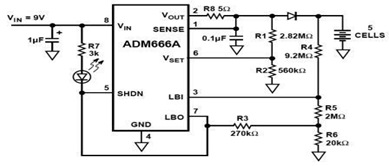
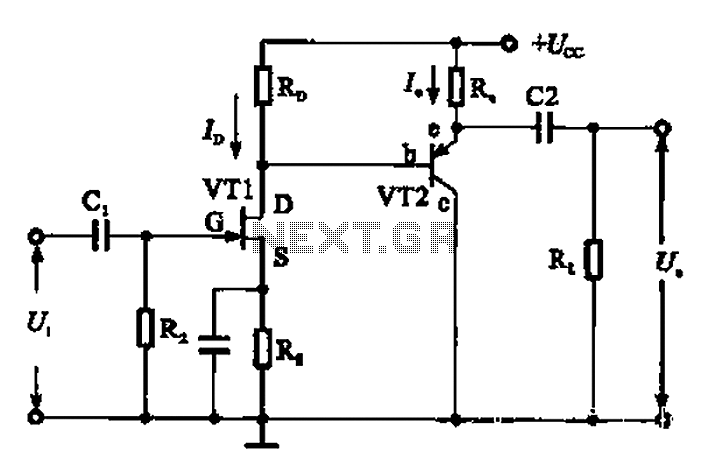
NCP571 low power regulator

In certain electronic projects, there may be a need for an uncommon regulated voltage, particularly when the required voltage is very low. In such cases, conventional methods like using Zener diodes may not be feasible due to space constraints. A suitable solution is to employ a voltage regulator circuit based on the NCP571 or NCV571, which are low current voltage regulators available in various standard output voltage versions (0.8 V, 0.9 V, 1.0 V, and 1.2 V). The NCP571 and NCV571 low dropout linear regulators are specifically designed for handheld communication devices and portable battery-powered applications that necessitate low quiescent current. These regulators feature an ultra-low quiescent current of 4.0 µA. The NCP571 and NCV571 devices incorporate a voltage reference unit, an error amplifier, a PMOS power transistor, and resistors for setting the output voltage, along with current limit and temperature limit protection circuits.
The NCP571 and NCV571 voltage regulator circuits are tailored for applications where space is limited and efficiency is paramount. These devices are characterized by their low dropout voltage, which allows them to maintain regulation even when the input voltage is only slightly higher than the output voltage. This is particularly beneficial in battery-operated devices where maximizing battery life is critical.
The internal architecture of the NCP571 and NCV571 includes a voltage reference that ensures stable output voltage across varying load conditions. The error amplifier continuously monitors the output voltage and adjusts the gate of the PMOS power transistor to maintain the desired voltage level. This feedback mechanism is essential for the accurate regulation of the output voltage, especially in scenarios with fluctuating load demands.
In addition to the primary regulation function, the NCP571 and NCV571 devices also incorporate protective features such as current limit and thermal shutdown. The current limit function prevents excessive current draw that could potentially damage the regulator or connected components, while the thermal shutdown feature protects the device from overheating by disabling the output when the junction temperature exceeds a predetermined threshold.
The output voltage can be set using external resistors, allowing for flexibility in design to meet specific application requirements. The low quiescent current of 4.0 µA makes these regulators ideal for applications where power conservation is essential, such as in portable devices that rely on battery power.
Overall, the NCP571 and NCV571 voltage regulators provide a compact and efficient solution for generating low regulated voltages in a variety of electronic applications, making them an excellent choice for engineers seeking reliable performance in space-constrained environments.In some electronic projects you will need an unusual regulated voltage, unusual, because the voltage required is very small and you can not use zenner diodes or some other tricks due of a compact design. In that case you can use this voltage regulator circuit based on the NCP571, NCV571 which are low current voltage regulators available in few
standard output voltage versions ( 0. 8 V, 0. 9 V, 1. 0 V and 1. 2 V ). The NCP571, NCV571 low dropout linear regulators are designed for handheld communication equipment and portable battery powered applications which require low quiescent current. The NCP571, NCV571 series features an ultra ’low quiescent current of 4. 0 uA. NCP571, NCV571 device contains a voltage reference unit, an error amplifier, a PMOS power transistor, resistors for setting output voltage, current limit, and temperature limit protection circuits.
🔗 External reference
The NCP571 and NCV571 voltage regulator circuits are tailored for applications where space is limited and efficiency is paramount. These devices are characterized by their low dropout voltage, which allows them to maintain regulation even when the input voltage is only slightly higher than the output voltage. This is particularly beneficial in battery-operated devices where maximizing battery life is critical.
The internal architecture of the NCP571 and NCV571 includes a voltage reference that ensures stable output voltage across varying load conditions. The error amplifier continuously monitors the output voltage and adjusts the gate of the PMOS power transistor to maintain the desired voltage level. This feedback mechanism is essential for the accurate regulation of the output voltage, especially in scenarios with fluctuating load demands.
In addition to the primary regulation function, the NCP571 and NCV571 devices also incorporate protective features such as current limit and thermal shutdown. The current limit function prevents excessive current draw that could potentially damage the regulator or connected components, while the thermal shutdown feature protects the device from overheating by disabling the output when the junction temperature exceeds a predetermined threshold.
The output voltage can be set using external resistors, allowing for flexibility in design to meet specific application requirements. The low quiescent current of 4.0 µA makes these regulators ideal for applications where power conservation is essential, such as in portable devices that rely on battery power.
Overall, the NCP571 and NCV571 voltage regulators provide a compact and efficient solution for generating low regulated voltages in a variety of electronic applications, making them an excellent choice for engineers seeking reliable performance in space-constrained environments.In some electronic projects you will need an unusual regulated voltage, unusual, because the voltage required is very small and you can not use zenner diodes or some other tricks due of a compact design. In that case you can use this voltage regulator circuit based on the NCP571, NCV571 which are low current voltage regulators available in few
standard output voltage versions ( 0. 8 V, 0. 9 V, 1. 0 V and 1. 2 V ). The NCP571, NCV571 low dropout linear regulators are designed for handheld communication equipment and portable battery powered applications which require low quiescent current. The NCP571, NCV571 series features an ultra ’low quiescent current of 4. 0 uA. NCP571, NCV571 device contains a voltage reference unit, an error amplifier, a PMOS power transistor, resistors for setting output voltage, current limit, and temperature limit protection circuits.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713