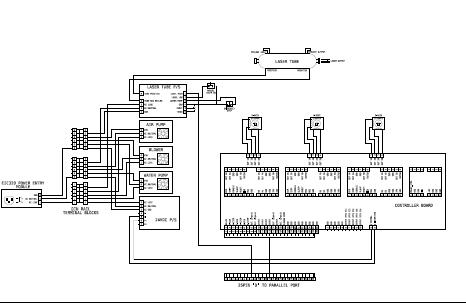
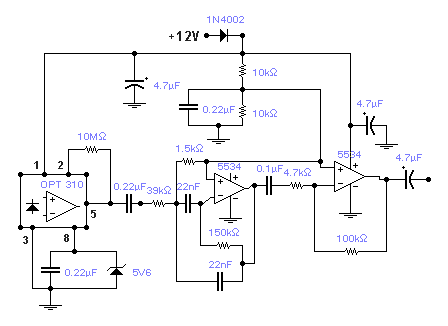
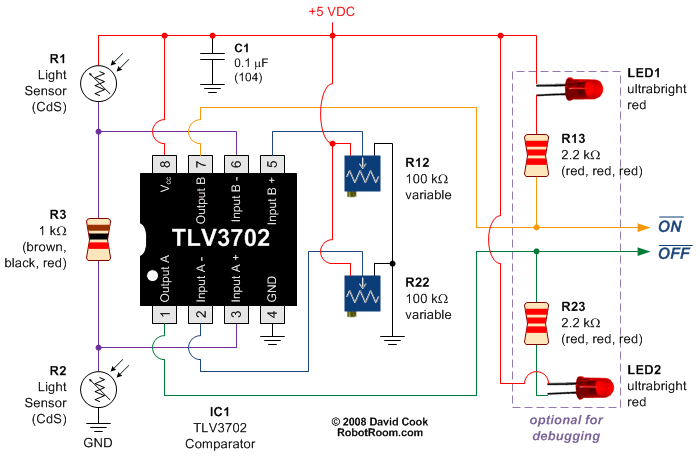
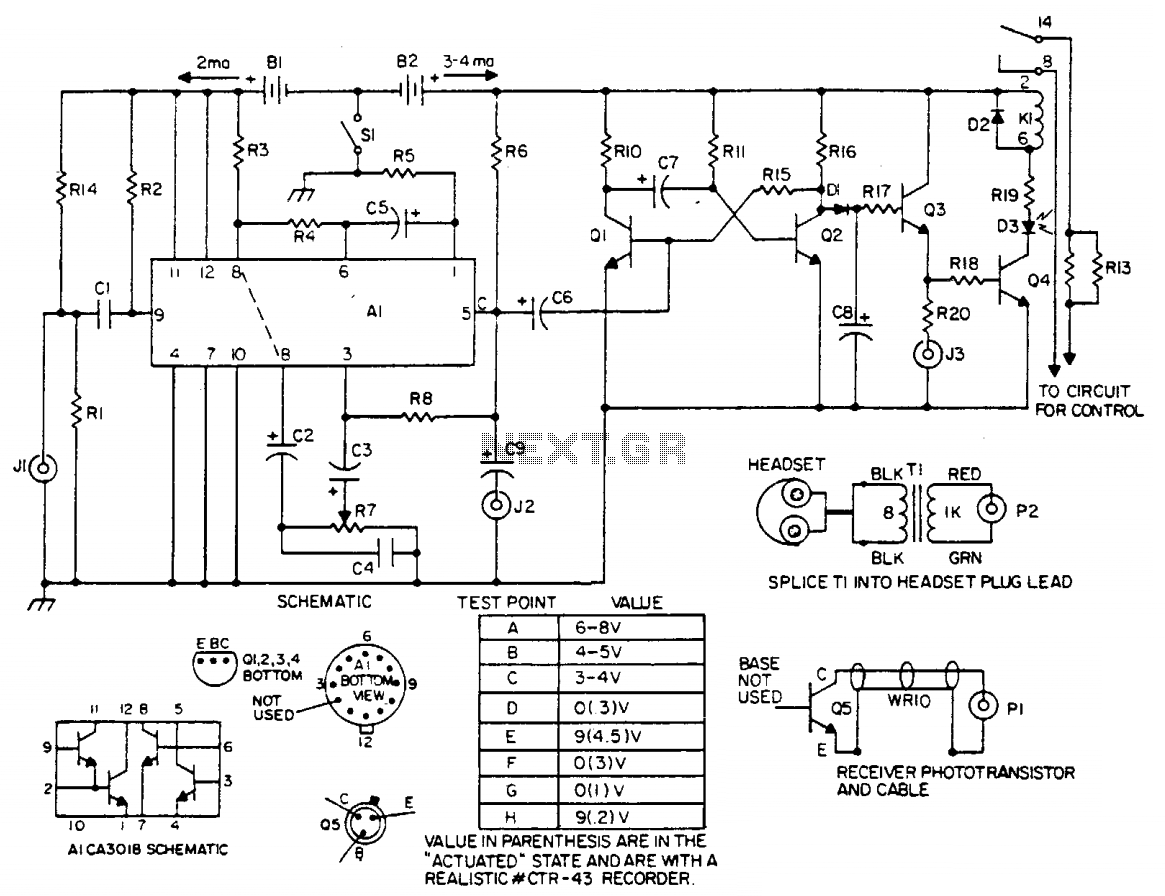
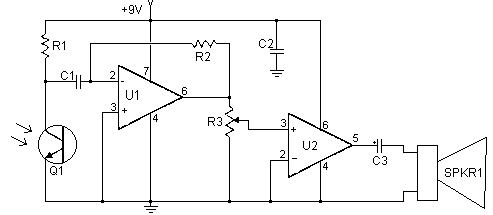
LASER Transmitter/Receiver
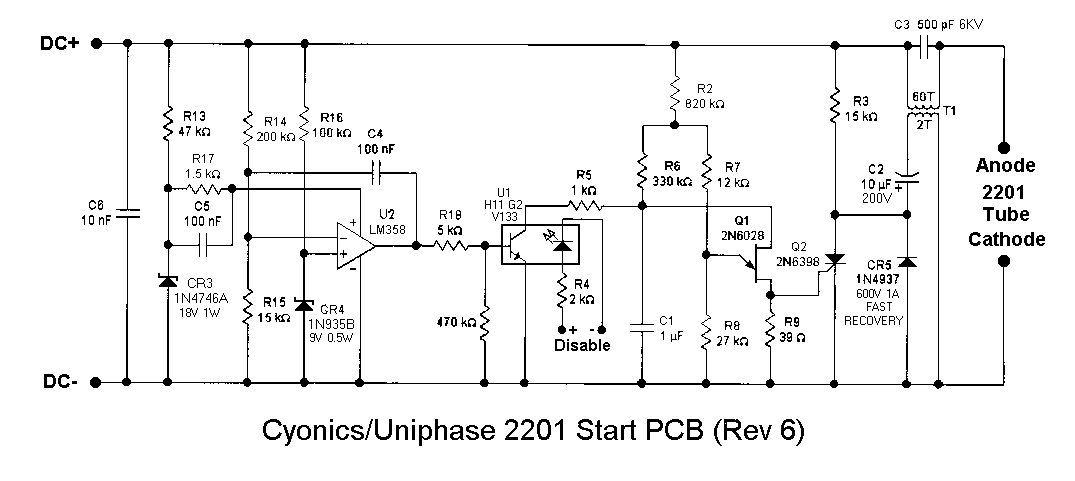
In the transmitter schematic, a ballast resistor is not depicted because most small laser power supplies are typically equipped with an integrated ballast resistor. However, variations in power supply designs may require the addition of an external resistor.
In laser applications, the ballast resistor plays a crucial role in stabilizing the current flowing through the laser diode. It ensures that the diode operates within its specified current range, preventing damage due to excessive current. The absence of a ballast resistor in the schematic indicates that the design assumes the presence of this component within the power supply circuit.
When designing or modifying a transmitter circuit, it is essential to verify the specifications of the power supply being used. If the power supply does not include a built-in ballast resistor, it is necessary to incorporate an external resistor to safeguard the laser diode. The value of the ballast resistor can be calculated based on the desired operating current of the laser diode and the voltage drop across the resistor.
Typically, the resistor value can be determined using Ohm's Law (V = I * R), where V is the voltage drop across the resistor, I is the desired current through the laser diode, and R is the resistance. It is advisable to select a resistor rated for sufficient power to handle the heat generated during operation.
In summary, while the schematic omits the ballast resistor due to the assumption of its presence in the power supply, careful consideration must be given to the specific requirements of the laser diode and the characteristics of the power supply to ensure reliable and safe operation.In the transmitter schematic, no ballast resistor is shown because most small LASER power supplies already have one built in. Yours may differ, and a resistor may be needed. 🔗 External reference
In laser applications, the ballast resistor plays a crucial role in stabilizing the current flowing through the laser diode. It ensures that the diode operates within its specified current range, preventing damage due to excessive current. The absence of a ballast resistor in the schematic indicates that the design assumes the presence of this component within the power supply circuit.
When designing or modifying a transmitter circuit, it is essential to verify the specifications of the power supply being used. If the power supply does not include a built-in ballast resistor, it is necessary to incorporate an external resistor to safeguard the laser diode. The value of the ballast resistor can be calculated based on the desired operating current of the laser diode and the voltage drop across the resistor.
Typically, the resistor value can be determined using Ohm's Law (V = I * R), where V is the voltage drop across the resistor, I is the desired current through the laser diode, and R is the resistance. It is advisable to select a resistor rated for sufficient power to handle the heat generated during operation.
In summary, while the schematic omits the ballast resistor due to the assumption of its presence in the power supply, careful consideration must be given to the specific requirements of the laser diode and the characteristics of the power supply to ensure reliable and safe operation.In the transmitter schematic, no ballast resistor is shown because most small LASER power supplies already have one built in. Yours may differ, and a resistor may be needed. 🔗 External reference