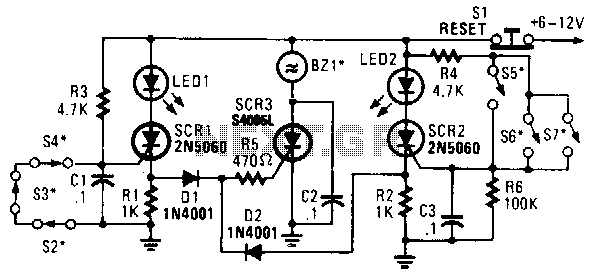
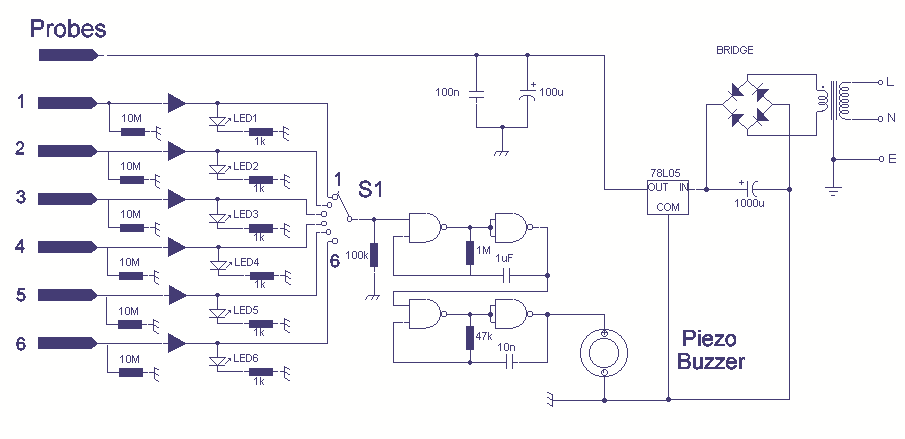
Miniature Loop Alarm
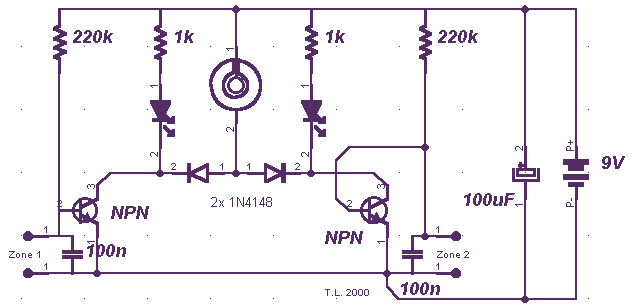
A few months ago, I decided to build a compact, yet effective alarm. My demands were: simple construction, reliable operation, very small power consumption, and, most of all, small size. I started with CMOS logic gates, but was soon forced to abandon the concept after a few unsuccessful (and far too complicated) attempts. Then I suddenly realized that a simple transistor switch might do the job and I was right. As you can clearly see from the schematics, the circuit is utterly primitive and consists of two identical transistor switches. Each has its own alarm LED and they’re coupled to a neat 82dB buzzer. The two 1N4148 diodes are used to prevent a signal from one sensor from triggering both LEDs. The sensors used are either wire loops or normally closed reed switches or even a combination of both. You could, for example, tie a wire loop to your suitcase and place a reed switch to the door of your hotel room.
The described alarm circuit operates on a straightforward principle utilizing two identical NPN transistors configured as switches. Each transistor controls an LED indicator and is connected to a common 82dB buzzer, which serves as the alarm sound output. The circuit is designed to be powered by a low-voltage source, ensuring minimal power consumption, which is crucial for portable applications.
The transistors are activated by sensors that can either be wire loops or normally closed reed switches. In the case of the reed switches, they remain closed during normal conditions and open when the door is opened, triggering the corresponding transistor. The wire loops can be strategically placed around valuable items, and when the loop is broken, it also activates the transistor.
Diodes 1N4148 are employed to isolate the two sensor circuits, ensuring that the activation of one sensor does not inadvertently trigger the other transistor and its associated LED. This feature enhances the reliability of the alarm system, as it prevents false alarms and ensures that the correct indicator is lit when a breach is detected.
The overall design emphasizes simplicity and effectiveness, making it suitable for various applications where security is a concern, such as personal belongings in hotel rooms, or other temporary setups. The compact nature of the circuit allows for easy integration into small enclosures, further enhancing its portability.A few months ago, I decided to build a compact, yet effective alarm. My demands were:- simple construction, reliable operation, very small power consumption, and, most of all, small size. I started with CMOS logic gates, but was soon forced to abandon the concept after a few unsuccessful (and far too complicated) attempts.
Then I suddenly realized that a simple transistor switch might do the job and I was right. As you can clearly see from the schematics, the circuit is utterly primitive and consists of two identical transistor switches. Each has its own alarm LED and they`re coupled to a neat 82dB buzzer. The two 1N4148 diodes are used to prevent a signal from one sensor from triggering both LEDs. The sensors used are either wire loops or normally closed reed switches or even a combination of both. You could, for example, tie a wire loop to your suitcase and place a reed switch to the door of your hotel room.
Since this little alarm is intended 🔗 External reference
The described alarm circuit operates on a straightforward principle utilizing two identical NPN transistors configured as switches. Each transistor controls an LED indicator and is connected to a common 82dB buzzer, which serves as the alarm sound output. The circuit is designed to be powered by a low-voltage source, ensuring minimal power consumption, which is crucial for portable applications.
The transistors are activated by sensors that can either be wire loops or normally closed reed switches. In the case of the reed switches, they remain closed during normal conditions and open when the door is opened, triggering the corresponding transistor. The wire loops can be strategically placed around valuable items, and when the loop is broken, it also activates the transistor.
Diodes 1N4148 are employed to isolate the two sensor circuits, ensuring that the activation of one sensor does not inadvertently trigger the other transistor and its associated LED. This feature enhances the reliability of the alarm system, as it prevents false alarms and ensures that the correct indicator is lit when a breach is detected.
The overall design emphasizes simplicity and effectiveness, making it suitable for various applications where security is a concern, such as personal belongings in hotel rooms, or other temporary setups. The compact nature of the circuit allows for easy integration into small enclosures, further enhancing its portability.A few months ago, I decided to build a compact, yet effective alarm. My demands were:- simple construction, reliable operation, very small power consumption, and, most of all, small size. I started with CMOS logic gates, but was soon forced to abandon the concept after a few unsuccessful (and far too complicated) attempts.
Then I suddenly realized that a simple transistor switch might do the job and I was right. As you can clearly see from the schematics, the circuit is utterly primitive and consists of two identical transistor switches. Each has its own alarm LED and they`re coupled to a neat 82dB buzzer. The two 1N4148 diodes are used to prevent a signal from one sensor from triggering both LEDs. The sensors used are either wire loops or normally closed reed switches or even a combination of both. You could, for example, tie a wire loop to your suitcase and place a reed switch to the door of your hotel room.
Since this little alarm is intended 🔗 External reference