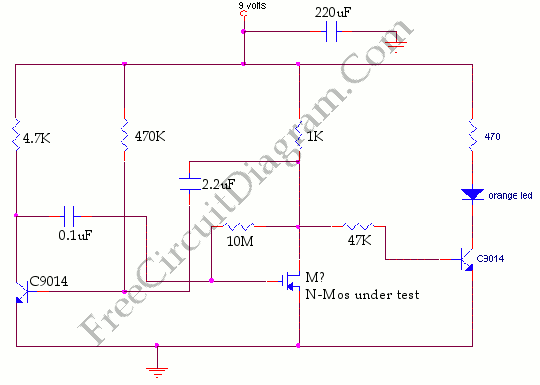
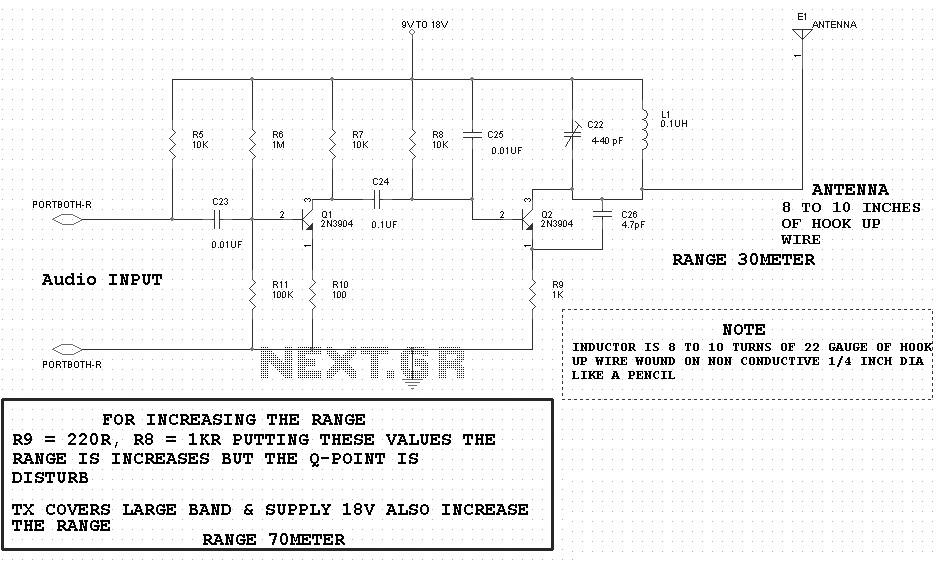
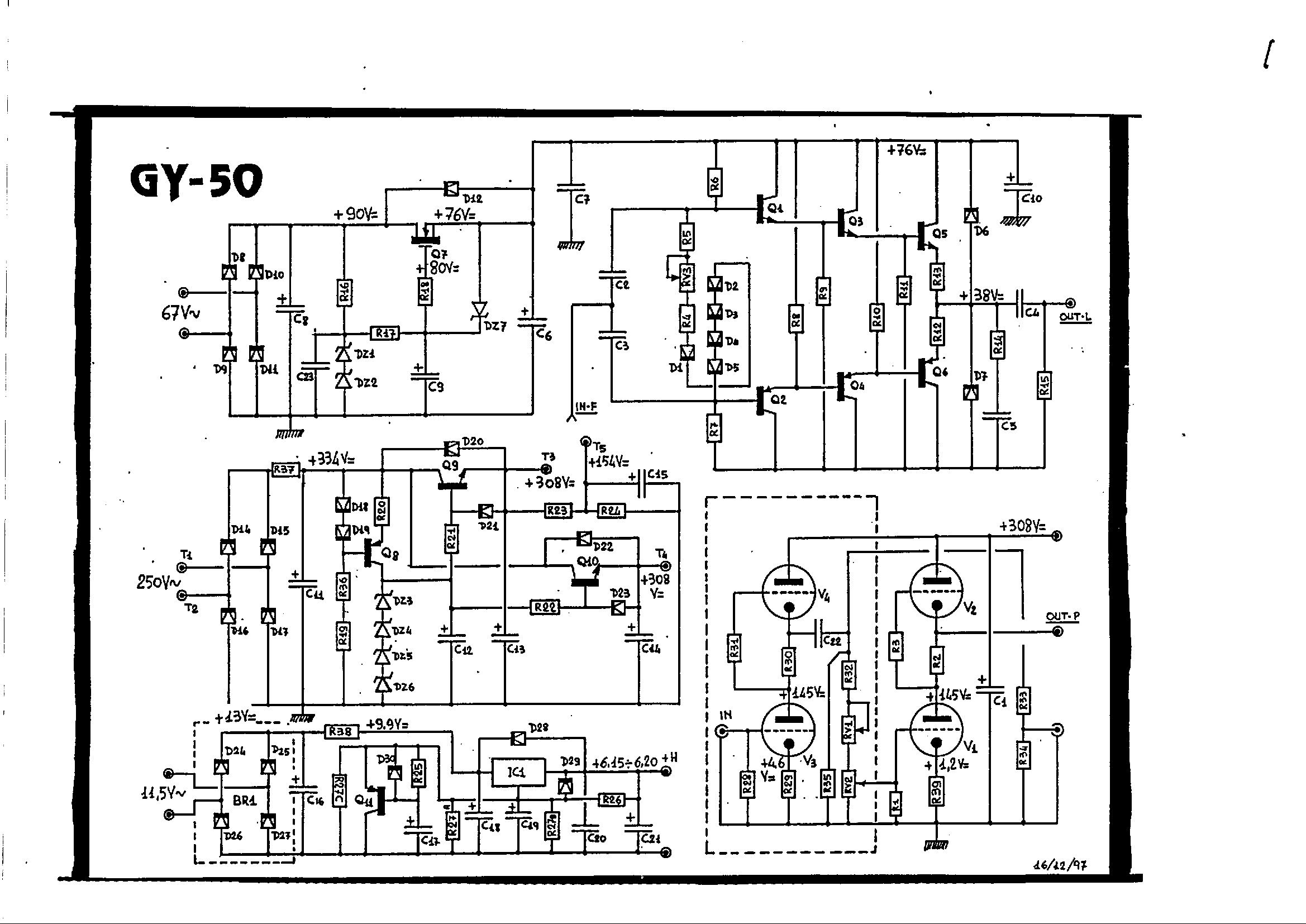
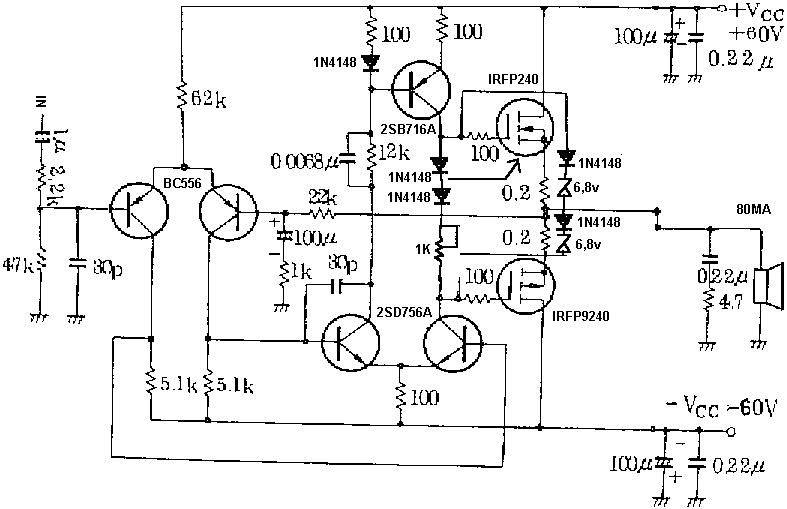
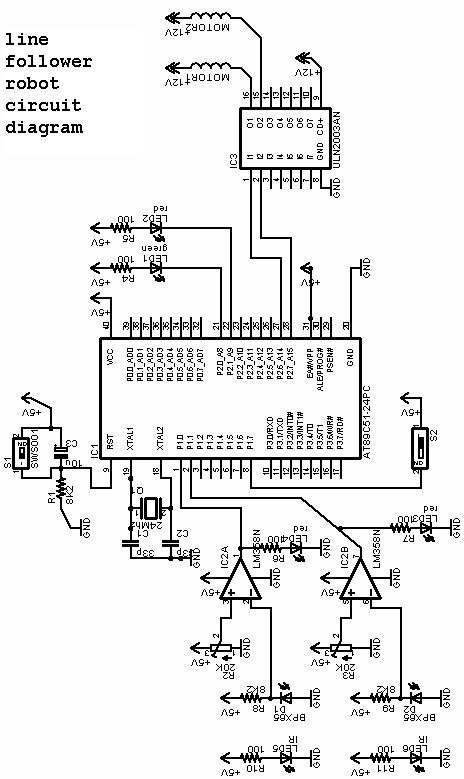
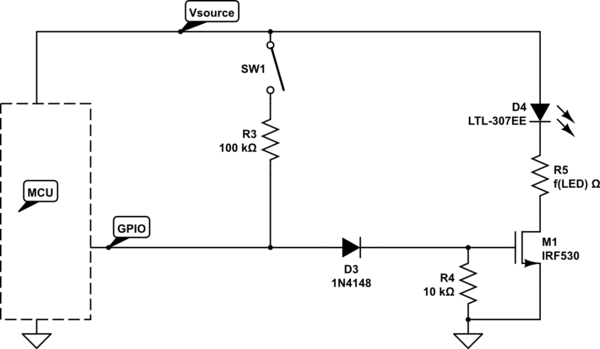
Pavels MOSFET Follower
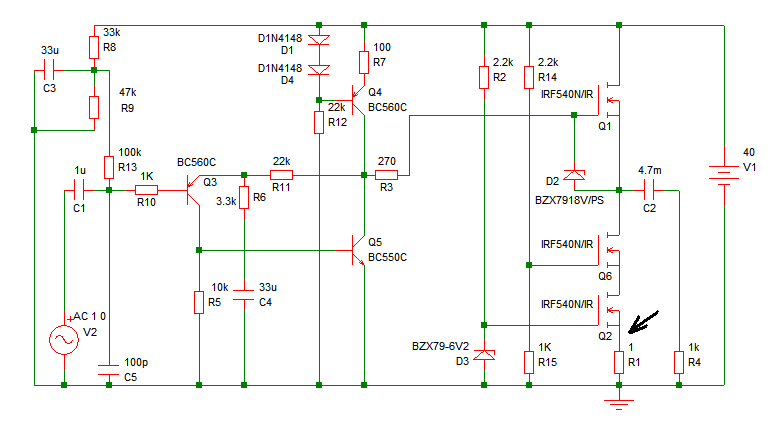
Increasing the quiescent current (Iq) will result in more power output at 4 ohms. It is understood that decreasing the supply voltage affects performance.
Increasing the quiescent current (Iq) in a circuit can lead to enhanced power output, particularly when driving a load of 4 ohms. Quiescent current is the current flowing through a transistor or amplifier when no input signal is present. By increasing Iq, the amplifier operates in a more linear region, which can improve efficiency and reduce distortion, thereby allowing for greater power delivery to the load.
When the supply voltage is decreased, it impacts the maximum output power that can be delivered to the load. The relationship between supply voltage, quiescent current, and load impedance is crucial in amplifier design. A lower supply voltage limits the headroom available for the output signal, which can lead to clipping and reduced dynamic range. Therefore, while increasing Iq can improve performance, it is essential to balance this with the supply voltage to ensure optimal operation.
In practical applications, designers often utilize feedback mechanisms to stabilize the quiescent current and maintain linearity across varying load conditions. This can involve the use of resistors, current mirror circuits, or specialized biasing techniques to achieve the desired Iq without compromising the overall efficiency of the amplifier. Additionally, thermal considerations must be taken into account, as higher quiescent currents can lead to increased heat dissipation, necessitating adequate thermal management solutions.
Overall, the interplay between quiescent current, supply voltage, and load impedance is a fundamental aspect of amplifier design that directly influences performance characteristics such as output power, distortion, and thermal stability.Originally Posted by shaan Increasing Iq will result in more 4ohm power? Ya I think I understand now. Ya, once I decreased the supply voltage and.. 🔗 External reference
Increasing the quiescent current (Iq) in a circuit can lead to enhanced power output, particularly when driving a load of 4 ohms. Quiescent current is the current flowing through a transistor or amplifier when no input signal is present. By increasing Iq, the amplifier operates in a more linear region, which can improve efficiency and reduce distortion, thereby allowing for greater power delivery to the load.
When the supply voltage is decreased, it impacts the maximum output power that can be delivered to the load. The relationship between supply voltage, quiescent current, and load impedance is crucial in amplifier design. A lower supply voltage limits the headroom available for the output signal, which can lead to clipping and reduced dynamic range. Therefore, while increasing Iq can improve performance, it is essential to balance this with the supply voltage to ensure optimal operation.
In practical applications, designers often utilize feedback mechanisms to stabilize the quiescent current and maintain linearity across varying load conditions. This can involve the use of resistors, current mirror circuits, or specialized biasing techniques to achieve the desired Iq without compromising the overall efficiency of the amplifier. Additionally, thermal considerations must be taken into account, as higher quiescent currents can lead to increased heat dissipation, necessitating adequate thermal management solutions.
Overall, the interplay between quiescent current, supply voltage, and load impedance is a fundamental aspect of amplifier design that directly influences performance characteristics such as output power, distortion, and thermal stability.Originally Posted by shaan Increasing Iq will result in more 4ohm power? Ya I think I understand now. Ya, once I decreased the supply voltage and.. 🔗 External reference