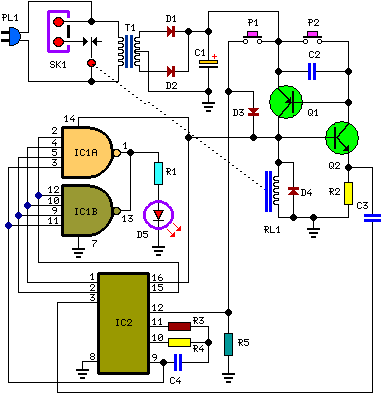
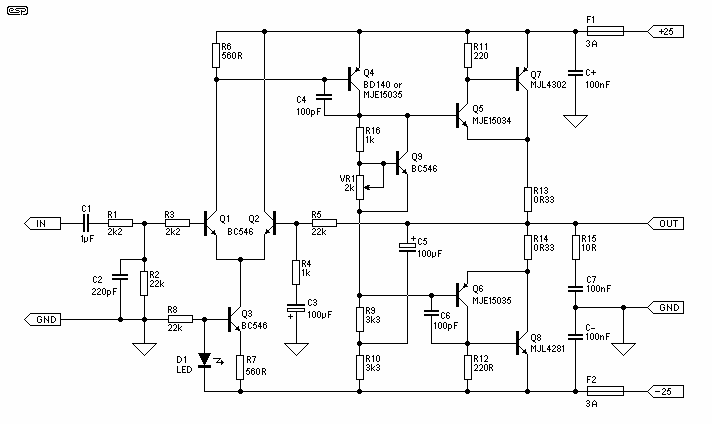
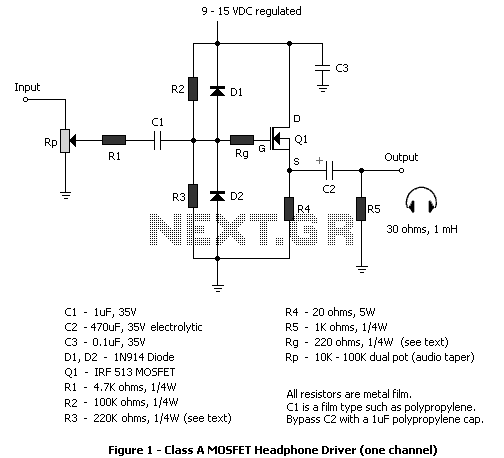
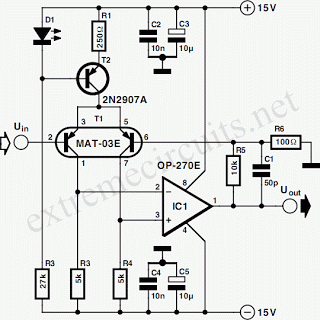
op amp op-amp vs direct control
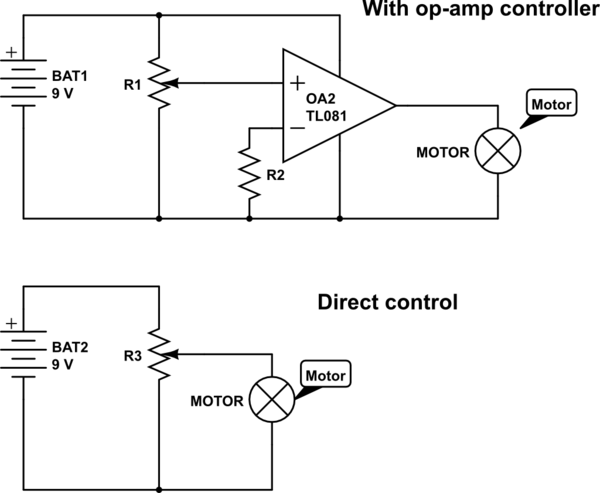
A 100 Ohm resistor connected to a 4.5 Volt supply (using three AA batteries) allows a current of 45 mA. However, at the upper end of the current sweep, the effective current will be significantly higher due to the load being in parallel. This current is primarily limited by the resistance of the load and the capacity of the battery.
In this circuit, a 100 Ohm resistor is used in conjunction with a power supply of 4.5 Volts, which can be achieved using three AA batteries connected in series. The nominal current flowing through the resistor under these conditions is calculated using Ohm's Law (I = V/R), where I is the current, V is the voltage, and R is the resistance. Therefore, with 4.5 Volts applied across a 100 Ohm resistor, a current of 45 mA is expected.
However, it is important to note that when additional loads are introduced in parallel to the resistor, the total current drawn from the power supply can increase substantially. This is due to the fact that parallel loads decrease the total resistance seen by the power supply, allowing more current to flow. The maximum current that can flow through the circuit is ultimately constrained by the internal resistance of the battery and its capacity, which determines how much current the battery can provide before its voltage drops significantly.
In practical applications, this configuration may be used in various electronic circuits where a specific current is required. Care must be taken to ensure that the load does not exceed the battery's capacity, as this could lead to overheating or damage to the components. The design should also consider the thermal characteristics of the resistor and load to prevent any potential failure due to excessive heat generation.100 Ohms at 4. 5 Volts (3xAA) allows 45 mA, but at the upper end of the sweep, due to the load being in parallel, it will be much higher - basically limited by the resistance of your load and your battery capacity. So yes, you can "smoke a pot" (heh!). Anindo Ghosh May 4 `13 at 6:36 🔗 External reference
In this circuit, a 100 Ohm resistor is used in conjunction with a power supply of 4.5 Volts, which can be achieved using three AA batteries connected in series. The nominal current flowing through the resistor under these conditions is calculated using Ohm's Law (I = V/R), where I is the current, V is the voltage, and R is the resistance. Therefore, with 4.5 Volts applied across a 100 Ohm resistor, a current of 45 mA is expected.
However, it is important to note that when additional loads are introduced in parallel to the resistor, the total current drawn from the power supply can increase substantially. This is due to the fact that parallel loads decrease the total resistance seen by the power supply, allowing more current to flow. The maximum current that can flow through the circuit is ultimately constrained by the internal resistance of the battery and its capacity, which determines how much current the battery can provide before its voltage drops significantly.
In practical applications, this configuration may be used in various electronic circuits where a specific current is required. Care must be taken to ensure that the load does not exceed the battery's capacity, as this could lead to overheating or damage to the components. The design should also consider the thermal characteristics of the resistor and load to prevent any potential failure due to excessive heat generation.100 Ohms at 4. 5 Volts (3xAA) allows 45 mA, but at the upper end of the sweep, due to the load being in parallel, it will be much higher - basically limited by the resistance of your load and your battery capacity. So yes, you can "smoke a pot" (heh!). Anindo Ghosh May 4 `13 at 6:36 🔗 External reference