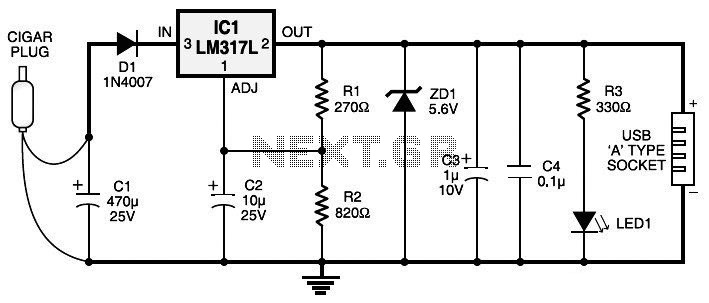
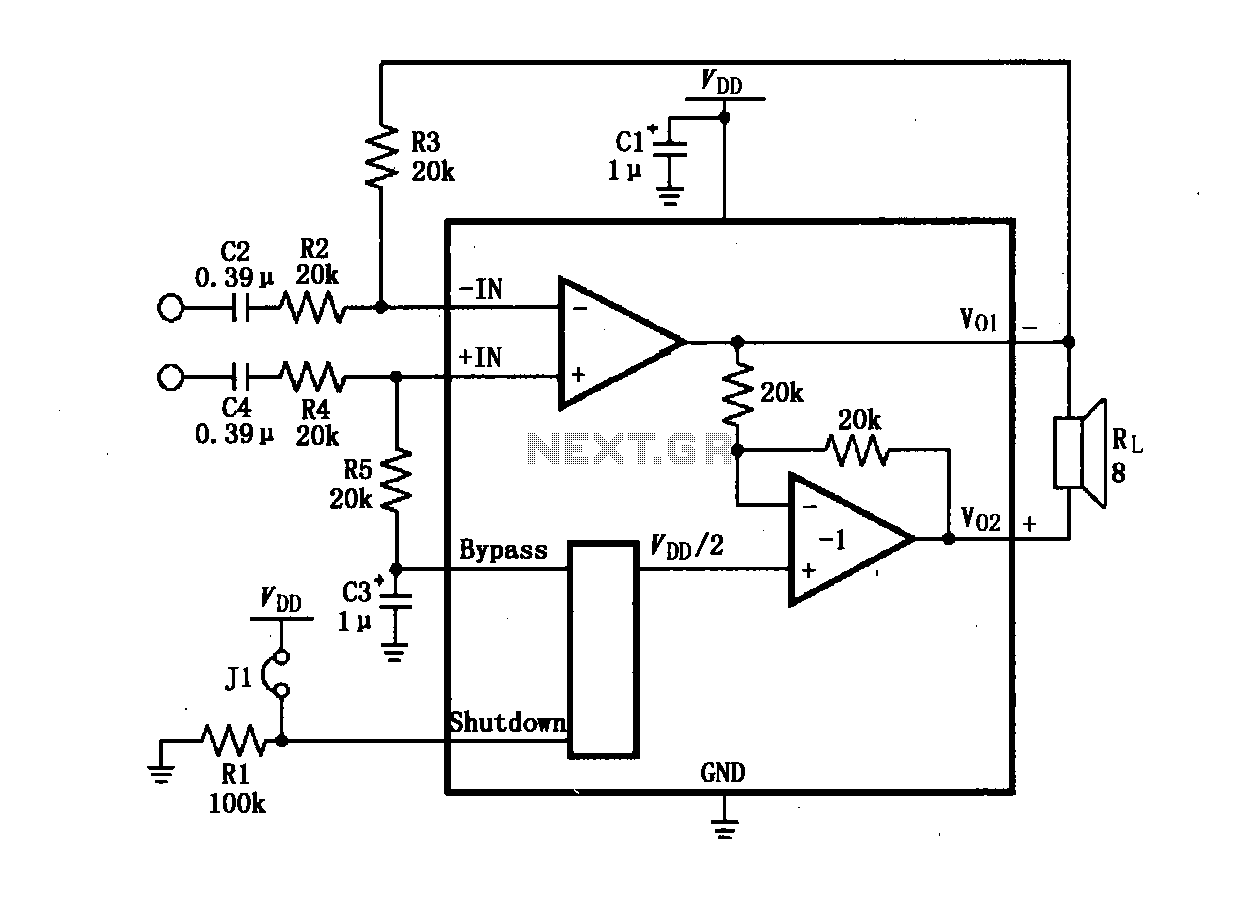
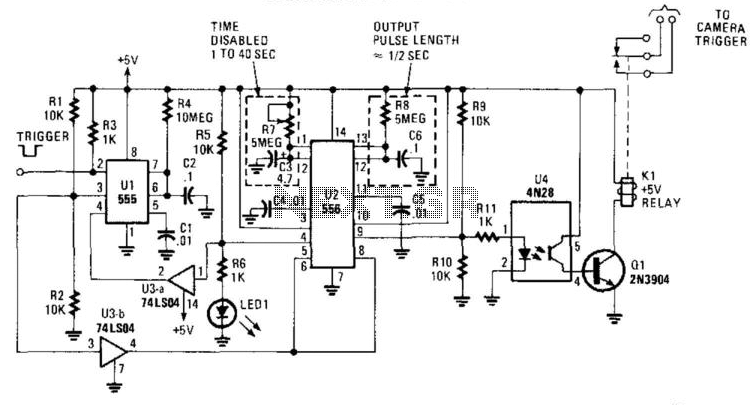
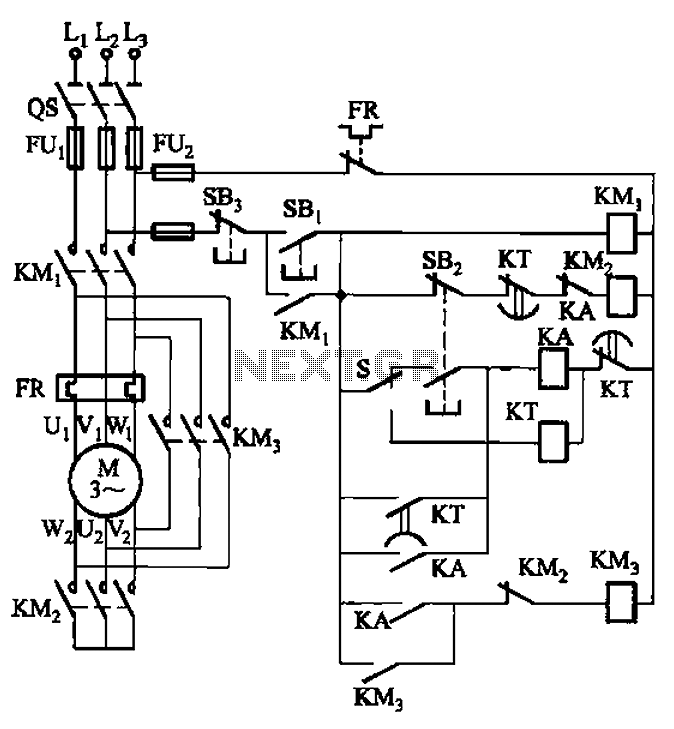
How Do LED light bulbs works on Mobile Phone Circuit
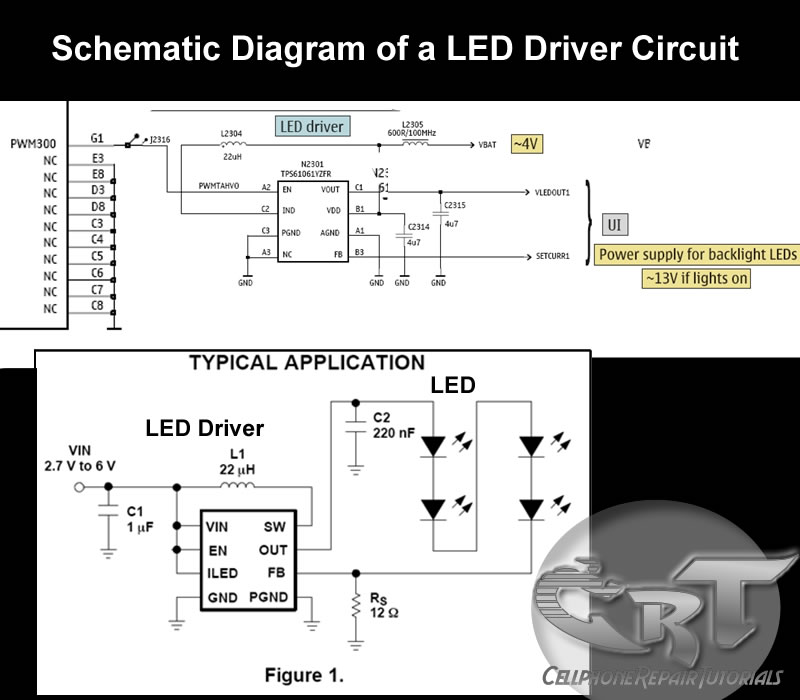
An LED (light-emitting diode) is utilized to illuminate keypad keys and LCD screen displays on all mobile phone handsets. It is controlled by the voltage or current drawn at its terminals. In the schematic diagram, the LEDs are driven by an LED driver chip and a switching control circuit, both integrated into a single chip. The LED driver stabilizes the voltage and current, controlling the ON and OFF status of the LEDs to determine whether they light up. The switching control circuit provides a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal to switch the LEDs on and off. A PWM signal is a type of digital frequency signal that can range up to 1 kHz, allowing control over LED brightness. Once the LED driver receives the PWM signal, it engages to release the voltage or current supplied by the mobile phone's battery. The LED driver functions as a high-frequency, synchronous boost converter with a constant current output capable of driving up to five white LEDs. This circuit is designed for maximum safety, incorporating overvoltage and short circuit protection to prevent damage when the output is shorted to ground. In mobile phone applications, the switching control circuit that generates the PWM signal is synchronized and programmed by the application processor (CPU), allowing full control over the conditions under which the LED lights up. The provided image illustrates an example of the LED circuit, detailing how the various stages and components are mounted on a phone's circuit board. It is important to note that the LED driver and switching control circuits are integrated into an Integrated Circuit (IC). For beginners, a series of simplified step-by-step procedures for troubleshooting LED issues in various mobile phone products will be posted here later. Regular visits to this blog are encouraged for updates.
The LED circuit in mobile phones is a critical component for user interaction and visual feedback. The LED driver chip is specifically designed to manage the power requirements of the LEDs efficiently. It utilizes a boost converter topology to increase the input voltage from the battery to the necessary level for driving the LEDs. This ensures that the LEDs can operate at their optimal brightness without drawing excessive current that could lead to overheating or damage.
The PWM signal generated by the switching control circuit is essential for dimming the LEDs. By varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the effective voltage seen by the LEDs can be adjusted, allowing for smooth transitions between different brightness levels. This capability is particularly useful in applications where ambient light conditions may change, requiring the LED brightness to adapt accordingly.
The integration of overvoltage and short circuit protection mechanisms within the LED driver chip enhances the reliability of the mobile phone. These features prevent damage under fault conditions, ensuring that the device remains functional even if an LED fails or if there is an unexpected load on the circuit.
The communication between the application processor and the LED driver is typically achieved through a serial interface, enabling the CPU to send commands that dictate the behavior of the LEDs. This level of control allows for advanced features such as notifications, alerts, and visual effects that enhance the user experience.
In summary, the LED circuit within mobile phones is a sophisticated system that combines various electronic components to provide illumination and visual feedback. The design considerations for safety, efficiency, and user interaction are paramount in ensuring the longevity and functionality of mobile devices.An LED - light emitting diode is used to illuminate keypads keys and LCD screen displays on all mobile phones handsets. It is being controlled by a voltage or current draws on its terminal leds. On schematic diagram we notice that the LEDs is driven by an LED driver chip`s, and an Switching Control circuit that also being packed in a chip.
The LED driver is being used to stabilized the voltage and current and do take control on engaging ON and OFF status of an LEDs to light up or not. The Switching control circuit feeds and release a Pulse Width Modulation Signal (PWM) to switch and light up the LEDs light bulbs.
A pulse width modulation signal is a type of digital frequency signal range up to 1khz to enable and implement to take control of LED brightness. Once that certain signal is being received by the LED driver, the LED driver now will engage and release the voltage or current that being feeds up from the mobile phones battery supply voltage; LED drivers is a high frequency, synchronous boost converter with constant current output to drive up to 5 white LEDs.
This device circuit is designed for maximum safety, it integrates overvoltage and short circuit protection when the output is being shorted to the ground. Meaning this chips circuitry will not easily breakdown for it is designed to protect when short circuit happens.
In mobile phones application methods; the switching control circuit that release pulse switching signal is also being synchronized programmed by the the application processor (CPU) to engaged a full control on how and which proper situation that the LED will be switch to light up or not. The above image is an example of the LED circuit, how those particular stages and components being mounted on a phones circuits.
Note that the LED driver and switching control circuits is being packed into an Integrated Circuit or ICs. To all beginners: A bunch of simplified STEP By STEP Procedures On Troubleshooting LED Problem issues on various mobile phones product will be Posted Here Later.
Just keep on visiting this blog more often. 🔗 External reference
The LED circuit in mobile phones is a critical component for user interaction and visual feedback. The LED driver chip is specifically designed to manage the power requirements of the LEDs efficiently. It utilizes a boost converter topology to increase the input voltage from the battery to the necessary level for driving the LEDs. This ensures that the LEDs can operate at their optimal brightness without drawing excessive current that could lead to overheating or damage.
The PWM signal generated by the switching control circuit is essential for dimming the LEDs. By varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the effective voltage seen by the LEDs can be adjusted, allowing for smooth transitions between different brightness levels. This capability is particularly useful in applications where ambient light conditions may change, requiring the LED brightness to adapt accordingly.
The integration of overvoltage and short circuit protection mechanisms within the LED driver chip enhances the reliability of the mobile phone. These features prevent damage under fault conditions, ensuring that the device remains functional even if an LED fails or if there is an unexpected load on the circuit.
The communication between the application processor and the LED driver is typically achieved through a serial interface, enabling the CPU to send commands that dictate the behavior of the LEDs. This level of control allows for advanced features such as notifications, alerts, and visual effects that enhance the user experience.
In summary, the LED circuit within mobile phones is a sophisticated system that combines various electronic components to provide illumination and visual feedback. The design considerations for safety, efficiency, and user interaction are paramount in ensuring the longevity and functionality of mobile devices.An LED - light emitting diode is used to illuminate keypads keys and LCD screen displays on all mobile phones handsets. It is being controlled by a voltage or current draws on its terminal leds. On schematic diagram we notice that the LEDs is driven by an LED driver chip`s, and an Switching Control circuit that also being packed in a chip.
The LED driver is being used to stabilized the voltage and current and do take control on engaging ON and OFF status of an LEDs to light up or not. The Switching control circuit feeds and release a Pulse Width Modulation Signal (PWM) to switch and light up the LEDs light bulbs.
A pulse width modulation signal is a type of digital frequency signal range up to 1khz to enable and implement to take control of LED brightness. Once that certain signal is being received by the LED driver, the LED driver now will engage and release the voltage or current that being feeds up from the mobile phones battery supply voltage; LED drivers is a high frequency, synchronous boost converter with constant current output to drive up to 5 white LEDs.
This device circuit is designed for maximum safety, it integrates overvoltage and short circuit protection when the output is being shorted to the ground. Meaning this chips circuitry will not easily breakdown for it is designed to protect when short circuit happens.
In mobile phones application methods; the switching control circuit that release pulse switching signal is also being synchronized programmed by the the application processor (CPU) to engaged a full control on how and which proper situation that the LED will be switch to light up or not. The above image is an example of the LED circuit, how those particular stages and components being mounted on a phones circuits.
Note that the LED driver and switching control circuits is being packed into an Integrated Circuit or ICs. To all beginners: A bunch of simplified STEP By STEP Procedures On Troubleshooting LED Problem issues on various mobile phones product will be Posted Here Later.
Just keep on visiting this blog more often. 🔗 External reference