Infrared (IR) Proximity (Distance) Sensor
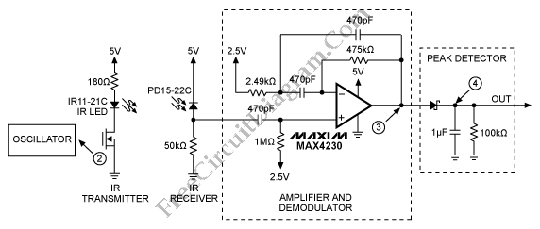
The photodiode is utilized to detect infrared (IR) light reflected from an object. However, it also picks up IR light generated by ambient conditions, which can lead to false detections. To mitigate this issue, it is essential to filter out the IR noise. Typically, the IR signal emitted by the LED is modulated at a specific frequency, allowing the detection circuit to focus solely on the modulated signal and effectively filter out the noise. Consequently, the photodiode will only detect IR light reflected from the object. This process can be simplified by employing an IR proximity sensor that features straightforward receiver and transmitter sections.
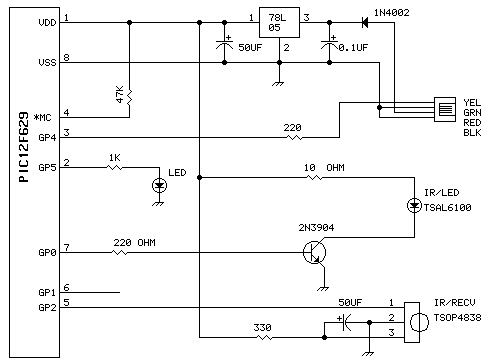
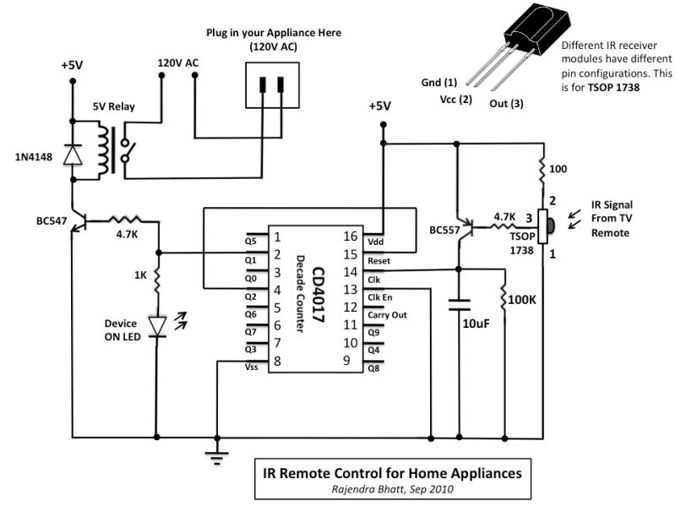
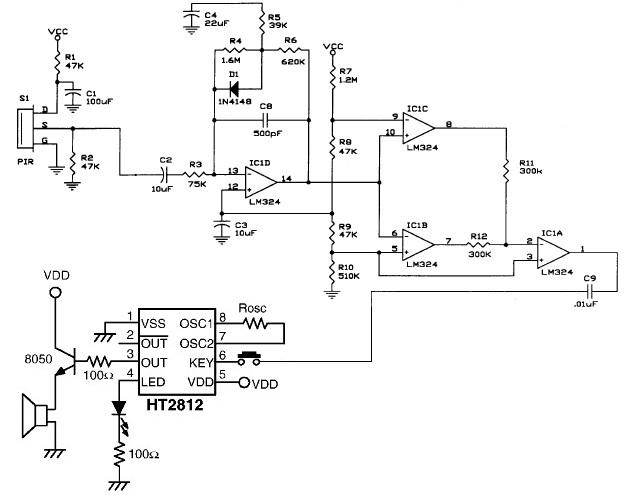
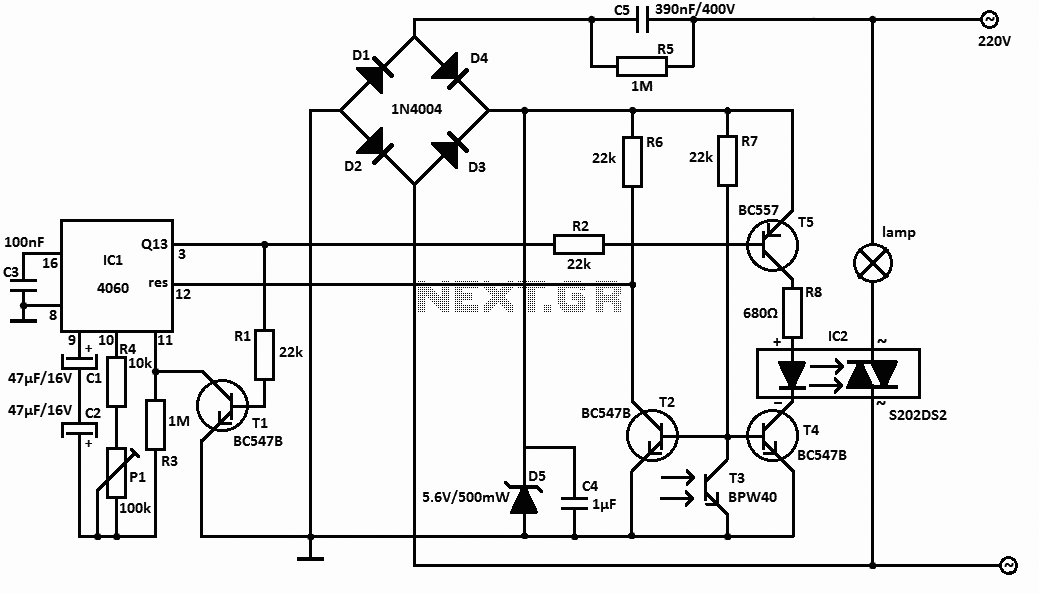
The schematic diagram of the IR proximity sensor includes a transmitter circuit composed of a 940nm IR LED (model IR11-21C). A 10kHz oscillator frequency is used to turn the IR LED on and off. The detection capability and the level of transmitted power can be adjusted by varying the current through the LED. The transmitter emits pulses with a small duty cycle, typically around 10%, to conserve power. The operational amplifier (op-amp) is biased at 2.5V in the absence of an input IR signal, and its output fluctuates around this voltage level with a dynamic range of 5V in response to the 10kHz IR signal incident on it. The output of the op-amp drives a simple diode detector, which provides a direct current (DC) signal proportional to the amplitude of the detected IR signal. This diode detector also rectifies the 10kHz signal. The resulting output signal is an analog representation of the distance of the object from the IR transmitter. This output can either be fed into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for further processing or utilized directly.
The IR proximity sensor is a practical solution for applications requiring distance measurement or object detection. The modulation of the IR LED ensures that the sensor remains sensitive only to the specific frequency of interest, thereby improving accuracy in detecting reflected IR light while minimizing interference from ambient IR sources. The simplicity of the design allows for easy integration into various electronic systems, making it a versatile choice for engineers and developers in the field of electronics.The photodiode can be used to detect IR reflected from the object. However, IR produced by the ambient conditions also detected by the photodiode. This IR noise must be filtered to prevent false detections. Usually, the LED`s IR signal is modulated with a convenient frequency and then using that modulation to detect only IR to filter the IR noise. So, the photodiode will detect only IR reflected from the object. This method can be simplified by using the IR proximity sensor that has simple receiver and transmitter sections. Here is the schematic diagram of the IR proximity sensor : The transmitter of this circuit consists of a 940nm IR LED (IR11-21C).
To turn ON and OFF the IR LED, the a 10kHz oscillator frequency is used. we can control the detection and the level of transmitted power by varying the LED current. The transmit pulses of this transmitter have a small duty cycle (typically 10%), to save power. The Op amp is biased at 2. 5V because there no input IR signal present. The op amp output varies around 2. 5V with a dynamic range of 5V because of a 10kHz IR signal incident. The output drives a simple diode detector. A DC signal proportional to its amplitude can be provided by a simple diode detector. Simple diode detector also rectifies the 10kHz signal. The output signal is an analog signal that is proportional to the distance of the object from the IR transmitter. We can fed the output signal to an ADC for further processing or use it directly. [Source: MAXIM Application Note] We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems.
We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference
The schematic diagram of the IR proximity sensor includes a transmitter circuit composed of a 940nm IR LED (model IR11-21C). A 10kHz oscillator frequency is used to turn the IR LED on and off. The detection capability and the level of transmitted power can be adjusted by varying the current through the LED. The transmitter emits pulses with a small duty cycle, typically around 10%, to conserve power. The operational amplifier (op-amp) is biased at 2.5V in the absence of an input IR signal, and its output fluctuates around this voltage level with a dynamic range of 5V in response to the 10kHz IR signal incident on it. The output of the op-amp drives a simple diode detector, which provides a direct current (DC) signal proportional to the amplitude of the detected IR signal. This diode detector also rectifies the 10kHz signal. The resulting output signal is an analog representation of the distance of the object from the IR transmitter. This output can either be fed into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for further processing or utilized directly.
The IR proximity sensor is a practical solution for applications requiring distance measurement or object detection. The modulation of the IR LED ensures that the sensor remains sensitive only to the specific frequency of interest, thereby improving accuracy in detecting reflected IR light while minimizing interference from ambient IR sources. The simplicity of the design allows for easy integration into various electronic systems, making it a versatile choice for engineers and developers in the field of electronics.The photodiode can be used to detect IR reflected from the object. However, IR produced by the ambient conditions also detected by the photodiode. This IR noise must be filtered to prevent false detections. Usually, the LED`s IR signal is modulated with a convenient frequency and then using that modulation to detect only IR to filter the IR noise. So, the photodiode will detect only IR reflected from the object. This method can be simplified by using the IR proximity sensor that has simple receiver and transmitter sections. Here is the schematic diagram of the IR proximity sensor : The transmitter of this circuit consists of a 940nm IR LED (IR11-21C).
To turn ON and OFF the IR LED, the a 10kHz oscillator frequency is used. we can control the detection and the level of transmitted power by varying the LED current. The transmit pulses of this transmitter have a small duty cycle (typically 10%), to save power. The Op amp is biased at 2. 5V because there no input IR signal present. The op amp output varies around 2. 5V with a dynamic range of 5V because of a 10kHz IR signal incident. The output drives a simple diode detector. A DC signal proportional to its amplitude can be provided by a simple diode detector. Simple diode detector also rectifies the 10kHz signal. The output signal is an analog signal that is proportional to the distance of the object from the IR transmitter. We can fed the output signal to an ADC for further processing or use it directly. [Source: MAXIM Application Note] We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems.
We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference