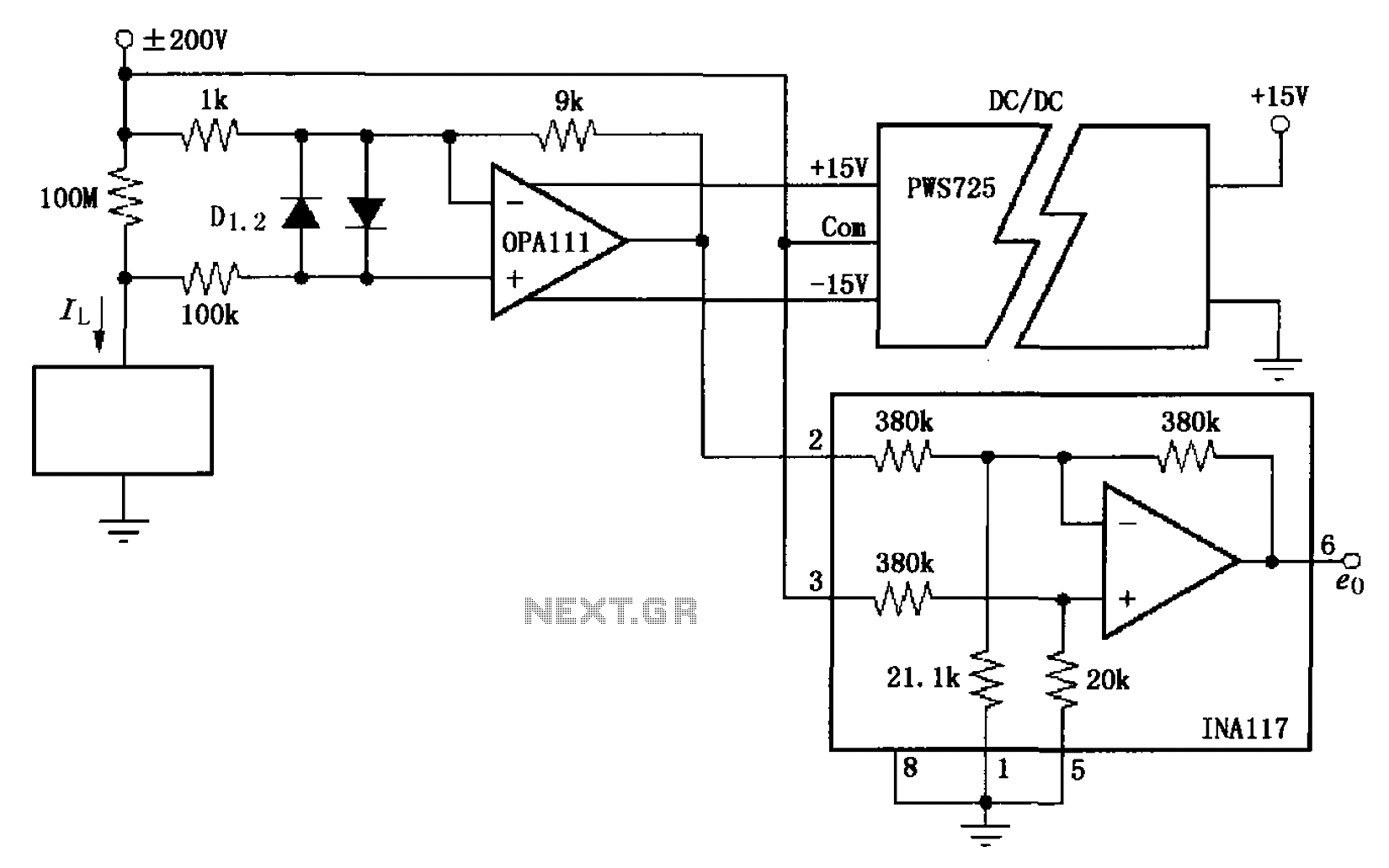
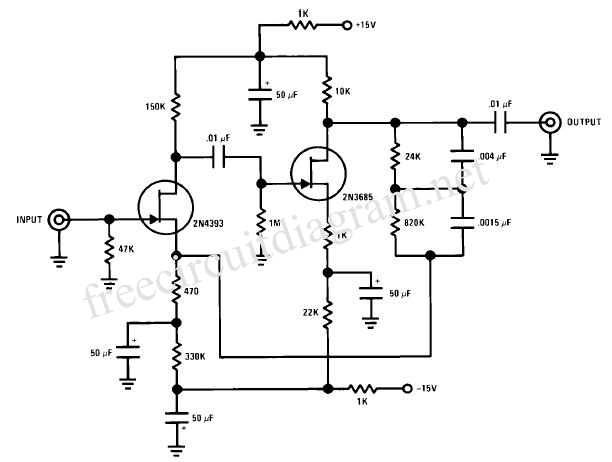
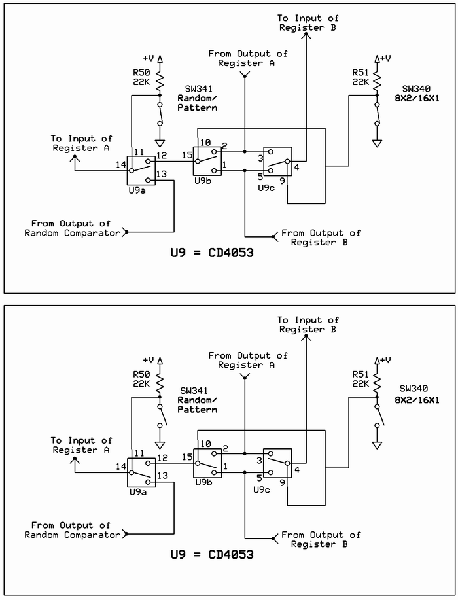
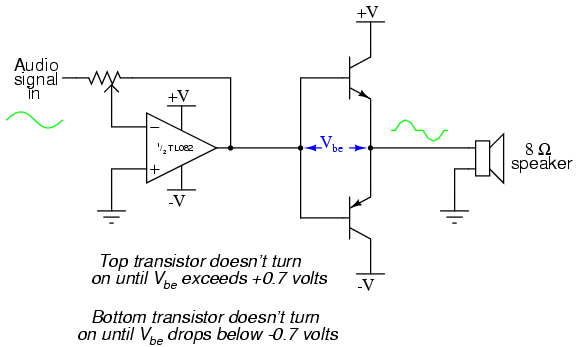
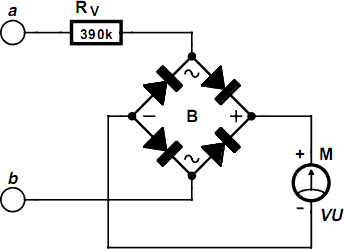
Improved differential circuit diagram

The modification of the differential circuit is illustrated. In Figure A1, an integrator is depicted, and the output is presented.
The circuit modification involves integrating the differential circuit with an integrator component, which plays a crucial role in signal processing applications. The integrator is designed to output a voltage that is proportional to the integral of the input signal over time. This is particularly useful in applications where the cumulative effect of a signal is required, such as in analog computing or control systems.
In Figure A1, the integrator is typically implemented using an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in an inverting mode. The input signal is applied to the inverting terminal of the op-amp through a resistor, while a capacitor is connected between the output and the inverting terminal, forming a feedback loop. The non-inverting terminal is grounded.
The output voltage of the integrator can be expressed mathematically as V_out(t) = -(1/RC) ∫ V_in(t) dt, where R is the resistance, C is the capacitance, and V_in(t) is the input voltage. This equation indicates that the output voltage is the negative integral of the input voltage, scaled by the time constant RC of the circuit.
Additionally, it is essential to consider the frequency response of the integrator, as it can significantly influence the performance of the overall differential circuit. The integrator will have a high gain at low frequencies and will attenuate high-frequency signals, which can lead to phase shifts and potential instability in certain applications. Therefore, proper selection of the resistor and capacitor values is critical to ensure that the integrator operates effectively within the desired frequency range.
Overall, the integration of the differential circuit with an integrator enhances its functionality, enabling it to process signals that require accumulation over time, thereby expanding the potential applications in various electronic systems. As shown for the modification of the differential circuit. Figure, A1 is an integrator, the output is
The circuit modification involves integrating the differential circuit with an integrator component, which plays a crucial role in signal processing applications. The integrator is designed to output a voltage that is proportional to the integral of the input signal over time. This is particularly useful in applications where the cumulative effect of a signal is required, such as in analog computing or control systems.
In Figure A1, the integrator is typically implemented using an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in an inverting mode. The input signal is applied to the inverting terminal of the op-amp through a resistor, while a capacitor is connected between the output and the inverting terminal, forming a feedback loop. The non-inverting terminal is grounded.
The output voltage of the integrator can be expressed mathematically as V_out(t) = -(1/RC) ∫ V_in(t) dt, where R is the resistance, C is the capacitance, and V_in(t) is the input voltage. This equation indicates that the output voltage is the negative integral of the input voltage, scaled by the time constant RC of the circuit.
Additionally, it is essential to consider the frequency response of the integrator, as it can significantly influence the performance of the overall differential circuit. The integrator will have a high gain at low frequencies and will attenuate high-frequency signals, which can lead to phase shifts and potential instability in certain applications. Therefore, proper selection of the resistor and capacitor values is critical to ensure that the integrator operates effectively within the desired frequency range.
Overall, the integration of the differential circuit with an integrator enhances its functionality, enabling it to process signals that require accumulation over time, thereby expanding the potential applications in various electronic systems. As shown for the modification of the differential circuit. Figure, A1 is an integrator, the output is