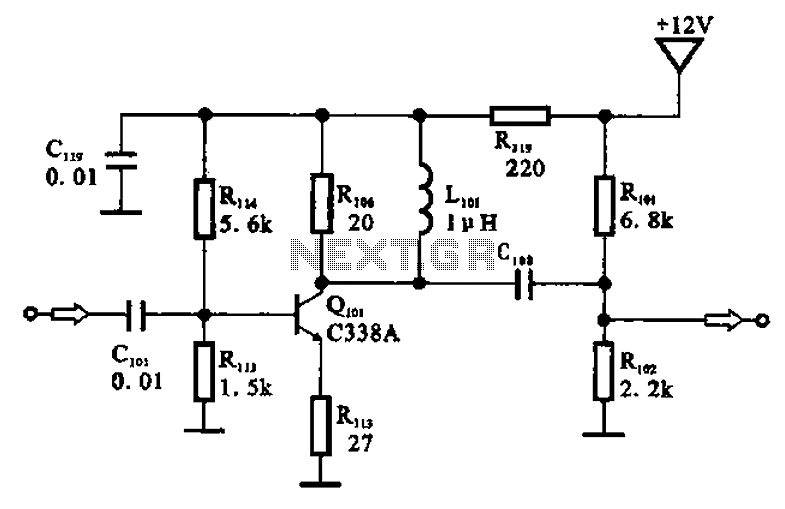
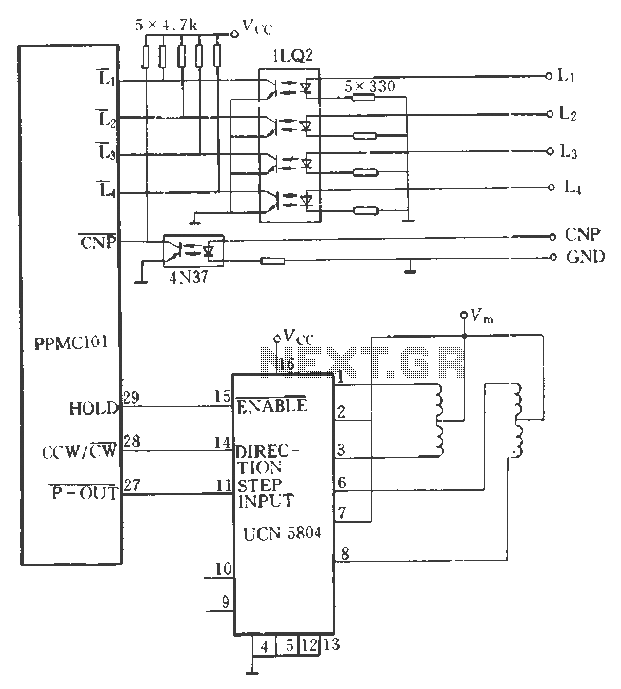
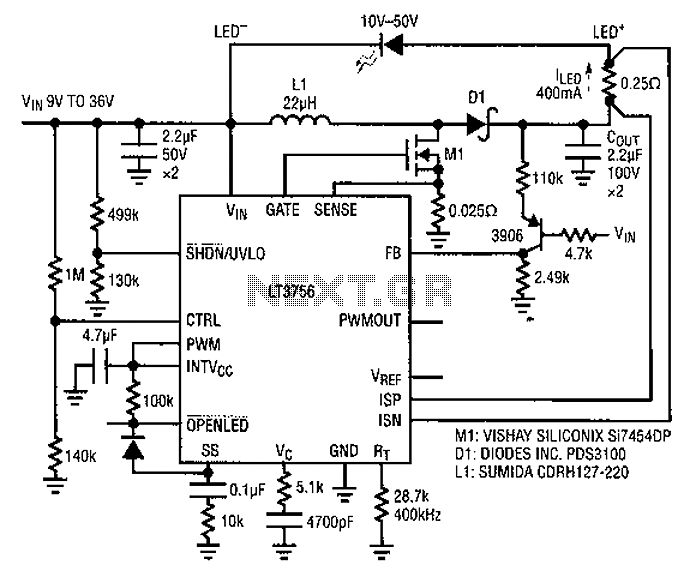
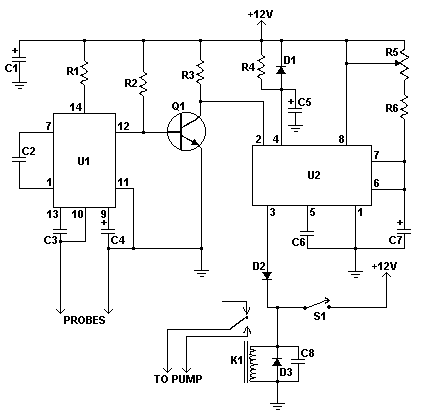
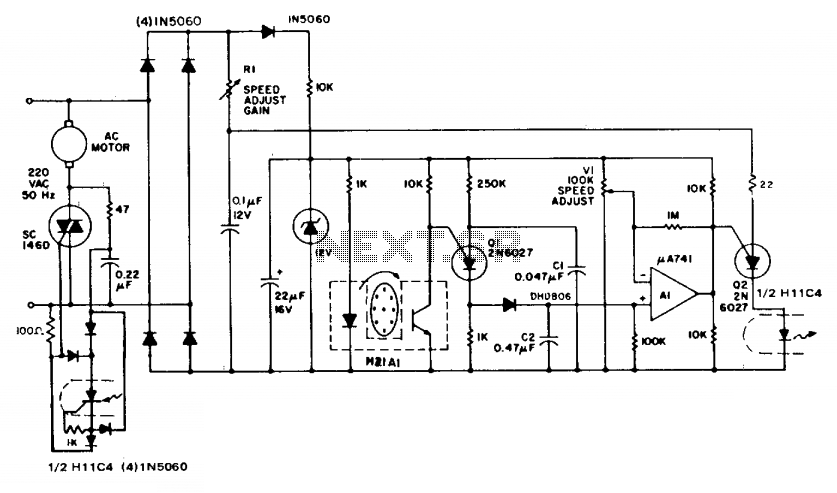
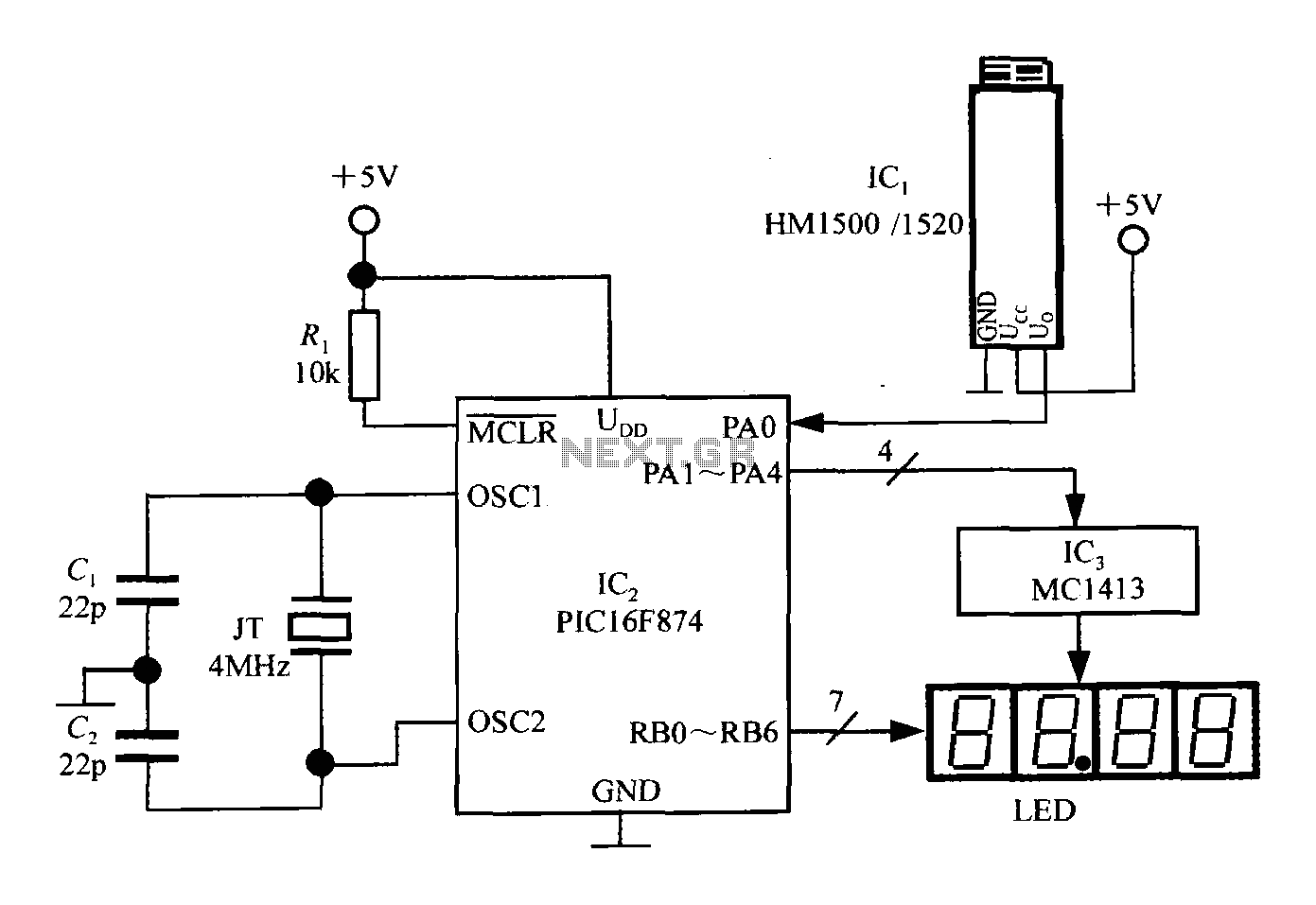
microcontroller 12V relay circuit converted to 5V relay under uC control
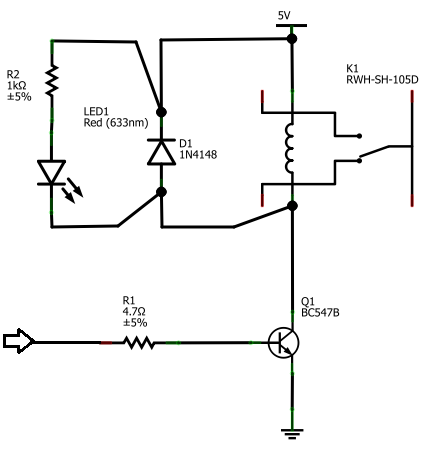
The BC547B transistor has a collector-base voltage (Vcbo) of 50V, a collector-emitter voltage (Vceo) of 45V, and an emitter-base voltage (Vebo) of 6V. In contrast, the BC548 transistor in the original circuit has a Vcbo of 30V, a Vceo of 30V, and a Vebo of 5V, while the remaining parameters are largely similar according to the datasheet, with a current gain (hFE) ranging from 220 to 450. The circuit involves a 1HP water pump operating at 220VAC and consuming 800W. One consideration is to utilize a higher current-rated relay (e.g., 30A). However, there are concerns regarding electromagnetic (EM) feedback, which could lead to arcing and potentially damage the electromagnetic relay. Currently, the circuit is being assembled on a veroboard made of inexpensive phenolic material. While this may suffice for controlling lamps or fans, there is uncertainty about whether a more robust solution is necessary for managing higher loads, such as the water pump. Questions arise regarding the minimum wire gauge required for this application and the types of connectors, such as terminal blocks, that could be employed.
The BC547B and BC548 transistors are both NPN bipolar junction transistors commonly used for switching and amplification applications in electronic circuits. The BC547B is rated for higher voltage levels, making it suitable for applications where higher collector-emitter voltages are present. When designing circuits that involve inductive loads, such as a water pump, it is essential to consider the implications of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and back EMF generated by the inductive load. This feedback can cause voltage spikes that may exceed the breakdown voltages of the transistors and relays, leading to component failure. To mitigate this risk, the use of snubber circuits or flyback diodes is recommended to safely dissipate the energy generated by the inductive load.
For the 1HP water pump, which operates at 220VAC and draws 800W, selecting an appropriate relay is crucial. A relay rated for at least 30A is advisable to ensure it can handle the inrush current when the pump starts. The relay should also have a suitable coil voltage to match the control circuit. Additionally, using a relay with built-in protection against arcing, such as those with zero-crossing detection, can further enhance reliability.
Regarding the assembly on a veroboard, while this may work for low-power applications, for higher loads like the water pump, it is prudent to consider more robust materials. Using a printed circuit board (PCB) designed for higher current applications can provide better durability and reliability. The minimum wire gauge for the pump should be determined based on the current rating; typically, a wire gauge of 14 AWG or thicker would be recommended for 30A applications to minimize voltage drop and heat generation.
For connectors, terminal blocks are an excellent choice as they provide secure connections and facilitate easy disconnection when maintenance is required. It is advisable to select terminal blocks rated for the same or higher current than the relay to ensure safety and reliability in the circuit. Proper insulation and strain relief should also be considered in the design to prevent accidental short circuits or disconnections during operation.The BC547B has Vcbo=50V, Vceo=45V, Vebo=6V, where-as the BC548 in original circuit has Vcbo=30V, Vceo=30V, Vebo=5V, rest of the parameters being pretty same as per datasheet (hFE:220-450). 1HP Water pump (220VAC, 800W) - One thought is to use higher current rated (e. g. 30A) relay. But, I think I need to worry about EM feedback which might cause arcing and destroy the EM relay. Q3) Right now I am making this on a veroboard (el-cheapo phenolic kinds). While I understand that this may be sufficient for the lamp/fan control, I am wondering if I need something better for higher loads, s. a. the Water-pump control What is the minimum gauge wire to be used for this purpose What kind of connectors (terminal blocks) could be used
🔗 External reference
The BC547B and BC548 transistors are both NPN bipolar junction transistors commonly used for switching and amplification applications in electronic circuits. The BC547B is rated for higher voltage levels, making it suitable for applications where higher collector-emitter voltages are present. When designing circuits that involve inductive loads, such as a water pump, it is essential to consider the implications of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and back EMF generated by the inductive load. This feedback can cause voltage spikes that may exceed the breakdown voltages of the transistors and relays, leading to component failure. To mitigate this risk, the use of snubber circuits or flyback diodes is recommended to safely dissipate the energy generated by the inductive load.
For the 1HP water pump, which operates at 220VAC and draws 800W, selecting an appropriate relay is crucial. A relay rated for at least 30A is advisable to ensure it can handle the inrush current when the pump starts. The relay should also have a suitable coil voltage to match the control circuit. Additionally, using a relay with built-in protection against arcing, such as those with zero-crossing detection, can further enhance reliability.
Regarding the assembly on a veroboard, while this may work for low-power applications, for higher loads like the water pump, it is prudent to consider more robust materials. Using a printed circuit board (PCB) designed for higher current applications can provide better durability and reliability. The minimum wire gauge for the pump should be determined based on the current rating; typically, a wire gauge of 14 AWG or thicker would be recommended for 30A applications to minimize voltage drop and heat generation.
For connectors, terminal blocks are an excellent choice as they provide secure connections and facilitate easy disconnection when maintenance is required. It is advisable to select terminal blocks rated for the same or higher current than the relay to ensure safety and reliability in the circuit. Proper insulation and strain relief should also be considered in the design to prevent accidental short circuits or disconnections during operation.The BC547B has Vcbo=50V, Vceo=45V, Vebo=6V, where-as the BC548 in original circuit has Vcbo=30V, Vceo=30V, Vebo=5V, rest of the parameters being pretty same as per datasheet (hFE:220-450). 1HP Water pump (220VAC, 800W) - One thought is to use higher current rated (e. g. 30A) relay. But, I think I need to worry about EM feedback which might cause arcing and destroy the EM relay. Q3) Right now I am making this on a veroboard (el-cheapo phenolic kinds). While I understand that this may be sufficient for the lamp/fan control, I am wondering if I need something better for higher loads, s. a. the Water-pump control What is the minimum gauge wire to be used for this purpose What kind of connectors (terminal blocks) could be used
🔗 External reference