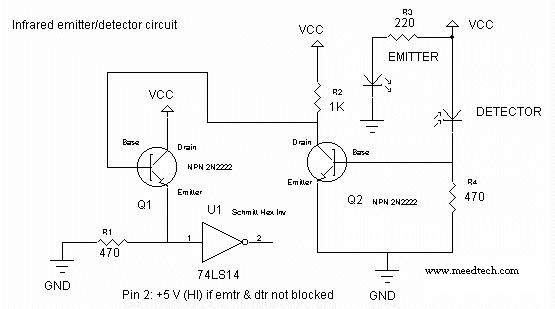
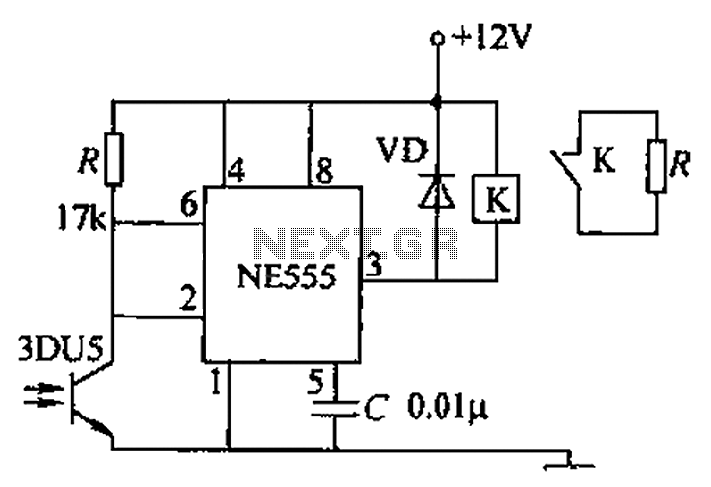
Infrared (IR) Proximity Detector
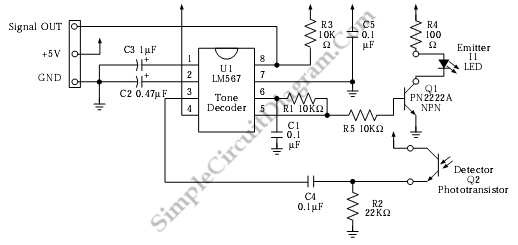
This is an infrared (IR) proximity detector circuit. A matched infrared emitter and detector pair is utilized in this circuit. The voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) section of the LM567 tone detector integrated circuit (IC) is employed to set the emitter LED pulses at a specific frequency. In this circuit, the center frequency of the VCO is configured to approximately 909 Hz through a combination of capacitor C1 and resistor R1. A signal is generated for the tone detector IC in response to the detected reflected light from the emitter. The input frequency is compared with the frequency generated by the decoder. If the frequencies differ significantly, resistor R3, a 10K pull-up resistor, maintains the output at 5 volts. If the frequencies are sufficiently close, pin 8 is driven to a low state (ground). An amplifying transistor can be incorporated for higher current requirements.
The infrared (IR) proximity detector circuit operates by using a matched pair of an infrared emitter and detector. The emitter emits IR light, which reflects off nearby objects and is detected by the detector. The LM567 tone detector IC plays a crucial role in this circuit, particularly through its voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) functionality. The VCO is designed to produce pulses at a frequency of approximately 909 Hz, which is determined by the values of capacitor C1 and resistor R1.
When the IR light reflects off an object and is received by the detector, it generates a signal that is fed into the tone detector IC. The IC compares the input frequency from the detector with its own generated frequency. If the input frequency deviates significantly from the expected frequency, the pull-up resistor R3 ensures that the output remains at a stable 5 volts. This condition indicates that no object is within proximity. Conversely, when an object is detected and the frequencies are close enough, the output at pin 8 transitions to a low state, indicating proximity.
For applications requiring higher current output, an amplifying transistor can be connected to the output stage of the circuit. This allows the circuit to drive larger loads or activate additional components based on the proximity detection. The overall design of the circuit is effective for various applications, including object detection in robotics, automation systems, and safety devices. Proper selection of the emitter and detector pairing, along with the tuning of the VCO frequency, is essential for optimizing the performance of this IR proximity detector circuit.This is infrared (IR) proximity detector circuit. A matched infrared emitter and detector pair is used in this circuit. The voltage controlled oscillator section of the LM567 tone detector IC is used to set the emitter LED pulses at frequency. In this circuit, the center frequency of the VCO is set to about 909 Hz by combination of capacitor C1 an
d Resistor R1. Here is the circuit: A signal is generated for the tone detector IC as the response to the detected reflected light from the emitter. The input frequency is compared with the generated frequency by the decoder. If the frequency is far, R3, 10K pull up resistor, holds it to 5 Volts. If the frequency is close enough, the pin 8 is sent to LOW (ground). An amplifying transistor can be added for higher currents as needed. [Circuit`s schematic diagram source: mondotronics. com] We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems.
We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference
The infrared (IR) proximity detector circuit operates by using a matched pair of an infrared emitter and detector. The emitter emits IR light, which reflects off nearby objects and is detected by the detector. The LM567 tone detector IC plays a crucial role in this circuit, particularly through its voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) functionality. The VCO is designed to produce pulses at a frequency of approximately 909 Hz, which is determined by the values of capacitor C1 and resistor R1.
When the IR light reflects off an object and is received by the detector, it generates a signal that is fed into the tone detector IC. The IC compares the input frequency from the detector with its own generated frequency. If the input frequency deviates significantly from the expected frequency, the pull-up resistor R3 ensures that the output remains at a stable 5 volts. This condition indicates that no object is within proximity. Conversely, when an object is detected and the frequencies are close enough, the output at pin 8 transitions to a low state, indicating proximity.
For applications requiring higher current output, an amplifying transistor can be connected to the output stage of the circuit. This allows the circuit to drive larger loads or activate additional components based on the proximity detection. The overall design of the circuit is effective for various applications, including object detection in robotics, automation systems, and safety devices. Proper selection of the emitter and detector pairing, along with the tuning of the VCO frequency, is essential for optimizing the performance of this IR proximity detector circuit.This is infrared (IR) proximity detector circuit. A matched infrared emitter and detector pair is used in this circuit. The voltage controlled oscillator section of the LM567 tone detector IC is used to set the emitter LED pulses at frequency. In this circuit, the center frequency of the VCO is set to about 909 Hz by combination of capacitor C1 an
d Resistor R1. Here is the circuit: A signal is generated for the tone detector IC as the response to the detected reflected light from the emitter. The input frequency is compared with the generated frequency by the decoder. If the frequency is far, R3, 10K pull up resistor, holds it to 5 Volts. If the frequency is close enough, the pin 8 is sent to LOW (ground). An amplifying transistor can be added for higher currents as needed. [Circuit`s schematic diagram source: mondotronics. com] We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems.
We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference