Magnetic Levitation Circuit
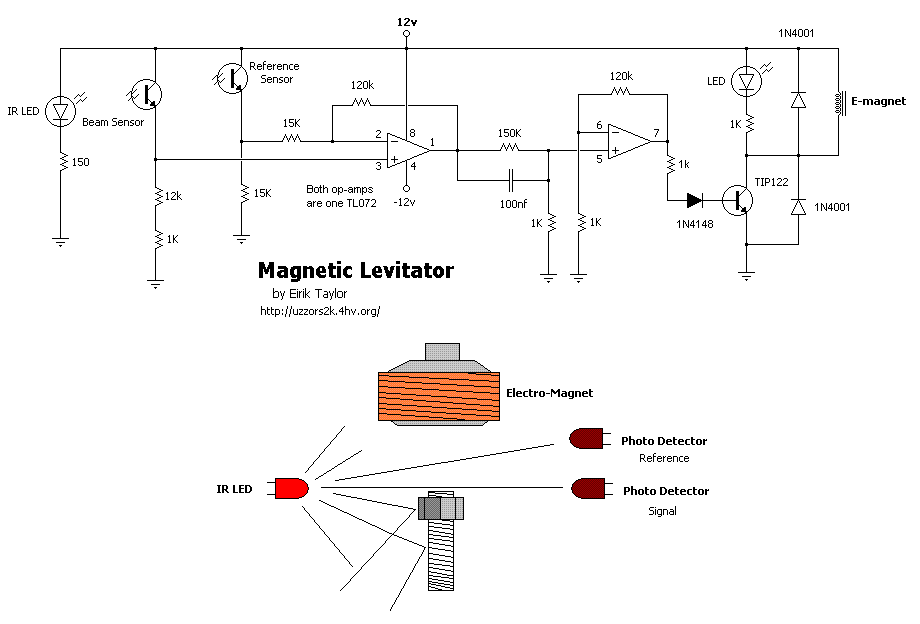
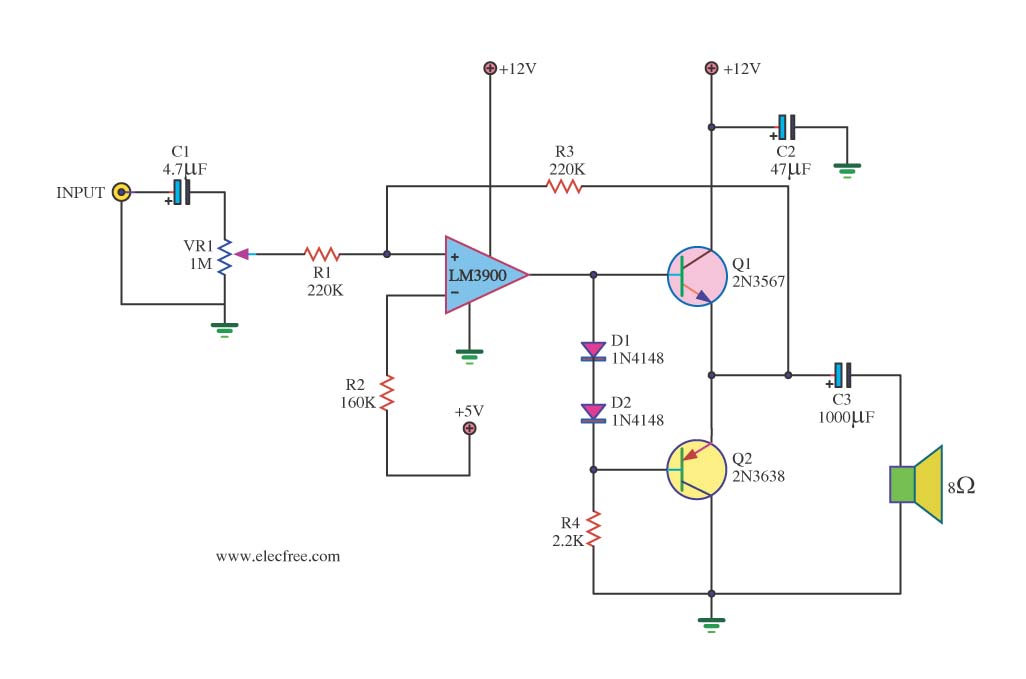
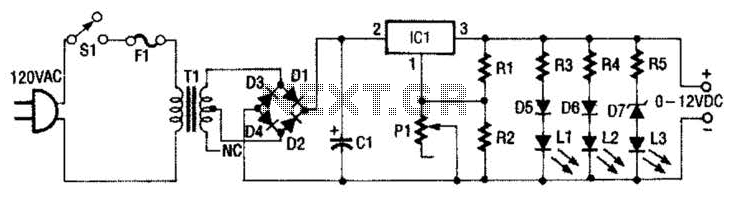
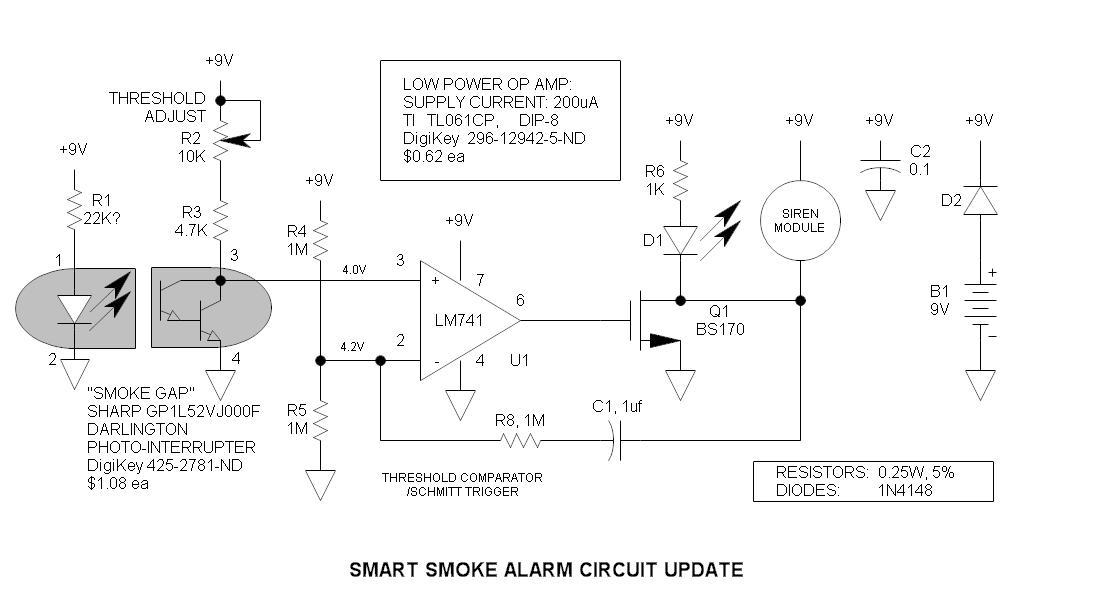
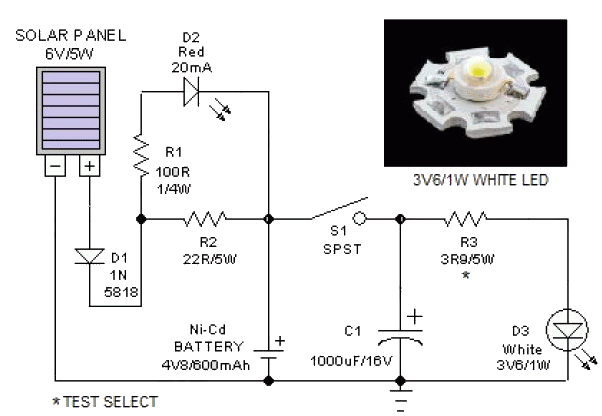
This is a simple magnetic levitation circuit that suspends objects at a specified distance below an electromagnet. The underlying physics involves providing a magnetic force that counteracts gravity.
The magnetic levitation circuit operates by utilizing an electromagnet, which generates a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. The primary components of the circuit include a power supply, an electromagnet, a control system (often incorporating a microcontroller), and a feedback mechanism to maintain stable levitation.
The power supply provides the necessary voltage and current to the electromagnet. The control system regulates the current flowing to the electromagnet based on the position of the levitated object. This regulation is typically achieved through a feedback loop that uses sensors, such as Hall effect sensors or infrared sensors, to detect the distance of the object from the electromagnet.
When the object is positioned below the electromagnet, the control system measures its distance and adjusts the current to the electromagnet accordingly. If the object moves closer, the current is decreased to reduce the magnetic force, allowing the object to drop slightly. Conversely, if the object moves away, the current is increased to strengthen the magnetic field and pull the object back up. This dynamic adjustment creates a stable levitation effect, allowing the object to hover at the desired height.
The circuit may also include additional components such as capacitors for smoothing voltage fluctuations, resistors for current limiting, and diodes for protection against back EMF generated by the electromagnet when the current is switched off. Overall, this simple magnetic levitation circuit showcases the principles of electromagnetism and control systems in a practical application, demonstrating the ability to manipulate forces to achieve stable levitation.This is a simple magnetic levitation circuit which suspends objects a set distance below an electromagnet. The physics behind it is to simply provide a mag.. 🔗 External reference
The magnetic levitation circuit operates by utilizing an electromagnet, which generates a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. The primary components of the circuit include a power supply, an electromagnet, a control system (often incorporating a microcontroller), and a feedback mechanism to maintain stable levitation.
The power supply provides the necessary voltage and current to the electromagnet. The control system regulates the current flowing to the electromagnet based on the position of the levitated object. This regulation is typically achieved through a feedback loop that uses sensors, such as Hall effect sensors or infrared sensors, to detect the distance of the object from the electromagnet.
When the object is positioned below the electromagnet, the control system measures its distance and adjusts the current to the electromagnet accordingly. If the object moves closer, the current is decreased to reduce the magnetic force, allowing the object to drop slightly. Conversely, if the object moves away, the current is increased to strengthen the magnetic field and pull the object back up. This dynamic adjustment creates a stable levitation effect, allowing the object to hover at the desired height.
The circuit may also include additional components such as capacitors for smoothing voltage fluctuations, resistors for current limiting, and diodes for protection against back EMF generated by the electromagnet when the current is switched off. Overall, this simple magnetic levitation circuit showcases the principles of electromagnetism and control systems in a practical application, demonstrating the ability to manipulate forces to achieve stable levitation.This is a simple magnetic levitation circuit which suspends objects a set distance below an electromagnet. The physics behind it is to simply provide a mag.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713