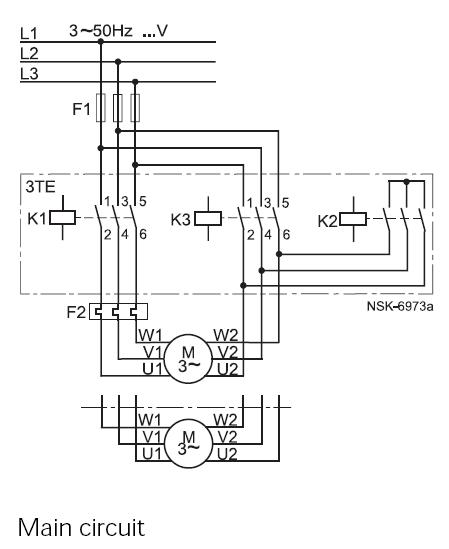
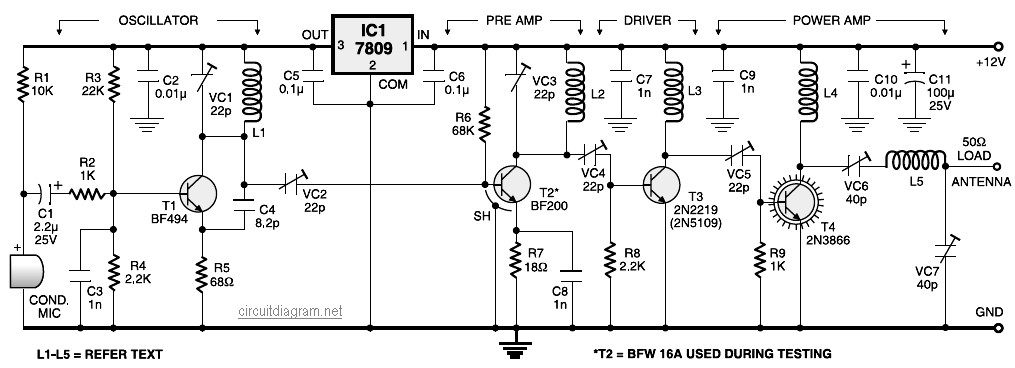
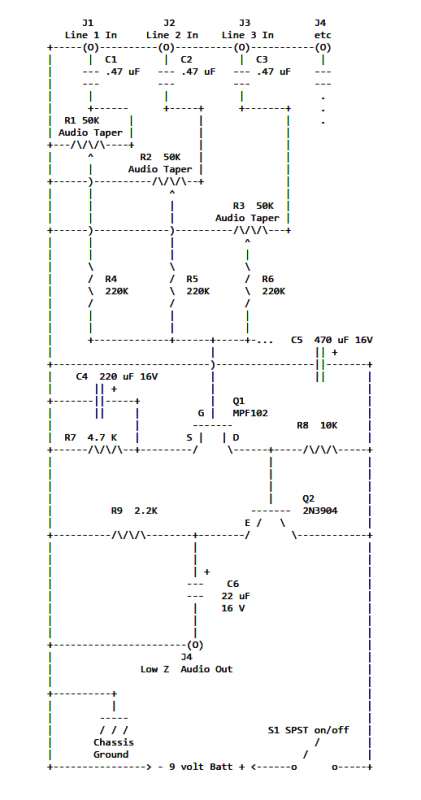
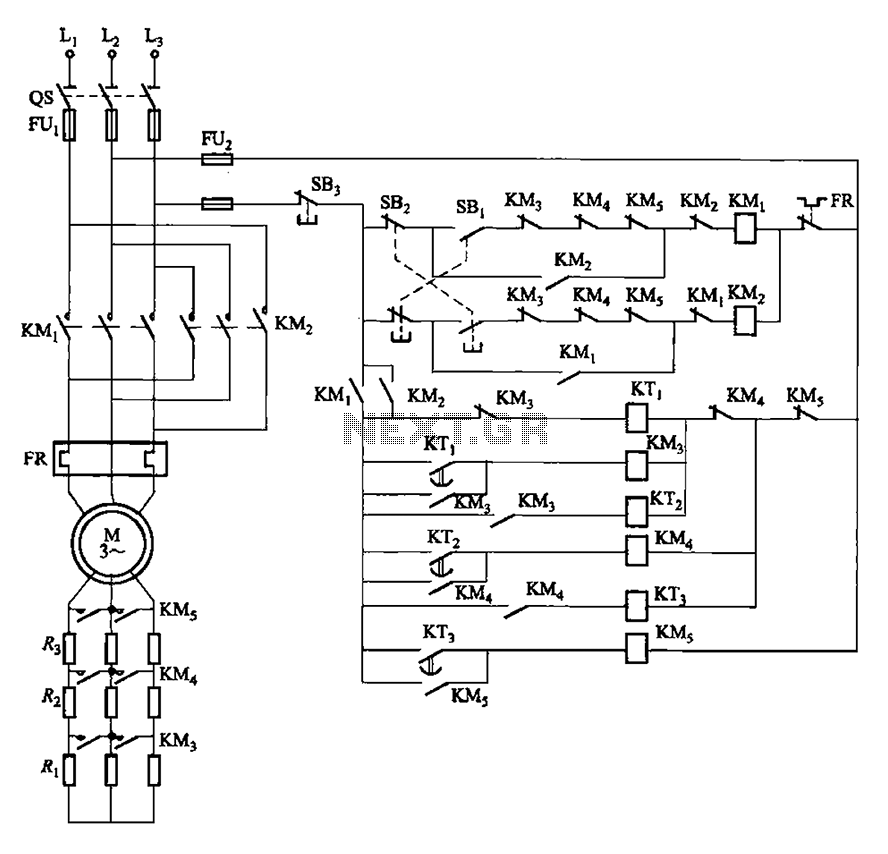
MAX8596Z drive circuit diagram of eight white LED
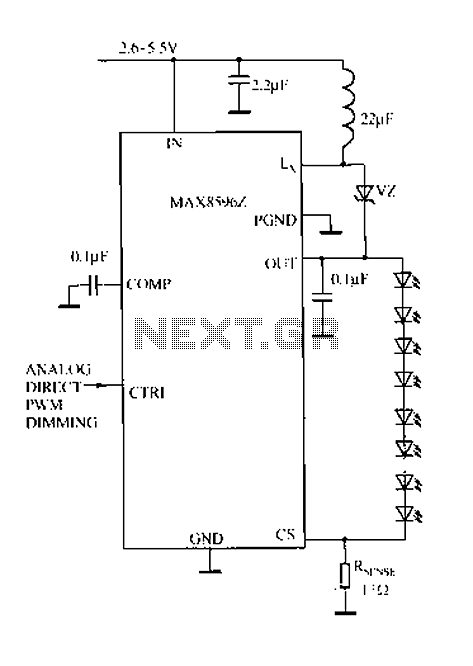
Driving a series of white LEDs allows for a consistent current to flow through each LED, resulting in uniform brightness. However, a disadvantage of this series configuration is that the driving voltage must account for the forward voltage drop of the white LEDs, and the total output voltage must meet the requirements for driving the series of LEDs. This setup necessitates the use of a tandem switch inductive boost converter to achieve high efficiency under high voltage conditions. When selecting this type of converter, it is essential to consider the LX pin's rated output voltage. The accompanying table illustrates various inductive boost switching converters' LX pin rated voltages and the number of series white LEDs they can drive. It is crucial to maintain a maximum voltage that is lower than the maximum rated voltage of the white LEDs in series, allowing for a safety margin for overvoltage protection. The appropriate series LED device drivers must be selected based on this information.
Driving a series of white LEDs requires careful consideration of the electrical parameters to ensure uniform brightness and operational efficiency. Each LED in the series must have the same current flowing through it, which is critical for achieving consistent luminance across the entire array. The forward voltage drop of each LED must be taken into account when calculating the total driving voltage, as the sum of these drops will dictate the minimum output voltage required from the power supply.
To facilitate the necessary voltage boost, a tandem switch inductive boost converter is employed. This type of converter is designed to step up the input voltage to a higher output voltage, which is essential when dealing with multiple LEDs in series. The efficiency of the converter is paramount, especially in high-pressure applications, as it minimizes energy loss and heat generation.
When selecting an inductive boost converter, it is vital to examine the rated output voltage of the LX pin, as this component plays a crucial role in determining the converter's capability to drive a specific number of LEDs. The converter's specifications should align with the voltage requirements of the LED string to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Additionally, the design must consider a safety margin between the maximum rated voltage of the LEDs and the LX pin voltage. This margin is critical to prevent overvoltage conditions that could damage the LEDs. As such, it is advisable to reference the provided table of inductive boost converters to identify suitable devices that can meet the voltage and current requirements of the LED series while ensuring adequate protection against voltage spikes.
In conclusion, the successful implementation of a series white LED driver circuit hinges on the careful selection of components, particularly the tandem switch inductive boost converter, to achieve the desired performance and reliability in LED illumination applications.Driving series white LED, flowing through the same song in each white LED current, it is possible to obtain a uniform brightness. The disadvantage of the tandem drive is the dr ive voltage for the white LED forward voltage drop and the sum of the drive output voltage amplitude should meet after the series LED drive voltage required. This configuration requires tandem switch inductive boost converter in order to obtain high efficiency at high pressure.
When choosing this type of converter must be considered LX pin rated output voltage. The table below shows several inductive boost switching converter Lx pin rated voltage and can drive series white LED number. The need to retain the maximum voltage between the maximum rated voltage of white LED in series with the Lx pin certain safety margin to allow for overvoltage shutdown.
Select the appropriate table series LED device drivers required
Driving a series of white LEDs requires careful consideration of the electrical parameters to ensure uniform brightness and operational efficiency. Each LED in the series must have the same current flowing through it, which is critical for achieving consistent luminance across the entire array. The forward voltage drop of each LED must be taken into account when calculating the total driving voltage, as the sum of these drops will dictate the minimum output voltage required from the power supply.
To facilitate the necessary voltage boost, a tandem switch inductive boost converter is employed. This type of converter is designed to step up the input voltage to a higher output voltage, which is essential when dealing with multiple LEDs in series. The efficiency of the converter is paramount, especially in high-pressure applications, as it minimizes energy loss and heat generation.
When selecting an inductive boost converter, it is vital to examine the rated output voltage of the LX pin, as this component plays a crucial role in determining the converter's capability to drive a specific number of LEDs. The converter's specifications should align with the voltage requirements of the LED string to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Additionally, the design must consider a safety margin between the maximum rated voltage of the LEDs and the LX pin voltage. This margin is critical to prevent overvoltage conditions that could damage the LEDs. As such, it is advisable to reference the provided table of inductive boost converters to identify suitable devices that can meet the voltage and current requirements of the LED series while ensuring adequate protection against voltage spikes.
In conclusion, the successful implementation of a series white LED driver circuit hinges on the careful selection of components, particularly the tandem switch inductive boost converter, to achieve the desired performance and reliability in LED illumination applications.Driving series white LED, flowing through the same song in each white LED current, it is possible to obtain a uniform brightness. The disadvantage of the tandem drive is the dr ive voltage for the white LED forward voltage drop and the sum of the drive output voltage amplitude should meet after the series LED drive voltage required. This configuration requires tandem switch inductive boost converter in order to obtain high efficiency at high pressure.
When choosing this type of converter must be considered LX pin rated output voltage. The table below shows several inductive boost switching converter Lx pin rated voltage and can drive series white LED number. The need to retain the maximum voltage between the maximum rated voltage of white LED in series with the Lx pin certain safety margin to allow for overvoltage shutdown.
Select the appropriate table series LED device drivers required
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713