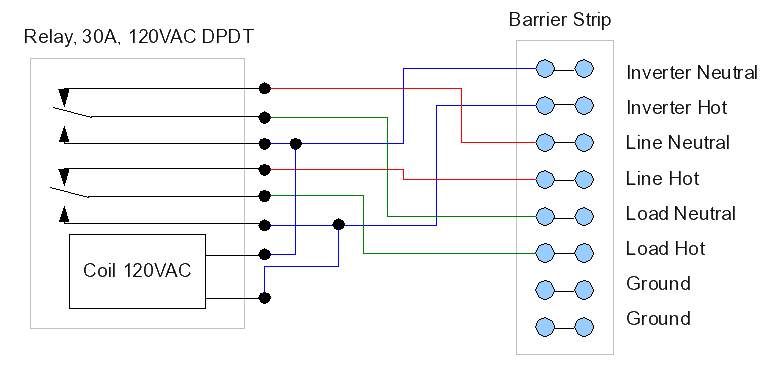
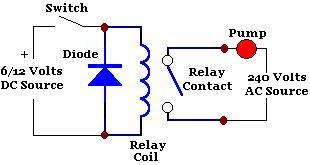
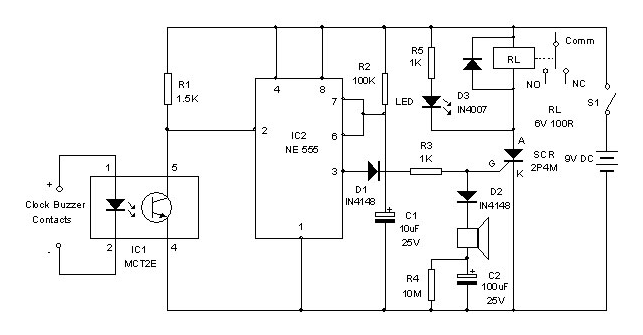
Light control relay control lamp
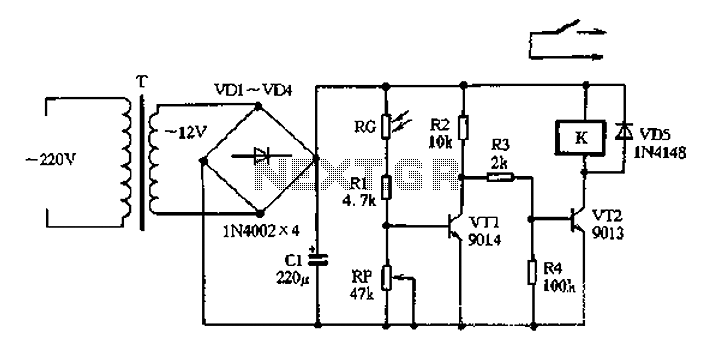
The circuit operates on 220V AC input, which is transformed to approximately 12V DC using a step-down transformer (T), a diode bridge rectifier (VDI-VD4), and a filter capacitor (C1). This setup is designed to power the entire circuit. The light control circuit consists of components including a light-sensitive resistor (RG), a transistor (VT1), and a relay control transistor (VT2). The resistor RG, which is sensitive to light exposure, exhibits low resistance in bright conditions, allowing transistor VT1 to conduct. This results in a low collector output, which keeps the relay control transistor VT2 in an off state, preventing the relay from activating and keeping the normally open contacts disengaged, thus ensuring that the lighting system remains off. In low light conditions, the resistance of RG increases, which reduces the base potential of VT1, causing it to cut off. Consequently, the collector output rises, switching VT2 into its conduction state. This action energizes the relay (K), closing its normally open contacts and activating the lamp. The resistor RP can be adjusted to modify the sensitivity of the light control circuit by changing the resistance, which in turn alters the base potential of transistor VT1.
The circuit design effectively utilizes a step-down transformer to convert high voltage AC to a lower voltage DC, making it suitable for low-voltage applications. The diode bridge rectifier ensures that the current is converted from AC to DC, while the filter capacitor smooths out any fluctuations in the output voltage, providing a stable 12V DC supply.
The light control mechanism is primarily based on the behavior of the light-sensitive resistor RG. Under bright conditions, RG's low resistance allows current to flow through VT1, keeping it in a conductive state. This results in a low voltage at the collector of VT1, which in turn keeps VT2 off. As a result, the relay remains deactivated, and the connected lighting system does not operate, conserving energy during daylight hours.
Conversely, as ambient light diminishes, RG's resistance increases, leading to a drop in the base potential of VT1. This transition causes VT1 to turn off, allowing the collector voltage to rise. Consequently, VT2 is activated, energizing the relay and closing the contacts, which powers the lamp.
The adjustability provided by resistor RP allows for fine-tuning of the circuit's sensitivity to light levels. By modifying the resistance value of RP, the threshold at which the circuit transitions from off to on can be altered, enabling the system to adapt to varying ambient light conditions.
This light control circuit is particularly useful in applications where automatic lighting control is desired, such as in outdoor lighting systems, garden lights, or security lighting, where the lights should only activate in response to low light levels. The simplicity and effectiveness of the design make it a practical solution for energy-efficient lighting control.220V AC by the step-down transformer T, a diode VDI-VD4 bridge rectifier and filter capacitor CI, output of about 12V DC voltage for the entire circuit use. Light control circu it consists of VTI, RG, Rl and the like RP components constitute the daytime sensitive electrical resistor RG affected by light exposure exhibits low resistance, the transistor VT conduction, the collector output low, the relay control transistor VT2 in the off state, relays loss of power does not act, the normally open contacts open, which controls the lighting does not work. Late Rooms, photoresistor RG light exposure and showed a high resistance, VT1 base potential to reduce the cut-off, the collector output high power level, VT2 off on the original state into the conduction state, the relay K is energized its normally open contact closure, can be switched according to the power supply so that the lamp lighting lights up.
RP s resistance to change can change the size of the transistor VT1 base potential, it can be used to adjust the sensitivity of the light control circuit.
The circuit design effectively utilizes a step-down transformer to convert high voltage AC to a lower voltage DC, making it suitable for low-voltage applications. The diode bridge rectifier ensures that the current is converted from AC to DC, while the filter capacitor smooths out any fluctuations in the output voltage, providing a stable 12V DC supply.
The light control mechanism is primarily based on the behavior of the light-sensitive resistor RG. Under bright conditions, RG's low resistance allows current to flow through VT1, keeping it in a conductive state. This results in a low voltage at the collector of VT1, which in turn keeps VT2 off. As a result, the relay remains deactivated, and the connected lighting system does not operate, conserving energy during daylight hours.
Conversely, as ambient light diminishes, RG's resistance increases, leading to a drop in the base potential of VT1. This transition causes VT1 to turn off, allowing the collector voltage to rise. Consequently, VT2 is activated, energizing the relay and closing the contacts, which powers the lamp.
The adjustability provided by resistor RP allows for fine-tuning of the circuit's sensitivity to light levels. By modifying the resistance value of RP, the threshold at which the circuit transitions from off to on can be altered, enabling the system to adapt to varying ambient light conditions.
This light control circuit is particularly useful in applications where automatic lighting control is desired, such as in outdoor lighting systems, garden lights, or security lighting, where the lights should only activate in response to low light levels. The simplicity and effectiveness of the design make it a practical solution for energy-efficient lighting control.220V AC by the step-down transformer T, a diode VDI-VD4 bridge rectifier and filter capacitor CI, output of about 12V DC voltage for the entire circuit use. Light control circu it consists of VTI, RG, Rl and the like RP components constitute the daytime sensitive electrical resistor RG affected by light exposure exhibits low resistance, the transistor VT conduction, the collector output low, the relay control transistor VT2 in the off state, relays loss of power does not act, the normally open contacts open, which controls the lighting does not work. Late Rooms, photoresistor RG light exposure and showed a high resistance, VT1 base potential to reduce the cut-off, the collector output high power level, VT2 off on the original state into the conduction state, the relay K is energized its normally open contact closure, can be switched according to the power supply so that the lamp lighting lights up.
RP s resistance to change can change the size of the transistor VT1 base potential, it can be used to adjust the sensitivity of the light control circuit.