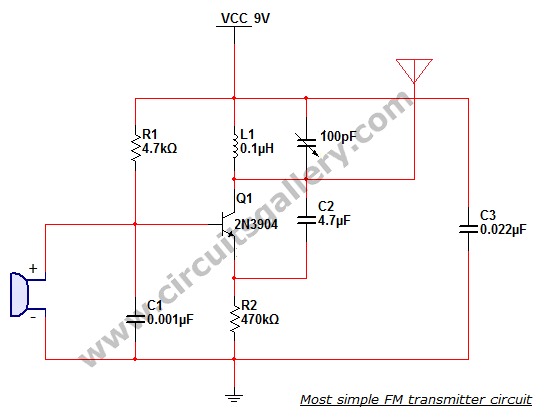
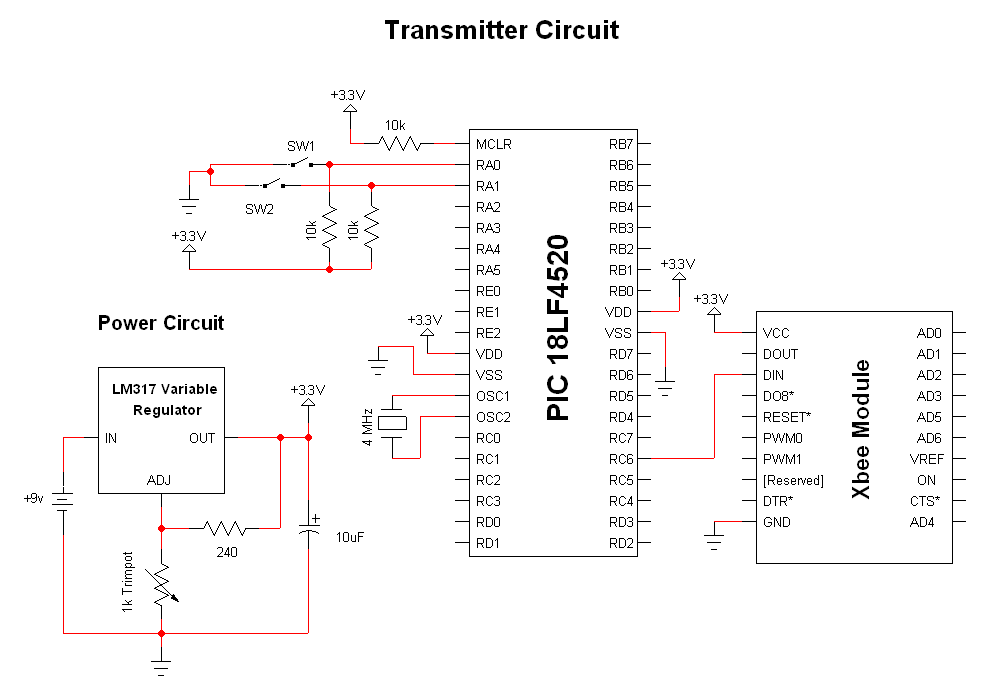
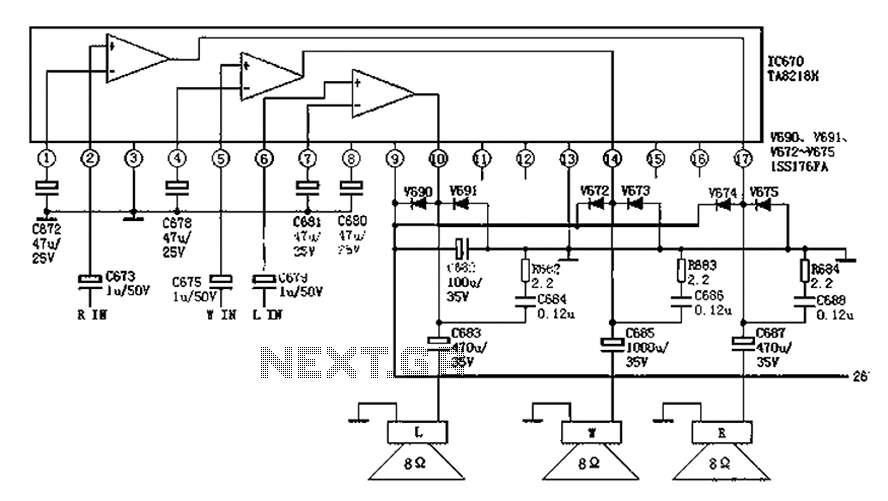
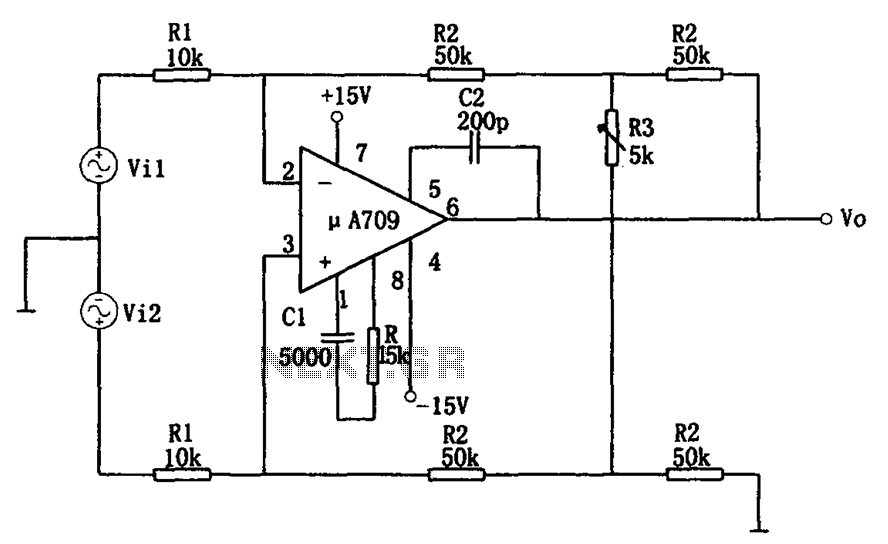
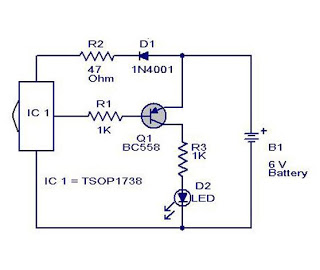
Joule Thief LED circuit 2
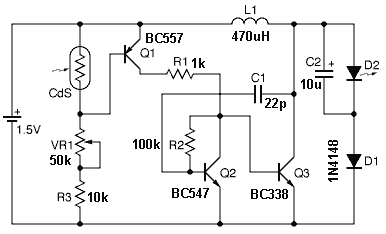
It is essential to draw a circuit using a layout and conventions that are universally recognized.
In electronic circuit design, adherence to standardized symbols and layout conventions is crucial for effective communication among engineers and technicians. A well-drawn schematic diagram serves as a visual representation of the circuit's functionality and interconnections, allowing for easier troubleshooting, collaboration, and documentation.
To create a circuit schematic, it is important to utilize established symbols for components such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits. Each symbol conveys specific information about the component's function, orientation, and electrical characteristics. For instance, a resistor is typically represented by a zigzag line or a rectangular box, while a capacitor is shown as two parallel lines or a pair of curved lines, depending on the type.
The layout of the circuit should follow a logical flow, often from left to right or top to bottom, which helps in understanding the signal path and power distribution. Connections between components should be clearly indicated with lines, and junctions must be marked where multiple lines intersect, usually with a dot to signify a connection or a break to indicate that the lines do not connect.
Labeling components with reference designators (e.g., R1 for the first resistor, C1 for the first capacitor) further enhances clarity. Additionally, including values for each component, such as resistance in ohms or capacitance in farads, aids in the accurate reproduction of the circuit.
In summary, the proper use of universally recognized symbols and conventions in circuit schematics is vital for ensuring that the design can be easily interpreted and implemented by others in the field. This practice not only facilitates the design process but also promotes collaboration and reduces the likelihood of errors in circuit construction and analysis.Thats why you have to draw a circuit using a placement and CONVENTION that everyone recognises. 🔗 External reference
In electronic circuit design, adherence to standardized symbols and layout conventions is crucial for effective communication among engineers and technicians. A well-drawn schematic diagram serves as a visual representation of the circuit's functionality and interconnections, allowing for easier troubleshooting, collaboration, and documentation.
To create a circuit schematic, it is important to utilize established symbols for components such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits. Each symbol conveys specific information about the component's function, orientation, and electrical characteristics. For instance, a resistor is typically represented by a zigzag line or a rectangular box, while a capacitor is shown as two parallel lines or a pair of curved lines, depending on the type.
The layout of the circuit should follow a logical flow, often from left to right or top to bottom, which helps in understanding the signal path and power distribution. Connections between components should be clearly indicated with lines, and junctions must be marked where multiple lines intersect, usually with a dot to signify a connection or a break to indicate that the lines do not connect.
Labeling components with reference designators (e.g., R1 for the first resistor, C1 for the first capacitor) further enhances clarity. Additionally, including values for each component, such as resistance in ohms or capacitance in farads, aids in the accurate reproduction of the circuit.
In summary, the proper use of universally recognized symbols and conventions in circuit schematics is vital for ensuring that the design can be easily interpreted and implemented by others in the field. This practice not only facilitates the design process but also promotes collaboration and reduces the likelihood of errors in circuit construction and analysis.Thats why you have to draw a circuit using a placement and CONVENTION that everyone recognises. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713