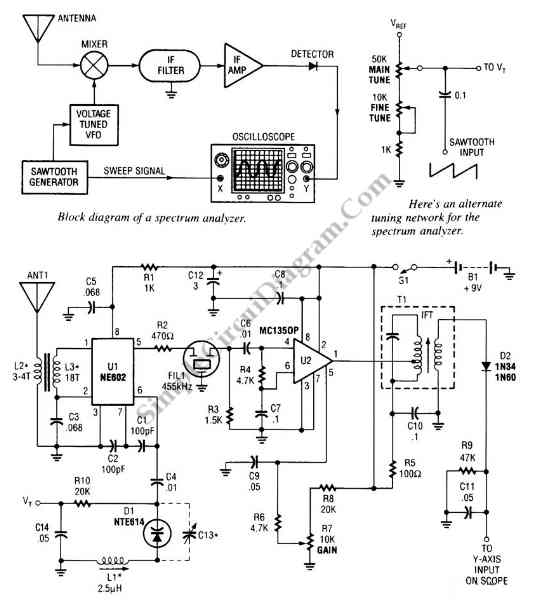
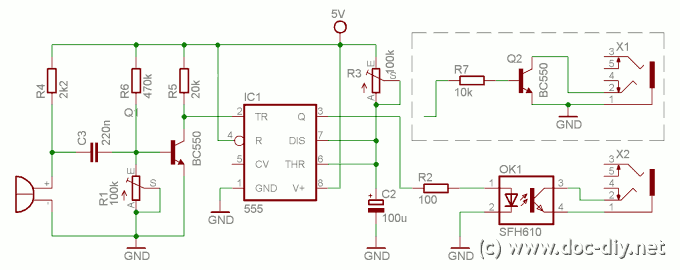
IR illuminator for night-vision tv cameras and scopes
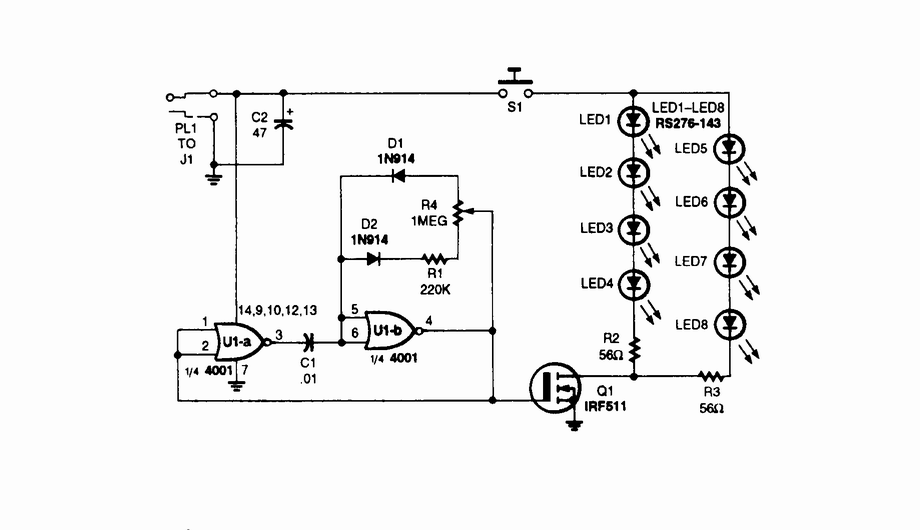
An infrared (IR) illuminator designed for night-vision television cameras and scopes. This device employs light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and an astable oscillator to manage the switch, duty cycle, and overall effective IR illumination output.
The IR illuminator functions by emitting infrared light, which is invisible to the naked eye but can be detected by night-vision devices. The core component of this system is the array of LEDs, which are selected for their efficiency in producing IR light at specific wavelengths that align with the sensitivity range of night-vision equipment.
The astable oscillator is crucial in this circuit as it generates a continuous square wave signal. This signal is used to drive the LEDs, effectively controlling their on and off states. The duty cycle of the oscillator determines the ratio of the time the LEDs are on versus the time they are off within each cycle. By adjusting the duty cycle, the intensity of the IR illumination can be modulated, allowing for optimal performance depending on the ambient light conditions and the specific requirements of the application.
The circuit typically includes a power supply unit that provides the necessary voltage and current to the LEDs and the oscillator. Additional components may include resistors to limit current, capacitors for smoothing the power supply, and possibly a photodiode or phototransistor to provide feedback for automatic brightness adjustment.
In applications where precise control over IR illumination is necessary, the integration of a microcontroller may be considered. This would allow for programmable settings, enabling features such as varying the intensity based on environmental conditions or user preferences.
Overall, the design of the IR illuminator is focused on maximizing the effectiveness of night-vision systems by providing a reliable and adjustable source of infrared light, ensuring enhanced visibility in low-light conditions.IR illuminator for night-vision tv cameras and scopes. This source uses LEDs and an astable oscillator to control the switch, duty-cycle, and effective IR illumination output 🔗 External reference
The IR illuminator functions by emitting infrared light, which is invisible to the naked eye but can be detected by night-vision devices. The core component of this system is the array of LEDs, which are selected for their efficiency in producing IR light at specific wavelengths that align with the sensitivity range of night-vision equipment.
The astable oscillator is crucial in this circuit as it generates a continuous square wave signal. This signal is used to drive the LEDs, effectively controlling their on and off states. The duty cycle of the oscillator determines the ratio of the time the LEDs are on versus the time they are off within each cycle. By adjusting the duty cycle, the intensity of the IR illumination can be modulated, allowing for optimal performance depending on the ambient light conditions and the specific requirements of the application.
The circuit typically includes a power supply unit that provides the necessary voltage and current to the LEDs and the oscillator. Additional components may include resistors to limit current, capacitors for smoothing the power supply, and possibly a photodiode or phototransistor to provide feedback for automatic brightness adjustment.
In applications where precise control over IR illumination is necessary, the integration of a microcontroller may be considered. This would allow for programmable settings, enabling features such as varying the intensity based on environmental conditions or user preferences.
Overall, the design of the IR illuminator is focused on maximizing the effectiveness of night-vision systems by providing a reliable and adjustable source of infrared light, ensuring enhanced visibility in low-light conditions.IR illuminator for night-vision tv cameras and scopes. This source uses LEDs and an astable oscillator to control the switch, duty-cycle, and effective IR illumination output 🔗 External reference