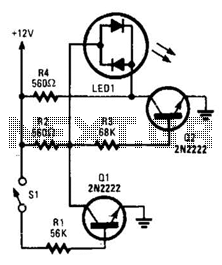
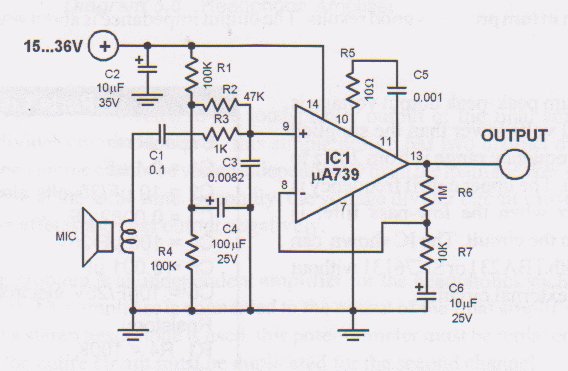
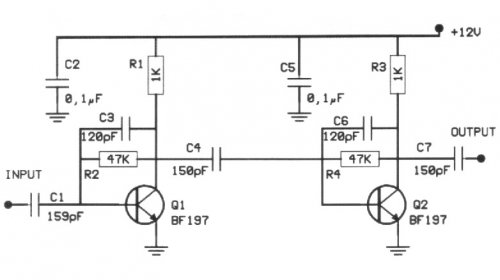
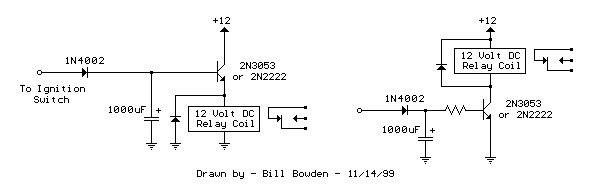
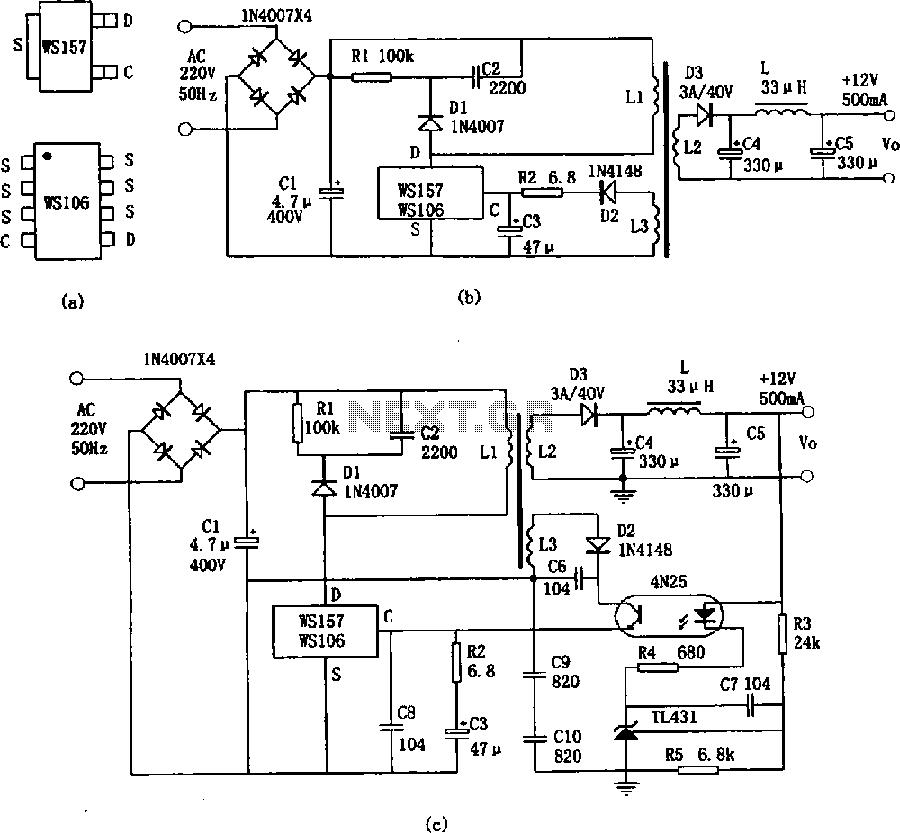
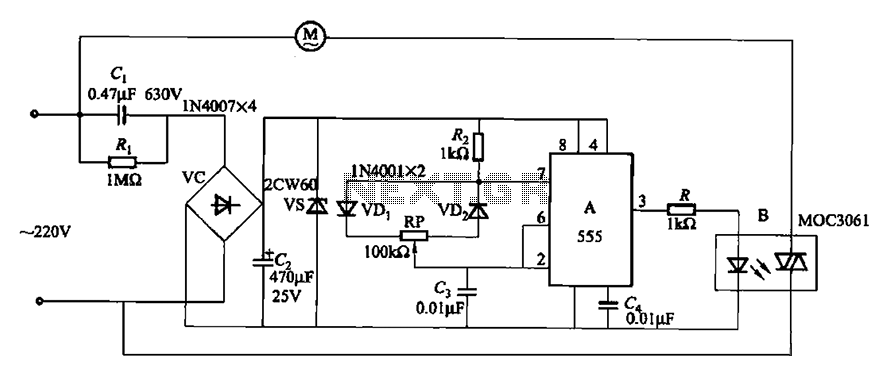
NiCd Battery Charger Circuit
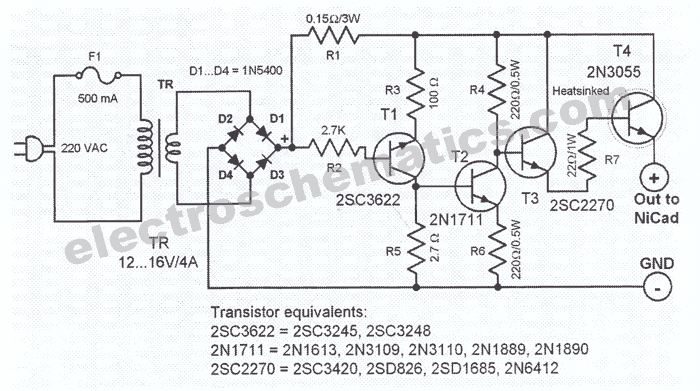
This NiCd battery charger circuit schematic can charge 6 volts as well as 12 volts NiCad batteries. It uses a transformer that can deliver 4 to 5 A current.
The NiCd battery charger circuit is designed to accommodate both 6V and 12V NiCad batteries, making it versatile for various applications. The core component of this circuit is a transformer, which is responsible for stepping down the AC voltage from the mains supply to a suitable level for charging the batteries. The transformer is rated to deliver a current in the range of 4 to 5 A, ensuring that it can efficiently supply the necessary power for charging.
The circuit typically includes a rectifier, which converts the AC output from the transformer into DC, suitable for charging the batteries. This is often achieved using a bridge rectifier configuration, which allows for full-wave rectification, improving the efficiency of the charging process. Following the rectification stage, a smoothing capacitor is used to filter out any ripple voltage, providing a stable DC output.
To prevent overcharging, the circuit may incorporate a charging control mechanism, such as a voltage regulator or a timer circuit. This ensures that the batteries are charged to their optimal voltage and prevents damage due to excessive charging. Additionally, the schematic may include protection diodes to prevent reverse current flow, which can occur when the batteries are disconnected from the charger.
The design should also consider thermal management, as charging can generate heat within the components. Adequate heat sinking for the rectifier and any voltage regulation components is essential to maintain performance and reliability.
Overall, this NiCd battery charger circuit schematic is a practical solution for charging both 6V and 12V NiCad batteries, with a focus on efficiency, safety, and reliability.This NiCd baterry charger circuit schematic can charge 6 volts as well as 12 volts NiCad batteries. It uses a transformer which can deliver 4 to 5 A curren.. 🔗 External reference
The NiCd battery charger circuit is designed to accommodate both 6V and 12V NiCad batteries, making it versatile for various applications. The core component of this circuit is a transformer, which is responsible for stepping down the AC voltage from the mains supply to a suitable level for charging the batteries. The transformer is rated to deliver a current in the range of 4 to 5 A, ensuring that it can efficiently supply the necessary power for charging.
The circuit typically includes a rectifier, which converts the AC output from the transformer into DC, suitable for charging the batteries. This is often achieved using a bridge rectifier configuration, which allows for full-wave rectification, improving the efficiency of the charging process. Following the rectification stage, a smoothing capacitor is used to filter out any ripple voltage, providing a stable DC output.
To prevent overcharging, the circuit may incorporate a charging control mechanism, such as a voltage regulator or a timer circuit. This ensures that the batteries are charged to their optimal voltage and prevents damage due to excessive charging. Additionally, the schematic may include protection diodes to prevent reverse current flow, which can occur when the batteries are disconnected from the charger.
The design should also consider thermal management, as charging can generate heat within the components. Adequate heat sinking for the rectifier and any voltage regulation components is essential to maintain performance and reliability.
Overall, this NiCd battery charger circuit schematic is a practical solution for charging both 6V and 12V NiCad batteries, with a focus on efficiency, safety, and reliability.This NiCd baterry charger circuit schematic can charge 6 volts as well as 12 volts NiCad batteries. It uses a transformer which can deliver 4 to 5 A curren.. 🔗 External reference