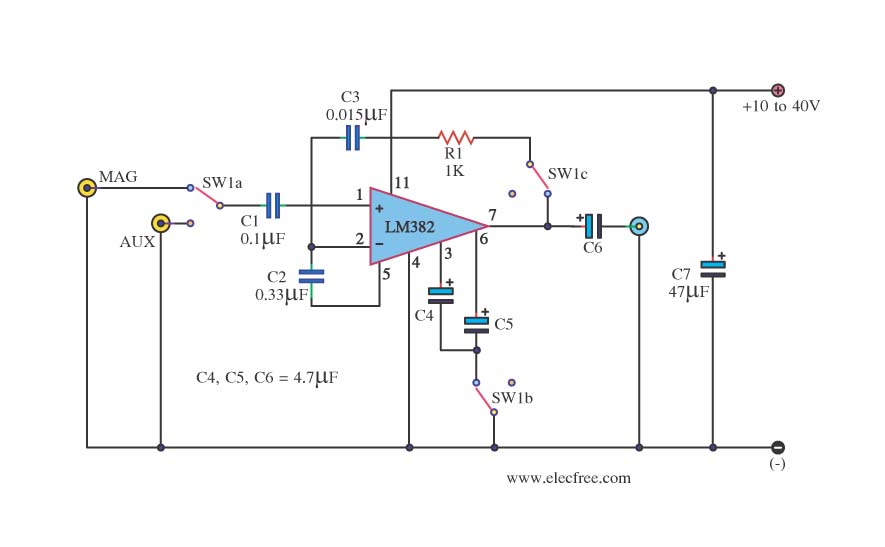
op amp based sound detector circuit

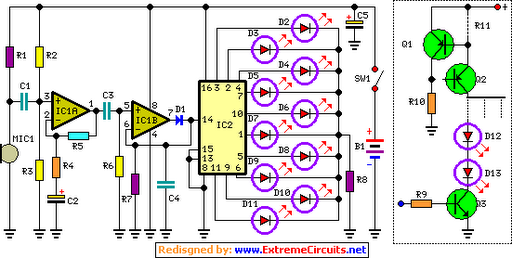
This circuit is designed for sound detection and generates an output signal when sound is detected. This output can trigger another circuit that activates an alarm, making it suitable for security applications. The circuit employs a condenser microphone to capture ambient sounds, which is a powered microphone, providing greater sensitivity than standard microphones. The microphone converts sound waves into an electronic signal that is sent to a 741 operational amplifier (op-amp). In this configuration, the 741 op-amp functions as a single-supply inverting amplifier. The resistor R1 can be adjusted to optimize the circuit's sensitivity. Capacitors C1 and C2 are incorporated to block the DC component of the signals, ensuring that only the AC component, which carries sound information, is transmitted to the output transistor Q1. It is important to note that the output taken from the collector of Q1 is inverted in relation to the output from the 741 amplifier.
This sound detection circuit utilizes a condenser microphone, which is known for its high sensitivity due to its powered nature. The microphone captures sound waves from the surrounding environment and converts them into an electrical signal. This signal is then amplified by the 741 op-amp, which is configured as an inverting amplifier. The inverting configuration allows for the manipulation of the signal phase, effectively inverting the output signal compared to the input.
Resistor R1 plays a crucial role in setting the gain of the op-amp, thus allowing for fine-tuning of the circuit's sensitivity to sound. By adjusting R1, the user can optimize the circuit for various sound levels, ensuring reliable detection in different environments. The capacitors C1 and C2 serve to filter out any unwanted DC offset that may be present in the signal, allowing only the alternating current (AC) component, which contains the sound information, to pass through to the output stage.
The output transistor Q1 is responsible for driving the subsequent alarm or notification circuit. The output signal taken from the collector of Q1 will be an inverted version of the amplified signal from the op-amp, which may need to be considered when interfacing with other components in the system. Overall, this circuit is an effective solution for sound detection applications, particularly in security systems where timely alerts are essential.This is a circuit that can be used for detecting sounds and providing an output signal when a sound is detected. This output signal may be fed to another circuit that sets off an alarm when the signal is received. This circuit is therefore useful in security applications. This is the figure of the circuit; The circuit uses a condenser microphone t o pick up sounds from the environment. This is a powered microphone, which makes it more sensitive than ordinary microphones. The microphone transforms the sound waves into an electronic signal that is fed to the 741 op amp. The 741 op amp in this circuit is configured as a single-supply inverting amplifier. Adjust R1 to maximize the sensitivity of your circuit. C1 and C2 are used to block the DC component of the signals, so that only the AC component carrying the sound information reaches the output transistor Q1. Note that the output, which is taken from the collector of Q1, is inverted with respect to the output of the 741 amplifier.
🔗 External reference
This sound detection circuit utilizes a condenser microphone, which is known for its high sensitivity due to its powered nature. The microphone captures sound waves from the surrounding environment and converts them into an electrical signal. This signal is then amplified by the 741 op-amp, which is configured as an inverting amplifier. The inverting configuration allows for the manipulation of the signal phase, effectively inverting the output signal compared to the input.
Resistor R1 plays a crucial role in setting the gain of the op-amp, thus allowing for fine-tuning of the circuit's sensitivity to sound. By adjusting R1, the user can optimize the circuit for various sound levels, ensuring reliable detection in different environments. The capacitors C1 and C2 serve to filter out any unwanted DC offset that may be present in the signal, allowing only the alternating current (AC) component, which contains the sound information, to pass through to the output stage.
The output transistor Q1 is responsible for driving the subsequent alarm or notification circuit. The output signal taken from the collector of Q1 will be an inverted version of the amplified signal from the op-amp, which may need to be considered when interfacing with other components in the system. Overall, this circuit is an effective solution for sound detection applications, particularly in security systems where timely alerts are essential.This is a circuit that can be used for detecting sounds and providing an output signal when a sound is detected. This output signal may be fed to another circuit that sets off an alarm when the signal is received. This circuit is therefore useful in security applications. This is the figure of the circuit; The circuit uses a condenser microphone t o pick up sounds from the environment. This is a powered microphone, which makes it more sensitive than ordinary microphones. The microphone transforms the sound waves into an electronic signal that is fed to the 741 op amp. The 741 op amp in this circuit is configured as a single-supply inverting amplifier. Adjust R1 to maximize the sensitivity of your circuit. C1 and C2 are used to block the DC component of the signals, so that only the AC component carrying the sound information reaches the output transistor Q1. Note that the output, which is taken from the collector of Q1, is inverted with respect to the output of the 741 amplifier.
🔗 External reference