Low-Noise Microphone Amplifier (OP270E)
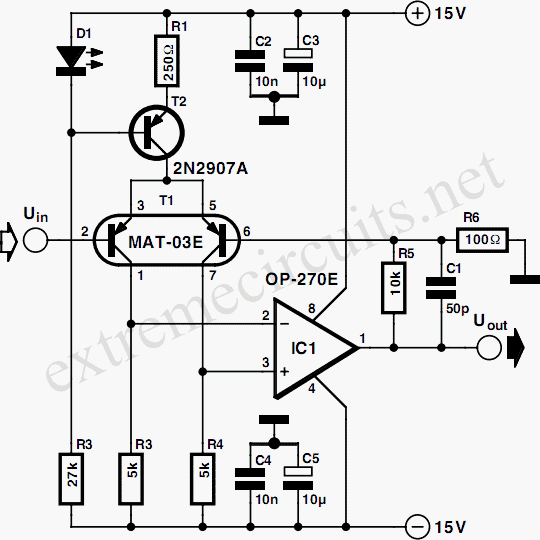
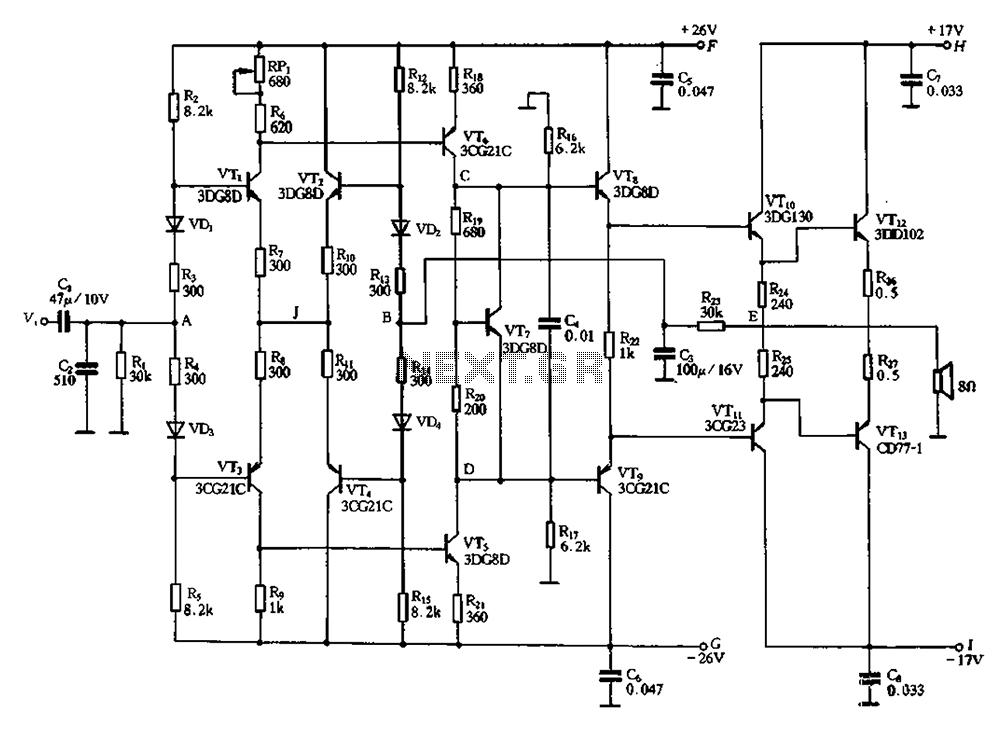
The signal from a microphone is too weak for a standard line input. This low-noise DC-coupled microphone amplifier provides a solution for anyone who wants to connect a microphone to a high-fidelity installation. As illustrated in the schematic diagram, an effective circuit does not need to be overly complex. A differential amplifier is constructed around T1 (T-03E), which is a low-noise dual transistor. The combination of T2 and LED D1 creates a constant-current source for the input stage. A low-noise operational amplifier (OP-270E) amplifies the differential signal that appears at the collectors of the dual transistor. The output is an analog signal at line level. The amplifier's bandwidth extends from 1 Hz to 20 kHz, and within the audio range (20 Hz to 20 kHz), the distortion is less than 0.005 percent. Since only one half of the OP-270E is utilized, the remaining operational amplifier can be employed in the output stage of a stereo configuration. The amplifier can be powered from a stabilized, symmetrical supply with a voltage between ±12 V and ±15 V, which is commonly available in many amplifiers.
The microphone amplifier circuit described utilizes a differential amplifier configuration to effectively boost the weak audio signal from a microphone to a usable line level. The core component, T1 (T-03E), is a low-noise dual transistor that minimizes noise and distortion, critical for maintaining audio fidelity. The circuit employs T2 and LED D1 to establish a constant-current source, ensuring stable operation of the input stage, which is vital for consistent signal amplification.
The operational amplifier used in the circuit, the OP-270E, is known for its low noise characteristics, making it suitable for audio applications. It amplifies the differential signal extracted from the collectors of the dual transistor, producing a clean analog output. The design allows for a broad bandwidth, accommodating frequencies from 1 Hz to 20 kHz, which encompasses the entire audible range. The low distortion rate of less than 0.005 percent within the audio spectrum ensures high-quality sound reproduction.
Moreover, the circuit is designed to utilize only one half of the OP-270E, leaving the other half available for use in a stereo setup, thus enhancing the versatility of the design. The power supply requirements are also practical, as it can operate with a symmetrical supply voltage ranging from ±12 V to ±15 V, a standard specification found in many audio equipment setups. This makes the microphone amplifier suitable for integration into existing audio systems, providing an effective solution for connecting low-output microphones to line-level inputs.The signal from a microphone is two weak for a standard line input. This low-noise DC-coupled microphone amplifier provides a solution for anyone who wants to connect a microphone to his or her hi- installation. As can be seen from the schematic diagram, a good circuit does not have to be complex. A differential amplifier is built around T1 (MA T-03E), which is a low-noise dual transistor. The combination of T2 and LED D1 forms a constant-current source for the input stage. A low-noise opamp (OP-270E) amplifies the difference signal that appears at the collectors of the dual transistor. The result is an analogue signal at line level. The bandwidth of the amplifier ranges from 1 Hz to 20 kHz. Within the audio range (20 Hz to 20 kHz), the distortion is less than 0. 005 percent. Since only half of the OP-270E is used, the remaining opamp could be used in the output stage of a stereo version.
The amplifier can be powered from a stabilized, symmetrical supply with a voltage between ±12 V and ±15 V. Such supply voltages are already present in many amplifier. 🔗 External reference
The microphone amplifier circuit described utilizes a differential amplifier configuration to effectively boost the weak audio signal from a microphone to a usable line level. The core component, T1 (T-03E), is a low-noise dual transistor that minimizes noise and distortion, critical for maintaining audio fidelity. The circuit employs T2 and LED D1 to establish a constant-current source, ensuring stable operation of the input stage, which is vital for consistent signal amplification.
The operational amplifier used in the circuit, the OP-270E, is known for its low noise characteristics, making it suitable for audio applications. It amplifies the differential signal extracted from the collectors of the dual transistor, producing a clean analog output. The design allows for a broad bandwidth, accommodating frequencies from 1 Hz to 20 kHz, which encompasses the entire audible range. The low distortion rate of less than 0.005 percent within the audio spectrum ensures high-quality sound reproduction.
Moreover, the circuit is designed to utilize only one half of the OP-270E, leaving the other half available for use in a stereo setup, thus enhancing the versatility of the design. The power supply requirements are also practical, as it can operate with a symmetrical supply voltage ranging from ±12 V to ±15 V, a standard specification found in many audio equipment setups. This makes the microphone amplifier suitable for integration into existing audio systems, providing an effective solution for connecting low-output microphones to line-level inputs.The signal from a microphone is two weak for a standard line input. This low-noise DC-coupled microphone amplifier provides a solution for anyone who wants to connect a microphone to his or her hi- installation. As can be seen from the schematic diagram, a good circuit does not have to be complex. A differential amplifier is built around T1 (MA T-03E), which is a low-noise dual transistor. The combination of T2 and LED D1 forms a constant-current source for the input stage. A low-noise opamp (OP-270E) amplifies the difference signal that appears at the collectors of the dual transistor. The result is an analogue signal at line level. The bandwidth of the amplifier ranges from 1 Hz to 20 kHz. Within the audio range (20 Hz to 20 kHz), the distortion is less than 0. 005 percent. Since only half of the OP-270E is used, the remaining opamp could be used in the output stage of a stereo version.
The amplifier can be powered from a stabilized, symmetrical supply with a voltage between ±12 V and ±15 V. Such supply voltages are already present in many amplifier. 🔗 External reference