Multiplication detector circuit with MC1496
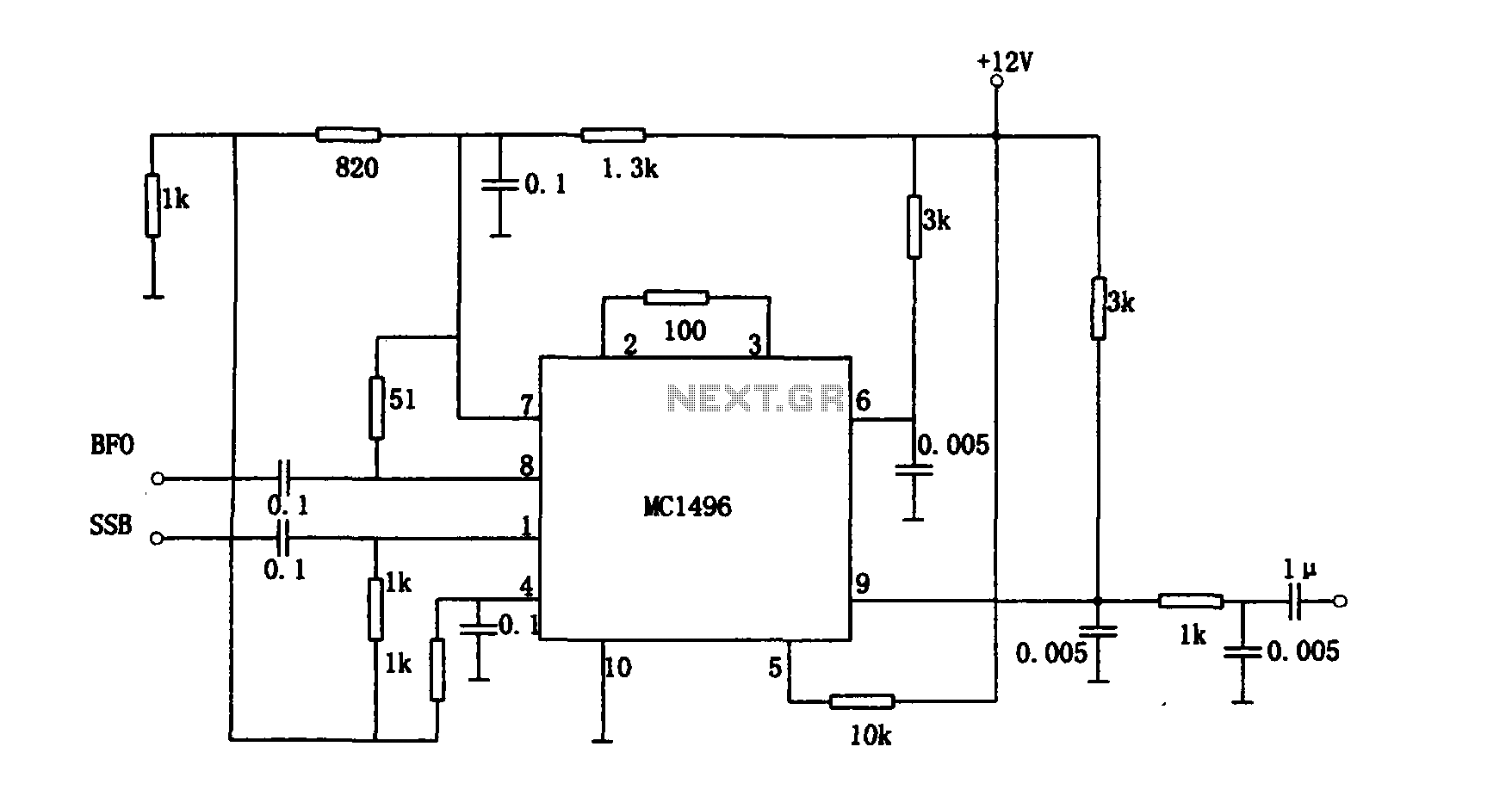
The provided information pertains to a detector circuit designed for multiplication. This circuit functions as a single-sideband amplitude modulation (SSB AM) signal detector, utilizing its principles to demodulate the received single-sideband signal and recover the transmitted signal. It employs carrier multiplying demodulation techniques. The circuit incorporates the MC1496 balanced modulator and demodulator, where the output voltage is derived from the product of the input voltage signal supplied by the carrier and the switching function. The operational parameters include an intermediate frequency sensitivity of 9 MHz and a dynamic range of 90 dB.
The circuit operates by utilizing the MC1496, which is a versatile integrated circuit designed for balanced modulation and demodulation applications. In this configuration, the MC1496 serves as both the modulator and demodulator, effectively handling the SSB signal. The input to the circuit consists of the SSB signal alongside a carrier frequency, which is essential for the demodulation process.
The principle of operation involves the multiplication of the incoming SSB signal with the carrier signal. This multiplication process results in the extraction of the original baseband signal from the modulated carrier. The output voltage is directly proportional to the product of these two signals, which is critical for recovering the transmitted information.
The circuit's intermediate frequency sensitivity of 9 MHz indicates its operational bandwidth, allowing it to process signals within this frequency range effectively. A sensitivity of 3 µV showcases the circuit's ability to detect weak signals, making it suitable for applications where signal strength may be a concern. Additionally, the dynamic range of 90 dB demonstrates the circuit's capability to handle a wide range of signal amplitudes, ensuring reliable performance in various operating conditions.
In summary, this detector circuit is a sophisticated solution for demodulating SSB signals, leveraging the MC1496 to achieve high sensitivity and a broad dynamic range, thereby facilitating effective communication in radio frequency applications.As shown for the detector circuit multiplication. The circuit is a single-sideband amplitude modulation signal detector, its principle is to demodulate the received single sideband (SSB) and the receiver to recover the signal transmission carrier multiplying demodulation completion work. FIG manifold MC1496 balanced modulator and demodulator, the output voltage of the circuit is the product of the input voltage signal provided by the carrier and switch function. The circuit operates at an intermediate frequency sensitivity 9MHz 3 mu V, a dynamic range of 90dB.
The circuit operates by utilizing the MC1496, which is a versatile integrated circuit designed for balanced modulation and demodulation applications. In this configuration, the MC1496 serves as both the modulator and demodulator, effectively handling the SSB signal. The input to the circuit consists of the SSB signal alongside a carrier frequency, which is essential for the demodulation process.
The principle of operation involves the multiplication of the incoming SSB signal with the carrier signal. This multiplication process results in the extraction of the original baseband signal from the modulated carrier. The output voltage is directly proportional to the product of these two signals, which is critical for recovering the transmitted information.
The circuit's intermediate frequency sensitivity of 9 MHz indicates its operational bandwidth, allowing it to process signals within this frequency range effectively. A sensitivity of 3 µV showcases the circuit's ability to detect weak signals, making it suitable for applications where signal strength may be a concern. Additionally, the dynamic range of 90 dB demonstrates the circuit's capability to handle a wide range of signal amplitudes, ensuring reliable performance in various operating conditions.
In summary, this detector circuit is a sophisticated solution for demodulating SSB signals, leveraging the MC1496 to achieve high sensitivity and a broad dynamic range, thereby facilitating effective communication in radio frequency applications.As shown for the detector circuit multiplication. The circuit is a single-sideband amplitude modulation signal detector, its principle is to demodulate the received single sideband (SSB) and the receiver to recover the signal transmission carrier multiplying demodulation completion work. FIG manifold MC1496 balanced modulator and demodulator, the output voltage of the circuit is the product of the input voltage signal provided by the carrier and switch function. The circuit operates at an intermediate frequency sensitivity 9MHz 3 mu V, a dynamic range of 90dB.