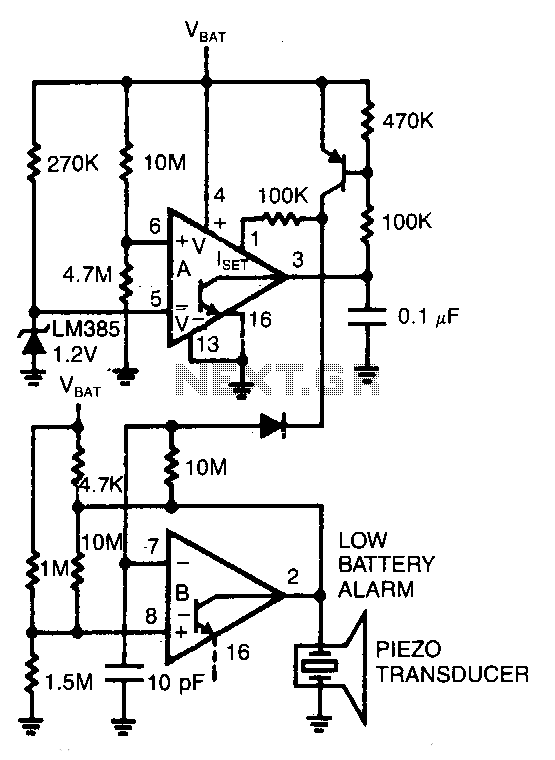
Nicad Battery Charger
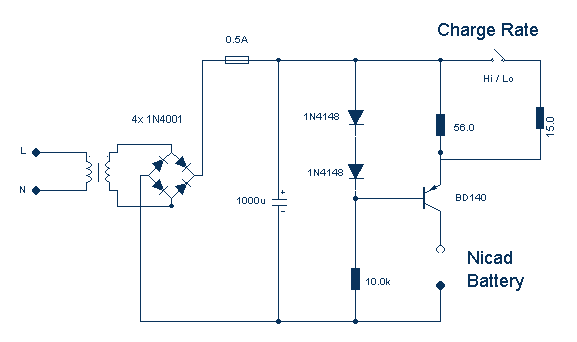
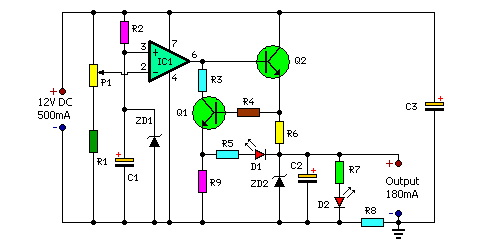
This simple charger uses a single transistor as a constant current source. The voltage across the pair of 1N4148 diodes biases the base of the BD140 medium power transistor. The base-emitter voltage of the transistor and the forward voltage drop across the diodes are relatively stable. The charging current is approximately 15mA or 45mA with the switch closed. This suits most 1.5V and 9V rechargeable batteries. The transformer should have a secondary rating of 12V ac at 0.5amp, the primary should be 220/240volts for Europe or 120volts ac for North America.
This circuit is designed to charge rechargeable batteries efficiently while maintaining a constant current output. The key component in the circuit is the BD140 medium power transistor, which operates in the active region to provide a stable charging current. The biasing of the transistor's base is achieved through the voltage drop across two 1N4148 diodes, which ensures that the base-emitter voltage remains constant, thus stabilizing the charging current.
The charging current can be adjusted based on the position of a switch in the circuit, allowing for two different output levels: approximately 15mA and 45mA. This feature is particularly useful for charging batteries with varying capacities, accommodating both smaller 1.5V cells and larger 9V batteries.
The transformer used in this design is crucial for stepping down the mains voltage to a suitable level for charging. It should have a secondary output of 12V AC at a current rating of 0.5A. The primary winding should be rated for either 220/240V AC for European applications or 120V AC for North American use, ensuring compatibility with regional power standards.
Safety precautions are paramount when working with this circuit, particularly due to the presence of AC voltage and the potential for high current. Proper insulation, circuit protection, and adherence to electrical safety standards are recommended to prevent accidents and ensure reliable operation.This simple charger uses a single transistor as a constant current source. The voltage across the pair of 1N4148 diodes biases the base of the BD140 medium power transistor. The base- emitter voltage of the transistor and the forward voltage drop across the diodes are relatively stable. The charging current is approximately 15mA or 45mA with the switch closed. This suits most 1.5V and 9V rechargeable batteries. The transformer should have a secondary rating of 12V ac at 0.5amp, the primary should be 220/240volts for Europe or 120volts ac for North America. WARNING: Take care with this circuit. Use a voltm 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to charge rechargeable batteries efficiently while maintaining a constant current output. The key component in the circuit is the BD140 medium power transistor, which operates in the active region to provide a stable charging current. The biasing of the transistor's base is achieved through the voltage drop across two 1N4148 diodes, which ensures that the base-emitter voltage remains constant, thus stabilizing the charging current.
The charging current can be adjusted based on the position of a switch in the circuit, allowing for two different output levels: approximately 15mA and 45mA. This feature is particularly useful for charging batteries with varying capacities, accommodating both smaller 1.5V cells and larger 9V batteries.
The transformer used in this design is crucial for stepping down the mains voltage to a suitable level for charging. It should have a secondary output of 12V AC at a current rating of 0.5A. The primary winding should be rated for either 220/240V AC for European applications or 120V AC for North American use, ensuring compatibility with regional power standards.
Safety precautions are paramount when working with this circuit, particularly due to the presence of AC voltage and the potential for high current. Proper insulation, circuit protection, and adherence to electrical safety standards are recommended to prevent accidents and ensure reliable operation.This simple charger uses a single transistor as a constant current source. The voltage across the pair of 1N4148 diodes biases the base of the BD140 medium power transistor. The base- emitter voltage of the transistor and the forward voltage drop across the diodes are relatively stable. The charging current is approximately 15mA or 45mA with the switch closed. This suits most 1.5V and 9V rechargeable batteries. The transformer should have a secondary rating of 12V ac at 0.5amp, the primary should be 220/240volts for Europe or 120volts ac for North America. WARNING: Take care with this circuit. Use a voltm 🔗 External reference