Loudspeaker Protection 2
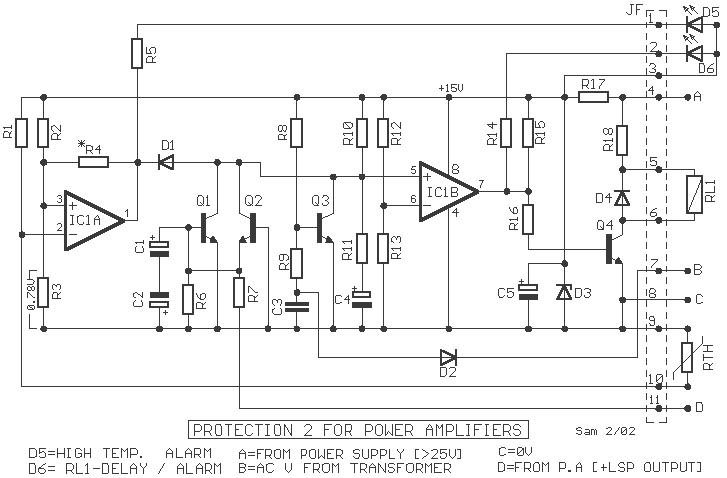
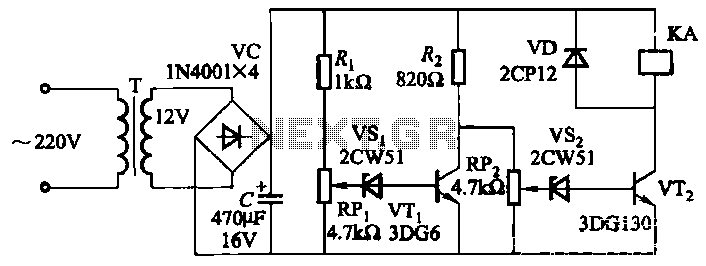
The circuit protection output of power amplifiers and loudspeakers disposes certain interesting elements, such as the isolation of loudspeakers from the exit of the amplifier when continuous voltage is presented at its exit or when the temperature of the heatsink rises excessively, providing a simultaneous time delay in the connection of loudspeakers to the amplifier to avoid passing annoying noises from the charge-discharge of supply capacitors. It is constituted by a binary comparator [IC1], the transistors Q1-2, and indicative LEDs D5-6. The supply of the circuit can come from the positive voltage [Point A] of the main power supply, which is stabilized by D3 and R17, at +15V. Point B is connected to one of the secondary AC coils of the main transformer. If the main switch of the AC line is closed, then an AC voltage (in the secondary coil of the transformer) is presented at Point B, rectified by D2, supplying negative voltage via R9 to Q3, which cuts off and begins to charge C4 via R10-11. As long as the charging of the capacitor lasts, the input [+] of comparator IC2B is at a low level concerning input [-]. The output of IC2B has a low level, therefore Q4 remains in cutoff and RL1 remains deactivated, with D6 being ON. Once C4 is charged, the situation of IC1B changes, activating RL1, connecting the loudspeakers to the amplifier output, and turning D6 OFF. When the supply is interrupted, all the processes are inverted, and the loudspeakers disconnect without passing annoying noises. If during operation the circuit detects continuous voltages at the amplifier's output, RL1 will turn off, protecting the loudspeakers. This is achieved with the help of Q1-2. The acoustic signal from the power amplifier's output is led to point D, where the alternating voltages are directed to ground via C1-2, creating a non-polar capacitor. Continuous voltages greater than +1.7V or less than -4.8V immediately activate Q1 or Q2, respectively. The activation of these transistors lowers the input [+] level of IC1B, causing RL1 to turn off. Another section of protection provided by the circuit is thermal protection, which is facilitated by the temperature sensor RTH, a type of PTC resistor, located above the heatsink where the power transistors are situated. Its resistance increases with temperature until the potential at input [-] of IC1A exceeds the level at input [+], determined by the voltage divider R2-3. When the level at input [-] exceeds the level at input [+], the output of IC1A returns to a low level, compelling IC2B to change state, turning off RL1 and activating D5, indicating thermal protection. The circuit has a thermal protection limit of 70°C. If instability is presented during the operation of RL1, R4 should be replaced with a lower value resistor. The circuit was published in the magazine "Elektor" 12/95.
Part List
R1-2=27 Kohms R13=1.5 Kohms Q1-2-3=BC337
R3=1.4 Kohms R15=4.7 Kohms Q4=BC639
R4=1 Mohms R16=33 Kohms D1=1N4148
R5-14-17=3.3 Kohms R18=1.5 Kohms 5W D2=1N4004
R6-7=100 Kohms RTH=KTY81-122 D3=15V 1.5W Zener
R8=47 Kohms C1-2=100uF 63V D4=1N4002
R9-11=120 Kohms C3=470nF 100V MKT D5-6=LED
R10=470 Kohms C4-5=47uF 25V RL1=24V Relay
R12=15 Kohms IC1=LM393
This circuit is designed to ensure the protection of loudspeakers connected to a power amplifier by isolating them under specific conditions, such as excessive continuous voltage or overheating. The integration of a binary comparator allows for monitoring and decision-making based on voltage levels, while the use of transistors ensures swift response to protect the loudspeakers. The circuit also incorporates both voltage and thermal protection features, enhancing its reliability in various operational scenarios. The inclusion of time delay mechanisms prevents speaker damage from transient signals, contributing to the overall robustness of the system.The circuit protection output of power amplifiers and loudspeakers, dispose certain interesting elements, as the isolation of loudspeakers from the exit of amplifier, when is presented continuous voltage in his exit or when the temperature of heatsink, goes up excessively, providing simultaneously and time delay in the connection loudspeakers in the amplifier, so that we avoid pass in them, the known annoying noises from the charge - discharge of capacitors of supply. It?s constituted by a binary comparator [ IC1 ], the transistors Q1-2 and indicative LED D5-6. The supply of circuit can become from positive voltage [ Point A ] of mainly power supply, which is stabilised by the D3 and the R17, in + 15V.
Point B is connected in one of the secondary AC coil of main transformer. If close the main switch of main line AC, then a AC voltage (in secondary coil of transformer), is presented in the point B, it?s rectified from the D2 and it supply with negative voltage, via the R9, the Q3, this cut off and it begin charge the C4 via the R10-11. As long as time therefore last the charge of capacitor, the input [+] of comparator IC2B is found in low level concerning input [-].
The exit of IC2B, has low level, therefore the Q4 remain in cutt off and the RL1 remain deactivate, the D6 he is ON. Just the C4 charged, change the situation of IC1B, is activated the RL1, the loudspeaker are connected in the amplifier output, the D6 it OFF.
When it?s interrupted the supply, all the process is inverted, and the loudspeaker disconnect, without pass annoying noises. If as long as it work the circuit, is presented problem of continuous voltages in the exit of amplifier then turn off of RL1 and protected the loudspeakers.
This become with help the Q1-2. The acoustic signal from the exit of power amplifier, is led to point D, the alternate voltages is led to the ground via the C1-2, that create a not polar capacitor. Continuous voltages, bigger than + 1.7V or smaller than ?4.8V, activate immediately the Q1 or the Q2, respectively.
With the activation of transistors goes down the level of input [+] of IC1B, so that turn off and the RL1. A other section of protection that for us provide the circuit is the thermic protection. This become with the help of sensor temperature the RTH, which is a resistor of type PTC (positive factor of temperature), and is found placed above in heatsink, where are found also the power transistors.
Her price increase, with the increase of temperature, until the potential in input [-] of IC1A, goes up above from the level of input [+], which is determined with the voltage divider R2-3. As soon as the level in input [-] exceed the level of input [+], the exit of IC1A, it return in low level, compelling and the IC2B to change situation, turn off the RL1 and to turn on the D5, that show the thermic protection.
In the circuit the limit above which it exist clue of thermic protection they are 70?C. If it?s presented instability, in this stage, in operation of RL1, should be changed the R4, with other of smaller price. The circuit was published in magazine ?Elektor? 12/95. Part List R1-2=27 Kohms R13=1.5 Kohms Q1-2-3=BC337 R3=1.4 Kohms R15=4.7 Kohms Q4=BC639 R4=1 Mohms R16=33 Kohms D1=1N4148 R5-14-17=3.3 Kohms R18=1.5 Kohms 5W D2=1N4004 R6-7=100 Kohms RTH=KTY81-122 D3=15V 1.5W Zener R8=47 Kohms C1-2=100uF 63V D4=1N4002 R9-11=120 Kohms C3=470nF 100V MKT D5-6=LED R10=470 Kohms C4-5=47uF 25V RL1=24V Relay R12=15 Kohms IC1=LM393
🔗 External reference
Part List
R1-2=27 Kohms R13=1.5 Kohms Q1-2-3=BC337
R3=1.4 Kohms R15=4.7 Kohms Q4=BC639
R4=1 Mohms R16=33 Kohms D1=1N4148
R5-14-17=3.3 Kohms R18=1.5 Kohms 5W D2=1N4004
R6-7=100 Kohms RTH=KTY81-122 D3=15V 1.5W Zener
R8=47 Kohms C1-2=100uF 63V D4=1N4002
R9-11=120 Kohms C3=470nF 100V MKT D5-6=LED
R10=470 Kohms C4-5=47uF 25V RL1=24V Relay
R12=15 Kohms IC1=LM393
This circuit is designed to ensure the protection of loudspeakers connected to a power amplifier by isolating them under specific conditions, such as excessive continuous voltage or overheating. The integration of a binary comparator allows for monitoring and decision-making based on voltage levels, while the use of transistors ensures swift response to protect the loudspeakers. The circuit also incorporates both voltage and thermal protection features, enhancing its reliability in various operational scenarios. The inclusion of time delay mechanisms prevents speaker damage from transient signals, contributing to the overall robustness of the system.The circuit protection output of power amplifiers and loudspeakers, dispose certain interesting elements, as the isolation of loudspeakers from the exit of amplifier, when is presented continuous voltage in his exit or when the temperature of heatsink, goes up excessively, providing simultaneously and time delay in the connection loudspeakers in the amplifier, so that we avoid pass in them, the known annoying noises from the charge - discharge of capacitors of supply. It?s constituted by a binary comparator [ IC1 ], the transistors Q1-2 and indicative LED D5-6. The supply of circuit can become from positive voltage [ Point A ] of mainly power supply, which is stabilised by the D3 and the R17, in + 15V.
Point B is connected in one of the secondary AC coil of main transformer. If close the main switch of main line AC, then a AC voltage (in secondary coil of transformer), is presented in the point B, it?s rectified from the D2 and it supply with negative voltage, via the R9, the Q3, this cut off and it begin charge the C4 via the R10-11. As long as time therefore last the charge of capacitor, the input [+] of comparator IC2B is found in low level concerning input [-].
The exit of IC2B, has low level, therefore the Q4 remain in cutt off and the RL1 remain deactivate, the D6 he is ON. Just the C4 charged, change the situation of IC1B, is activated the RL1, the loudspeaker are connected in the amplifier output, the D6 it OFF.
When it?s interrupted the supply, all the process is inverted, and the loudspeaker disconnect, without pass annoying noises. If as long as it work the circuit, is presented problem of continuous voltages in the exit of amplifier then turn off of RL1 and protected the loudspeakers.
This become with help the Q1-2. The acoustic signal from the exit of power amplifier, is led to point D, the alternate voltages is led to the ground via the C1-2, that create a not polar capacitor. Continuous voltages, bigger than + 1.7V or smaller than ?4.8V, activate immediately the Q1 or the Q2, respectively.
With the activation of transistors goes down the level of input [+] of IC1B, so that turn off and the RL1. A other section of protection that for us provide the circuit is the thermic protection. This become with the help of sensor temperature the RTH, which is a resistor of type PTC (positive factor of temperature), and is found placed above in heatsink, where are found also the power transistors.
Her price increase, with the increase of temperature, until the potential in input [-] of IC1A, goes up above from the level of input [+], which is determined with the voltage divider R2-3. As soon as the level in input [-] exceed the level of input [+], the exit of IC1A, it return in low level, compelling and the IC2B to change situation, turn off the RL1 and to turn on the D5, that show the thermic protection.
In the circuit the limit above which it exist clue of thermic protection they are 70?C. If it?s presented instability, in this stage, in operation of RL1, should be changed the R4, with other of smaller price. The circuit was published in magazine ?Elektor? 12/95. Part List R1-2=27 Kohms R13=1.5 Kohms Q1-2-3=BC337 R3=1.4 Kohms R15=4.7 Kohms Q4=BC639 R4=1 Mohms R16=33 Kohms D1=1N4148 R5-14-17=3.3 Kohms R18=1.5 Kohms 5W D2=1N4004 R6-7=100 Kohms RTH=KTY81-122 D3=15V 1.5W Zener R8=47 Kohms C1-2=100uF 63V D4=1N4002 R9-11=120 Kohms C3=470nF 100V MKT D5-6=LED R10=470 Kohms C4-5=47uF 25V RL1=24V Relay R12=15 Kohms IC1=LM393
🔗 External reference