interafce 16x2 lcd with avr
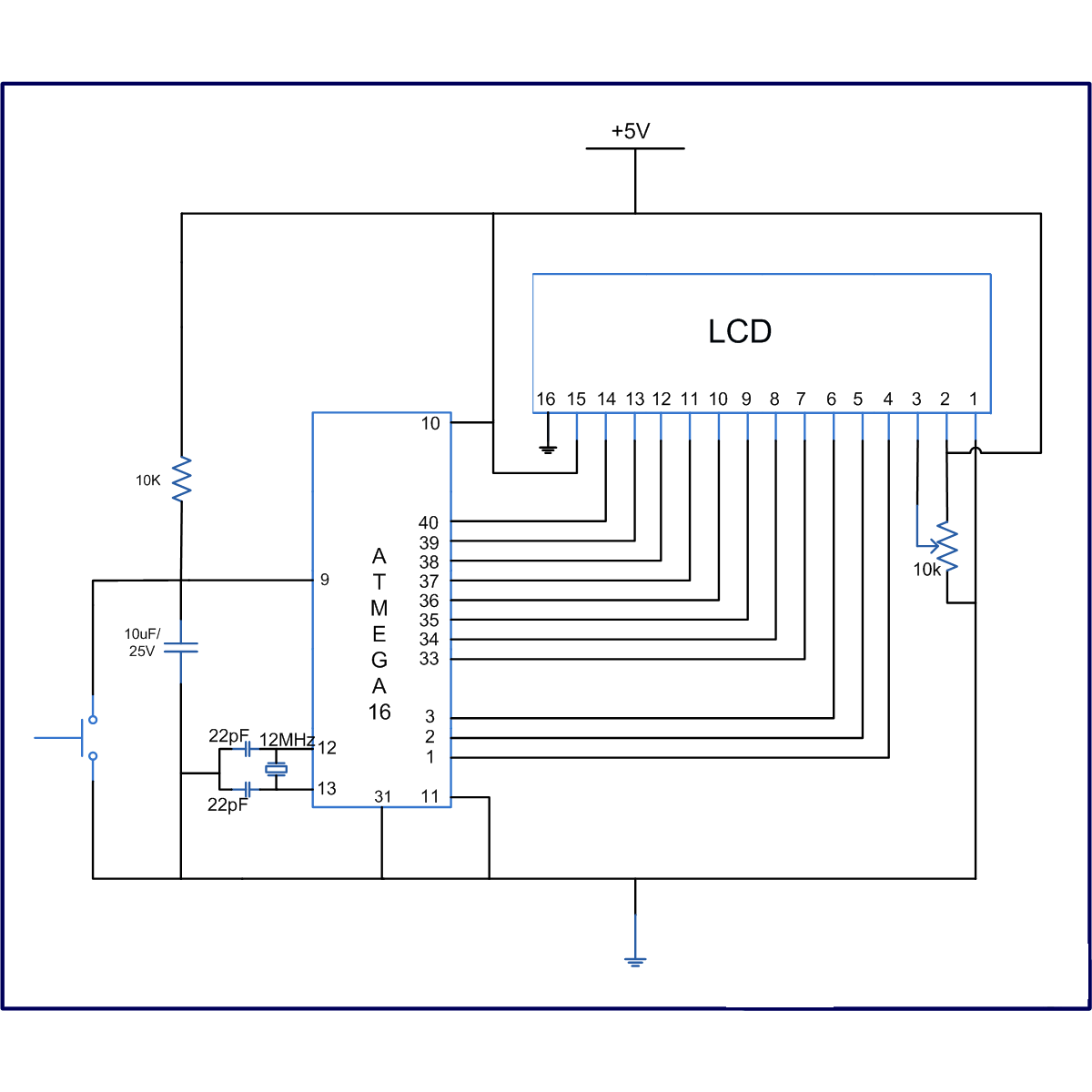
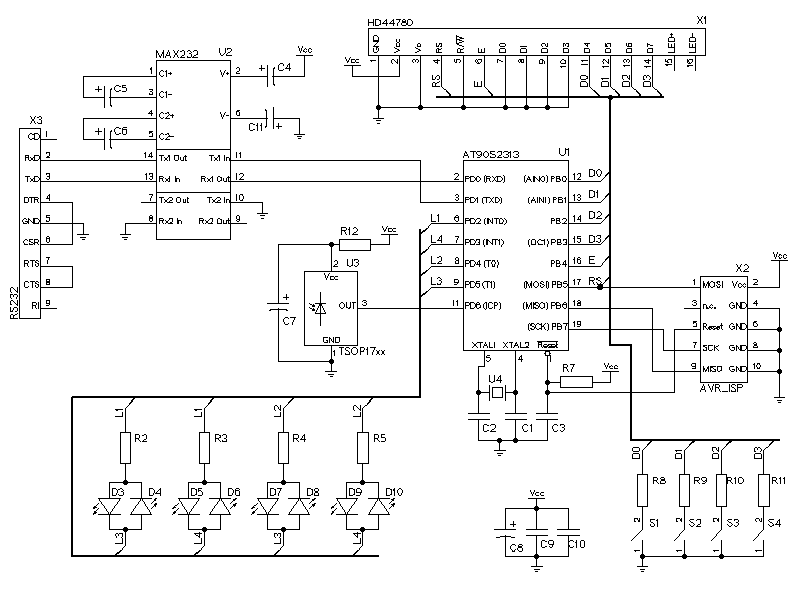
LCDs are available in various configurations, with the 16x2 matrix display being the most popular. This article demonstrates the interfacing of an ATmega16 microcontroller with an LCD by displaying a simple character. In this project, the LCD operates in 8-bit mode, meaning that the data sent to the LCD must be in 8-bit format. Port A of the ATmega16 is connected to the data pins of the LCD and is defined as LCD_DATA. Port B is designated for control pins (RS, R/W, and EN).
The interfacing of an ATmega16 microcontroller with a 16x2 LCD involves several key components and configurations that facilitate the display of characters. The 16x2 LCD consists of two rows, each capable of displaying 16 characters, and operates using a parallel communication protocol.
In this setup, the microcontroller communicates with the LCD in 8-bit mode, which allows for the transmission of data in 8-bit chunks. The data pins of the LCD are connected to Port A of the ATmega16, which is configured as an output port. This configuration enables the microcontroller to send character data directly to the LCD for display. The specific data pins are typically labeled D0 through D7, corresponding to the 8-bit data format.
Control signals are crucial for proper operation, and they are managed through Port B of the ATmega16. The control pins include:
- RS (Register Select): This pin determines whether the data being sent is command or character data. When RS is low, the microcontroller sends a command; when high, it sends data.
- R/W (Read/Write): This pin indicates the direction of data flow. When low, the microcontroller writes data to the LCD; when high, it reads data from the LCD.
- EN (Enable): This pin is used to latch the data into the LCD. A rising edge on this pin signals the LCD to read the data present on the data pins.
The initialization sequence of the LCD is critical for ensuring proper functionality. This typically involves configuring the LCD to operate in 8-bit mode, setting the number of display lines, and enabling the display. After initialization, the microcontroller can send characters to be displayed by writing to the appropriate data and control pins in a timed sequence.
In summary, the interfacing of an ATmega16 microcontroller with a 16x2 LCD in 8-bit mode involves connecting the data pins to Port A and the control pins to Port B, ensuring proper signal management for effective character display. This setup is fundamental in various applications, including embedded systems and user interfaces.LCD comes in various configurations and the most popular one is 16x2 matrix display. This article shows the interfacing of ATmega16 with LCD by displaying a simple character on the LCD. In this project LCD is working in 8-bit mode i. e. , the data transferred to the LCD must be in 8-bit data form. The PortA of ATmega16 is connected to data pins of LCD and is defined as LCD_DATA. PortB is defined as control pins (Rs, R/W and En). 🔗 External reference
The interfacing of an ATmega16 microcontroller with a 16x2 LCD involves several key components and configurations that facilitate the display of characters. The 16x2 LCD consists of two rows, each capable of displaying 16 characters, and operates using a parallel communication protocol.
In this setup, the microcontroller communicates with the LCD in 8-bit mode, which allows for the transmission of data in 8-bit chunks. The data pins of the LCD are connected to Port A of the ATmega16, which is configured as an output port. This configuration enables the microcontroller to send character data directly to the LCD for display. The specific data pins are typically labeled D0 through D7, corresponding to the 8-bit data format.
Control signals are crucial for proper operation, and they are managed through Port B of the ATmega16. The control pins include:
- RS (Register Select): This pin determines whether the data being sent is command or character data. When RS is low, the microcontroller sends a command; when high, it sends data.
- R/W (Read/Write): This pin indicates the direction of data flow. When low, the microcontroller writes data to the LCD; when high, it reads data from the LCD.
- EN (Enable): This pin is used to latch the data into the LCD. A rising edge on this pin signals the LCD to read the data present on the data pins.
The initialization sequence of the LCD is critical for ensuring proper functionality. This typically involves configuring the LCD to operate in 8-bit mode, setting the number of display lines, and enabling the display. After initialization, the microcontroller can send characters to be displayed by writing to the appropriate data and control pins in a timed sequence.
In summary, the interfacing of an ATmega16 microcontroller with a 16x2 LCD in 8-bit mode involves connecting the data pins to Port A and the control pins to Port B, ensuring proper signal management for effective character display. This setup is fundamental in various applications, including embedded systems and user interfaces.LCD comes in various configurations and the most popular one is 16x2 matrix display. This article shows the interfacing of ATmega16 with LCD by displaying a simple character on the LCD. In this project LCD is working in 8-bit mode i. e. , the data transferred to the LCD must be in 8-bit data form. The PortA of ATmega16 is connected to data pins of LCD and is defined as LCD_DATA. PortB is defined as control pins (Rs, R/W and En). 🔗 External reference