How to make a Simple Infra Red Remote Control Circuit
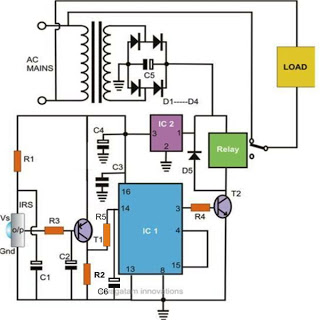
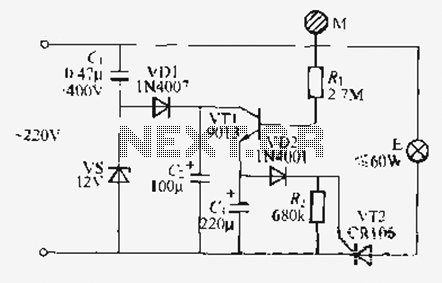
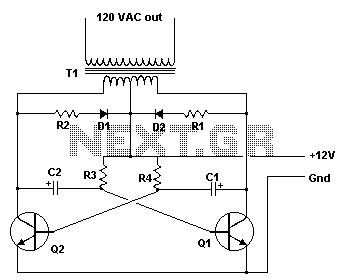
Controlling household electrical gadgets or any electrical equipment remotely can be enjoyable. While using a remote to control devices like a TV or DVD player is a common experience, managing other domestic appliances such as water pumps and lights typically requires physical movement to implement the switches. This article draws inspiration from the conventional TV remote concept and applies it to enable remote control of various household electrical appliances. The circuit allows users to perform operations without having to move from their resting position. This is made possible by a highly versatile, miniature infrared (IR) sensor unit, which serves as the core of the circuit. The sensor converts the received IR signals from the transmitter unit into corresponding logic pulses, which are then fed into the flip-flop stage. The sensor consists of three leads: the input, output, and biasing voltage input. This simplicity in design facilitates easy integration into practical circuits. The sensor operates at a regulated voltage of 5 volts, necessitating the inclusion of a 7805 voltage regulator IC. This 5-volt supply also powers the flip-flop IC 4017. The PNP transistor T1 reacts to the negative trigger pulse from the sensor, quickly pulling the positive voltage at its emitter to the collector through resistor R2. The voltage developed across R2 sends a positive logic high signal to input pin #14 of the IC 4017, causing it to flip its output and change its polarity. The entire circuit is powered by a standard transformer and bridge rectifier network, and it can be housed within a compact plastic enclosure, with appropriate wiring extending from the box for necessary connections.
This circuit utilizes an infrared (IR) sensor to facilitate remote control of household appliances, enhancing convenience and user experience. The IR sensor, a critical component, is designed to detect infrared signals emitted from a remote control. Upon receiving these signals, the sensor converts them into digital logic pulses. The simplicity of the sensor, with only three leads, allows for straightforward integration into various applications, making it an ideal choice for DIY electronics enthusiasts.
The 7805 voltage regulator is essential for maintaining a stable 5V supply, ensuring that both the IR sensor and the flip-flop IC 4017 operate within their specified voltage ranges. The IC 4017 is a decade counter that can drive multiple outputs based on the input pulse it receives. In this application, it serves as a controller for the connected appliances, with each output corresponding to a specific device.
The use of a PNP transistor (T1) in this circuit plays a crucial role in signal amplification and switching. When the IR sensor detects a signal, it sends a negative pulse that triggers the transistor. This action allows current to flow through resistor R2, creating a positive voltage at the base of the transistor, which in turn activates the flip-flop IC. The output from the IC can be connected to various household appliances, enabling them to be turned on or off remotely.
The entire assembly can be conveniently housed in a small plastic box, providing a compact and organized solution for remote control applications. The design allows for easy access to the output connections, facilitating integration with various electrical devices. This project exemplifies the application of basic electronic components to create a functional and user-friendly remote control system for household appliances.Controlling household electrical gadgets or any electrical equipment remotely can be fun. Controlling gadgets like a TV set or a DVD player through a remote may look pretty common to us and we are very used to with the experience, however for controlling many other domestic equipment like a water pump, lights etc we are compelled to walk around fo r implementing the switching. The article is inspired by our usual TV remote concept and has been applied for controlling other house hold electrical appliances remotely. The circuit facilitates and helps the user to do the operations without moving an inch from his resting place.
Thanks to the highly versatile, miniature IR sensor unit which forms the heart of the circuit and directly coverts the received IR waves from the tranamitter unit into the relevant logic pulses for feeding the fllip flop stage. The sensor basically consists of just three leads viz: the input, the output and the biasing voltage input lead.
The involvmant of only three leads makes the unit very easy to configure into a practical circuit. The sensor is specified for operating at 5 volts regulated voltage which makes the inclusion of the 7805 IC stage important. The 5 voltage supply also becomes useful for the flip flop IC 4017 and is appropriately supplied to the relevant stage.
The PNP transistor T1 responds to the negative trigger pulse from the sensor and quickly pulls the positive potential at its emitter to the collector across the resistor R2. The potential developed across R2 provides a positive logic high to the IC 4017 input pin #14. The IC instantly flips its output and changes it`s polarity. The entire circuit is powered from an ordinary transformer/bridge network and the entire circuit may be housed inside a small plastic box with the relevant wires coming out of the box for the desired connections.
🔗 External reference
This circuit utilizes an infrared (IR) sensor to facilitate remote control of household appliances, enhancing convenience and user experience. The IR sensor, a critical component, is designed to detect infrared signals emitted from a remote control. Upon receiving these signals, the sensor converts them into digital logic pulses. The simplicity of the sensor, with only three leads, allows for straightforward integration into various applications, making it an ideal choice for DIY electronics enthusiasts.
The 7805 voltage regulator is essential for maintaining a stable 5V supply, ensuring that both the IR sensor and the flip-flop IC 4017 operate within their specified voltage ranges. The IC 4017 is a decade counter that can drive multiple outputs based on the input pulse it receives. In this application, it serves as a controller for the connected appliances, with each output corresponding to a specific device.
The use of a PNP transistor (T1) in this circuit plays a crucial role in signal amplification and switching. When the IR sensor detects a signal, it sends a negative pulse that triggers the transistor. This action allows current to flow through resistor R2, creating a positive voltage at the base of the transistor, which in turn activates the flip-flop IC. The output from the IC can be connected to various household appliances, enabling them to be turned on or off remotely.
The entire assembly can be conveniently housed in a small plastic box, providing a compact and organized solution for remote control applications. The design allows for easy access to the output connections, facilitating integration with various electrical devices. This project exemplifies the application of basic electronic components to create a functional and user-friendly remote control system for household appliances.Controlling household electrical gadgets or any electrical equipment remotely can be fun. Controlling gadgets like a TV set or a DVD player through a remote may look pretty common to us and we are very used to with the experience, however for controlling many other domestic equipment like a water pump, lights etc we are compelled to walk around fo r implementing the switching. The article is inspired by our usual TV remote concept and has been applied for controlling other house hold electrical appliances remotely. The circuit facilitates and helps the user to do the operations without moving an inch from his resting place.
Thanks to the highly versatile, miniature IR sensor unit which forms the heart of the circuit and directly coverts the received IR waves from the tranamitter unit into the relevant logic pulses for feeding the fllip flop stage. The sensor basically consists of just three leads viz: the input, the output and the biasing voltage input lead.
The involvmant of only three leads makes the unit very easy to configure into a practical circuit. The sensor is specified for operating at 5 volts regulated voltage which makes the inclusion of the 7805 IC stage important. The 5 voltage supply also becomes useful for the flip flop IC 4017 and is appropriately supplied to the relevant stage.
The PNP transistor T1 responds to the negative trigger pulse from the sensor and quickly pulls the positive potential at its emitter to the collector across the resistor R2. The potential developed across R2 provides a positive logic high to the IC 4017 input pin #14. The IC instantly flips its output and changes it`s polarity. The entire circuit is powered from an ordinary transformer/bridge network and the entire circuit may be housed inside a small plastic box with the relevant wires coming out of the box for the desired connections.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713