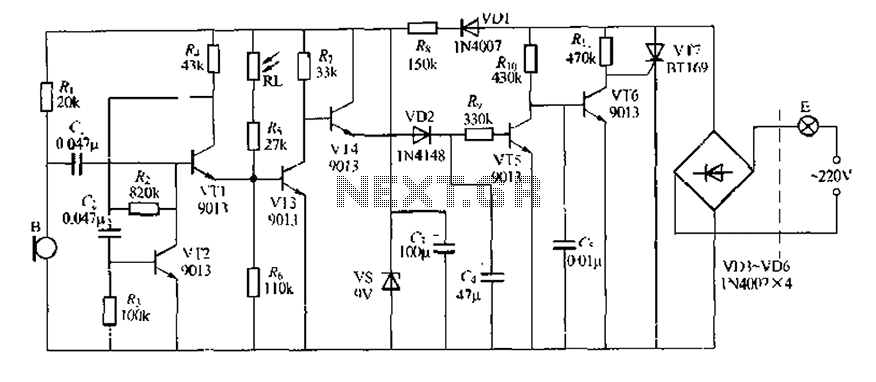
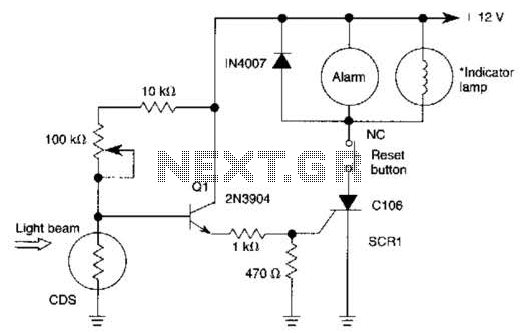
IGNITION TIMING LIGHT
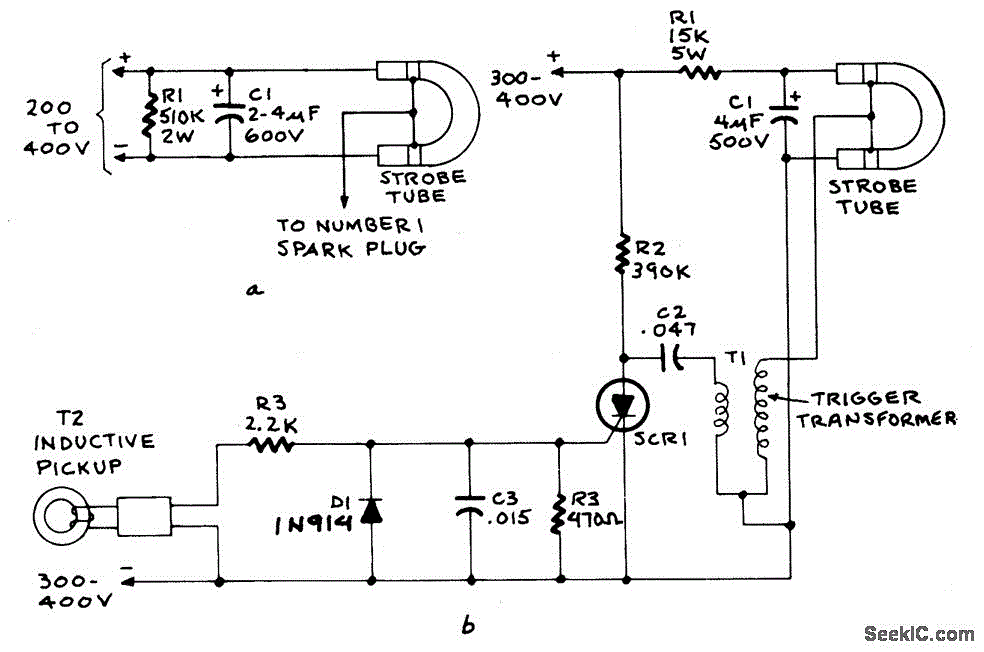
Figure A illustrates the circuit of a direct-trigger timing light. The trigger voltage is obtained from the car's ignition circuit through a direct connection to a spark plug. Figure B depicts a circuit that employs an inductive pickup. A trigger transformer is utilized to generate the high-voltage pulse necessary for triggering. The triggering circuit comprises T1, C1, SCR1, and an inductive pickup.
The direct-trigger timing light circuit operates by capturing the ignition pulse from the vehicle's ignition system, which is essential for timing adjustments in automotive applications. The connection to the spark plug allows the timing light to sense the precise moment of ignition, providing real-time feedback for tuning purposes.
In the circuit design, T1 represents a transformer that steps up the voltage from the ignition pulse to a level suitable for triggering the subsequent components. C1 is a capacitor that helps in smoothing the voltage spikes generated during the ignition process, ensuring stable operation of the timing light. SCR1, or Silicon Controlled Rectifier, is used to control the flow of current in the circuit. It is triggered by the voltage from the transformer and allows the high-voltage pulse to pass through to the timing light.
In Figure B, the inductive pickup serves as an alternative method for sensing the ignition pulse. This component detects the magnetic field generated around the spark plug wire, eliminating the need for a direct connection to the spark plug itself. This method can enhance safety and reduce the risk of damaging the ignition system. The output from the inductive pickup is then fed into the triggering circuit, which processes the signal similarly to the direct connection method.
Overall, these circuits are crucial for automotive technicians who require accurate timing information to optimize engine performance. The design ensures reliability and precision in measuring ignition timing, which is vital for maintaining engine efficiency and performance.Figure A shows the circuit of a direct-trigger timing light. The trigger voltage is taken from the car`s ignition circuit by a direct connection to a spark plug. A circuit using an inductive pickup is shown in Fig. B. A trigger transformer is used to develop the high-voltage pulse for triggering. The triggering circuit consists of T1, C1, SCR1, inductive pic.. 🔗 External reference
The direct-trigger timing light circuit operates by capturing the ignition pulse from the vehicle's ignition system, which is essential for timing adjustments in automotive applications. The connection to the spark plug allows the timing light to sense the precise moment of ignition, providing real-time feedback for tuning purposes.
In the circuit design, T1 represents a transformer that steps up the voltage from the ignition pulse to a level suitable for triggering the subsequent components. C1 is a capacitor that helps in smoothing the voltage spikes generated during the ignition process, ensuring stable operation of the timing light. SCR1, or Silicon Controlled Rectifier, is used to control the flow of current in the circuit. It is triggered by the voltage from the transformer and allows the high-voltage pulse to pass through to the timing light.
In Figure B, the inductive pickup serves as an alternative method for sensing the ignition pulse. This component detects the magnetic field generated around the spark plug wire, eliminating the need for a direct connection to the spark plug itself. This method can enhance safety and reduce the risk of damaging the ignition system. The output from the inductive pickup is then fed into the triggering circuit, which processes the signal similarly to the direct connection method.
Overall, these circuits are crucial for automotive technicians who require accurate timing information to optimize engine performance. The design ensures reliability and precision in measuring ignition timing, which is vital for maintaining engine efficiency and performance.Figure A shows the circuit of a direct-trigger timing light. The trigger voltage is taken from the car`s ignition circuit by a direct connection to a spark plug. A circuit using an inductive pickup is shown in Fig. B. A trigger transformer is used to develop the high-voltage pulse for triggering. The triggering circuit consists of T1, C1, SCR1, inductive pic.. 🔗 External reference