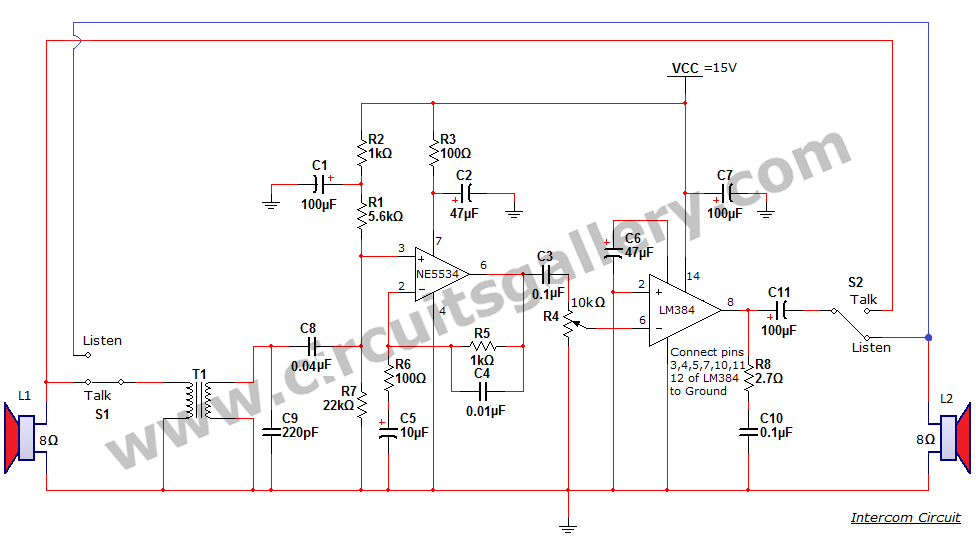
Most simple FM transmitter circuit diagram
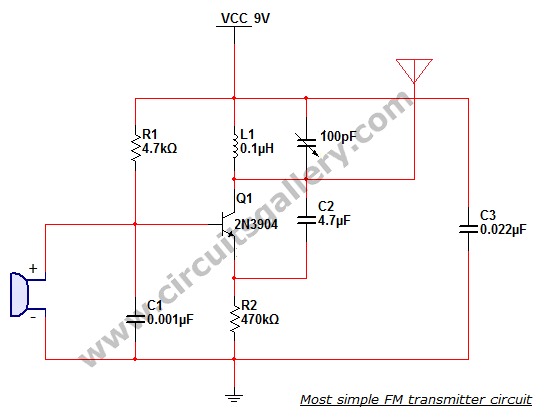
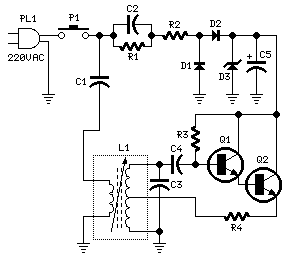
This is the simplest single transistor FM wireless transmitter circuit ever posted in CircuitsGallery. In the field of telecommunications, frequency modulation (FM) transmits information by altering the frequency of a carrier wave based on the message signal. FM utilizes VHF radio frequencies, typically ranging from 87.5 to 108.0 MHz, for transmitting and receiving FM signals. This article will provide explanations about FM transmitters, instructions on how to construct one, and insights into the design and assembly of a simple FM transmitter. The performance and operation of a wireless audio transmitter circuit primarily depend on the specifications of the inductor coil and the value of the variable capacitor. Even minor adjustments to inductance or capacitance can shift the harmonic frequency within the VHF (88-108 MHz) band. This article will guide you on how to build an FM radio transmitter and instill confidence in constructing your own FM transmitter. A condenser microphone is employed to capture sound signals. Within the microphone, a capacitive sensor diaphragm is present, which vibrates in response to changes in air pressure, generating AC signals. The inductor L1 and variable capacitor (trimmer) form an oscillating tank circuit in conjunction with the transistor 2N3904, a common NPN transistor used for general-purpose amplification. As long as current flows through the inductor coil L1 and the variable capacitor, the tank circuit oscillates at the resonant carrier frequency for FM modulation. Capacitor C2 serves as negative feedback to the oscillating tank circuit. Every FM transmitter circuit requires an oscillator component to generate the radio frequency (RF) carrier waves. The term "tank circuit" is derived from the ability of the LC circuit to store energy for oscillations. The modulated signal from the antenna is radiated as radio waves within the FM frequency band. The antenna consists of a simple copper wire, approximately 20 cm in length and 24 gauge in thickness. Factors such as length, inner diameter, and the number of turns are crucial when designing the inductor.
The FM wireless transmitter circuit is a fundamental project for those interested in electronics and telecommunications. It typically incorporates a few essential components: a transistor (2N3904), a condenser microphone, an inductor, a variable capacitor, and a simple copper wire antenna. The circuit operates by converting sound waves into electrical signals using the condenser microphone. The microphone's diaphragm, which reacts to sound pressure variations, produces an alternating current (AC) signal that represents the audio input.
The heart of the FM transmitter is the oscillating tank circuit formed by the inductor L1 and the variable capacitor. This tank circuit is crucial for generating the oscillations required for frequency modulation. The transistor amplifies the signal, allowing it to drive the antenna effectively. The oscillation frequency can be fine-tuned by adjusting the variable capacitor, ensuring that the transmitter operates within the desired VHF band.
The antenna, a straightforward copper wire, acts as a radiating element for the modulated signal. Its dimensions and design influence the efficiency and range of the transmission. Consequently, careful consideration of the inductor's specifications and the antenna's design parameters is essential for optimal performance.
In summary, the described FM wireless transmitter circuit serves as an excellent introduction to frequency modulation technology, offering practical insights into circuit design and assembly. It highlights the importance of component selection and configuration in achieving successful wireless transmission of audio signals.This is the most simplest and single transistor FM wireless transmitter circuit that ever posted in CircuitsGallery. In telecommunication field, frequency modulation (FM) transmits information by changing the frequency of a carrier wave according to message signal.
FM uses VHF radio frequencies usually 87. 5 108. 0 MHz to transmit and receive t he FM signals. Here I will give you theexplanations about FM transmitter, how to make a FM transmitter andhow a simple FM transmitter is designed and assembled etc. The performance and working of a wireless audio transmitter circuit mainly depends on inductor coil specification and the value of variable capacitor.
Even a slight change of inductance or capacitor can shift the harmonic frequency from the VHF (88-108 MHz) band. This article will enable you to answer how to build an FM radio transmitter . Also you will get the confidence tobuild your own FM transmitter. A condenser microphone is used to accept the sound signals. Inside the mic, a capacitive sensor diaphragm is present. It vibrates according to the air pressure changes and generates AC signals. The inductor L1 and variable capacitor (trimmer) forms an oscillating tank circuit along with the transistor 2N3904.
It is the common NPN transistor used for general purpose amplifications. As long as the current exists across the inductor coil L1 and the variable capacitor, the tank circuit will oscillate at the resonant carrier frequency for FM modulation. Capacitor C2 acts as a negative feedback to the oscillating tank circuit. Every FM transmitter circuit requires an oscillator part to generate the radio Frequency (RF) carrier waves.
The name Tank` circuit is derived from the capacity of the LC circuit to store energy for oscillations. The modulated signal from the antenna is radiated as radio waves at FM frequency band. Antenna is nothing but a simple copper wire of 20 cm long and 24 gauge. The length, inner diameter, number of turns etc. are the important factors to be considered while inductor designing. You can design inductor using the following formula, 🔗 External reference
The FM wireless transmitter circuit is a fundamental project for those interested in electronics and telecommunications. It typically incorporates a few essential components: a transistor (2N3904), a condenser microphone, an inductor, a variable capacitor, and a simple copper wire antenna. The circuit operates by converting sound waves into electrical signals using the condenser microphone. The microphone's diaphragm, which reacts to sound pressure variations, produces an alternating current (AC) signal that represents the audio input.
The heart of the FM transmitter is the oscillating tank circuit formed by the inductor L1 and the variable capacitor. This tank circuit is crucial for generating the oscillations required for frequency modulation. The transistor amplifies the signal, allowing it to drive the antenna effectively. The oscillation frequency can be fine-tuned by adjusting the variable capacitor, ensuring that the transmitter operates within the desired VHF band.
The antenna, a straightforward copper wire, acts as a radiating element for the modulated signal. Its dimensions and design influence the efficiency and range of the transmission. Consequently, careful consideration of the inductor's specifications and the antenna's design parameters is essential for optimal performance.
In summary, the described FM wireless transmitter circuit serves as an excellent introduction to frequency modulation technology, offering practical insights into circuit design and assembly. It highlights the importance of component selection and configuration in achieving successful wireless transmission of audio signals.This is the most simplest and single transistor FM wireless transmitter circuit that ever posted in CircuitsGallery. In telecommunication field, frequency modulation (FM) transmits information by changing the frequency of a carrier wave according to message signal.
FM uses VHF radio frequencies usually 87. 5 108. 0 MHz to transmit and receive t he FM signals. Here I will give you theexplanations about FM transmitter, how to make a FM transmitter andhow a simple FM transmitter is designed and assembled etc. The performance and working of a wireless audio transmitter circuit mainly depends on inductor coil specification and the value of variable capacitor.
Even a slight change of inductance or capacitor can shift the harmonic frequency from the VHF (88-108 MHz) band. This article will enable you to answer how to build an FM radio transmitter . Also you will get the confidence tobuild your own FM transmitter. A condenser microphone is used to accept the sound signals. Inside the mic, a capacitive sensor diaphragm is present. It vibrates according to the air pressure changes and generates AC signals. The inductor L1 and variable capacitor (trimmer) forms an oscillating tank circuit along with the transistor 2N3904.
It is the common NPN transistor used for general purpose amplifications. As long as the current exists across the inductor coil L1 and the variable capacitor, the tank circuit will oscillate at the resonant carrier frequency for FM modulation. Capacitor C2 acts as a negative feedback to the oscillating tank circuit. Every FM transmitter circuit requires an oscillator part to generate the radio Frequency (RF) carrier waves.
The name Tank` circuit is derived from the capacity of the LC circuit to store energy for oscillations. The modulated signal from the antenna is radiated as radio waves at FM frequency band. Antenna is nothing but a simple copper wire of 20 cm long and 24 gauge. The length, inner diameter, number of turns etc. are the important factors to be considered while inductor designing. You can design inductor using the following formula, 🔗 External reference